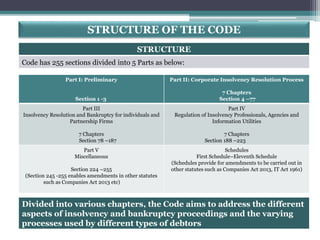
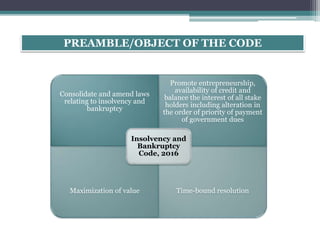
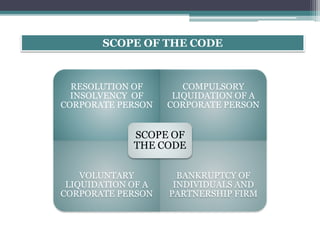
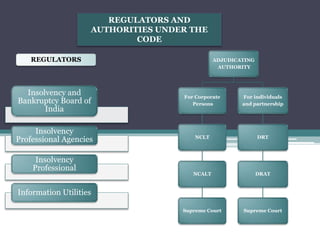
The document provides an overview of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code of 2016 in India. It discusses the key reasons for introducing the code, including reducing time to resolve insolvency, developing investor confidence, and addressing non-performing assets. The code aims to create a single framework for insolvency and bankruptcy proceedings. It allows for insolvency resolution and bankruptcy procedures for both corporate entities and individuals/partnership firms. The document outlines the structure and various parts of the code, as well as the roles and responsibilities of different authorities and professionals involved in insolvency resolution processes under the code.


![WHAT DOES IT CHANGE FOR THE BORROWERS
Any creditor can file an insolvency petition on default of INR 1
lakh or more
Insolvency Professional to take over the management and
operations of the borrower during Corporate Insolvency
Resolution Process
Need to be proactive in identifying issues/claims,
communicating with lenders and developing/implementing a
turnaround plan
In case of fraudulent diversion of assets, personal contribution
can be sought; imprisonment possible [Section 68]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-4-320.jpg)
![APPLICABILITY OF THE CODE
The Code applies to whole of India except
Part III (Insolvency Resolution and
Bankruptcy for individuals and Partnership
Firms) which does not apply to Jammu and
Kashmir [Section 1]
The provision of the Code applies to:
a) Companies incorporated under
Companies Act, 2013 or under any
previous company law;
b) Company governed by any special Act
except so far as the said provisions are
not inconsistent with provision of such
special act;
c) LLP incorporated under Limited Liability
Partnership Act, 2008
d) Any body corporate incorporated under
any law for time being in force, as Central
Government may, by notification specify
in this behalf;
e) Personal Guarantors of Corporate
Debtor;
f) Partnership firms and Proprietorship
firms; and
g) Any other individuals.
[Section 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-8-320.jpg)
![INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION AND LIQUIDATION FOR
CORPORATE PERSON [Part II of the Code]
When can the insolvency resolution process get triggered?
When the minimum amount of default by Corporate Debtor is Rs. 1,00,000/-
Central Government may, by notification, specify the minimum amount of
default of higher value which shall not be more than Rs. 100,00,000/- [Section
4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-10-320.jpg)
![Who can trigger the insolvency
resolution process?
Who cannot trigger the insolvency
process?
The Code provides for three types of
applicants who can trigger the corporate
insolvency resolution process:-
The Insolvency Code specifically
provides for following persons who
cannot trigger the corporate insolvency
resolution process:-
Financial Creditors;
Operational Creditors;
Corporate Applicants/Corporate Debtors
itself. [Section 7,9,10 read with Rule 4, 6
and 7 of Insolvency and Bankruptcy
(Application to Adjudicating Authority)
Rules, 2016]
A corporate debtor undergoing a corporate
insolvency resolution process;
A corporate debtor having completed
corporate insolvency process 12 months
preceding the date of making application;
A corporate debtor or financial creditor who
has violated any of the terms of resolution
plan which was approved 12 months before
the date of making application under this
chapter;
A corporate debtor in respect of whom a
liquidation order has been made. [Section 11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-11-320.jpg)
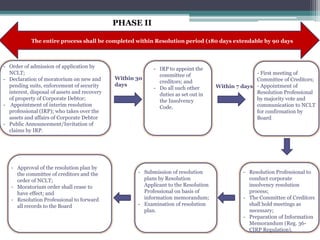
![TIME BOUND CORPORATE INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION PROCESS [S.6-54
read with Rule Insolvency and Bankruptcy (Application to Adjudicating Authority) Rules, 2016]
PHASE I
FINANCIAL CREDITOR
- Filing of application on
occurrence of default. Default
here means default not only
qua the applicant financial
creditor but also by any other
Financial creditor.
