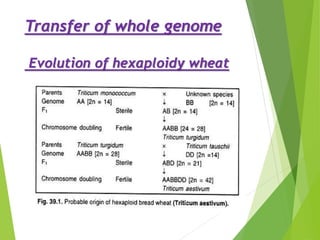
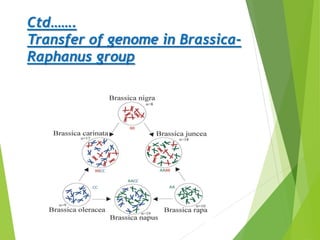
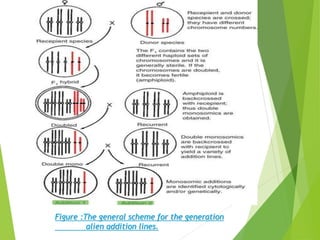
This document summarizes techniques for intervarietal chromosomal substitution in plants. It describes methods such as developing alien addition lines by adding individual chromosomes from one species to another, and alien substitution lines by replacing chromosomes from one species with those of another. Specific examples of developing alien addition and substitution lines are provided for rice, sugar beet, cotton, tobacco, and oats to transfer traits like disease resistance between species. Chromosomal additions and substitutions are identified through morphological analysis, karyotyping, or intercrossing.