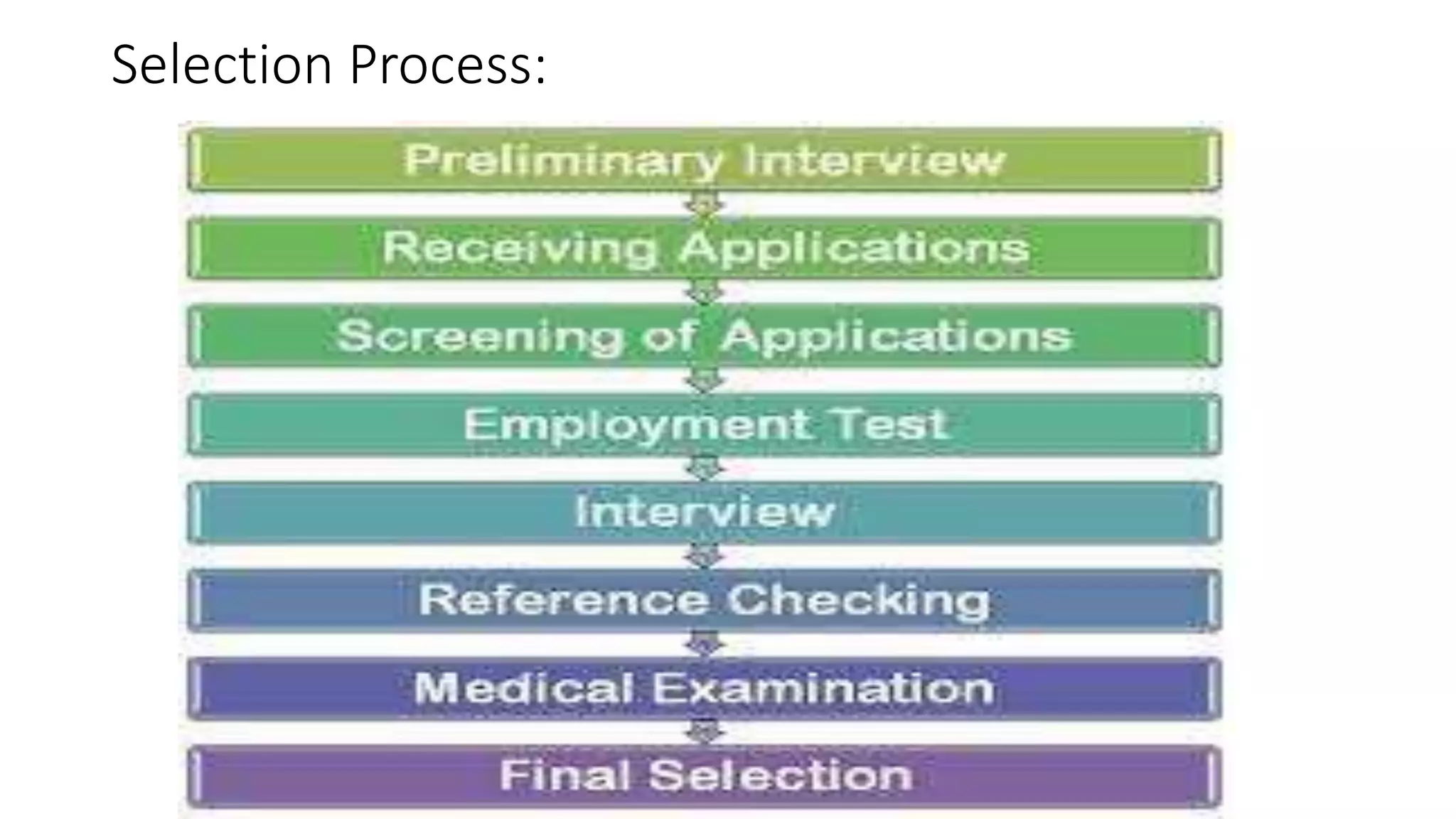
The document discusses the process of selection in organizations. It begins by explaining that selection involves identifying the best candidates for jobs based on matching their skills to organizational requirements. An effective selection process involves multiple steps, including screening applications, testing candidates using tools like interviews, personality tests and situational tests. The document then outlines various types of interviews commonly used in selection like informal interviews, stress interviews and panel interviews. It emphasizes that selection should follow principles like having sufficient applicants, clear standards, and competent evaluators to identify the most suitable candidates for roles.