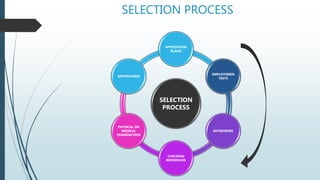
The selection process involves multiple steps to identify the best candidates for a role. It begins with collecting application blanks to gather initial information. Candidates then take various employment tests assessing their aptitude, interests, intelligence, and personality. Top performers proceed to interviews which evaluate their potential, abilities, and personality through different styles like preliminary, extensive, and group interviews. References are checked and physical/medical examinations conducted. The final step is appointing the most qualified candidate who emerges strongest after completing all stages of screening.