- Along with application, to
furnish record of default and
to propose of interim
resolution professional
OPERATIONAL CREDITOR
- Deliver a default notice to the corporate
debtor on occurrence of default
Within 10 days
Adequate reply Inadequate reply
Settlement
of dues
Dispute
Or
Filing of
application
CORPORATE APPLICANT
- Filing of application on occurrence
of default
- Along with application, to
furnish record of default and
to propose name of interim
resolution professional
Within 14 days
- To ascertain the existence of default. If satisfied, it shall accept, otherwise reject.
Accept
Proceed with
Phase II
Prior to rejection
Suggest rectification
Reapply Reject](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-12-320.jpg)

![Liquidation Estate –Inclusions and Exclusions
Inclusions [S. 36(3)] Exclusions [S. 36(4)]
Any assets over which the corporate debtor has
ownership rights.
Assets that may/ may not be in possession of the
corporate debtor, including encumbered assets.
Tangible assets (movable/ immovable).
Intangible assets (such as IPs), shares held in a
subsidiary, financial instruments, insurance policies,
contractual rights.
Assets subject to determination of ownership by the court
or authority.
Assets recovered through proceedings for avoidance of
transactions.
Assets in respect of which secured creditor has
relinquished security interest.
Any other property belonging to or vested in the
corporate debtor on the insolvency commencement date.
Proceeds of liquidation when realized.
Assets in the possession of corporate debtor but owned
by third parties.
Assets in security collateral held by financial service
providers and are subject to netting and set-off in multi-
lateral trading or clearing transaction.
Personal assets of shareholder or partner of corporate
debtor provided they are not held on account of
avoidance transaction.
Assets of subsidiaries (Indian/ foreign) of the corporate
debtor.
Any other assets as may be specified by the IBBI.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-17-320.jpg)
![ Application for fast track insolvency resolution may be made in respect of following
corporate debtors, namely:
a small company as defined under clause (85) of section 2 of Companies Act, 2013 (18 of
2013)
a Start-up (other than the partnership firm) as defined in the notification of the
Government of India in the Ministry of Commerce and Industry dated the 23rd May,
2017
an unlisted company with total assets, as reported in the financial statement of the
immediately preceding financial year, not exceeding rupees one crore.
Fast Track Insolvency process to be completed within 90 days from commencement date.
Provision for 1 extension only, for a period of 45 days.
Process may be initiated by a creditor or corporate debtor by furnishing proof of default
or any other specified details.
Process largely the same as that for regular insolvency resolution.
FAST TRACK CORPORATE INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION [S. 55-58]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-18-320.jpg)
![VOLUNTARY LIQUIDATION [S. 59-67]
• May be initiated by the corporate debtor even without existence of default.
• Declarations from majority of directors needed, to be verified by an affidavit of solvency and that the
company is not being liquidated to defraud any creditor.
• Special resolution of members needs to be passed within 4 weeks of declaration by directors requiring
the company to be liquidated and appointing an Insolvency Professional to act as a liquidator.
• If the company owes debt then resolution to be approved by creditors representing 2/3rd value of debt
within 7 days of the members resolution.
• RoC and the Board to be notified of the decision to voluntarily liquidate within 7 days of passing such
resolution and subsequent approval by the creditors.
• Liquidation process shall be deemed to have commence from date of passing resolution.
• Liquidator to make application to NCLT for dissolution when the affairs are wound up and assets have
been completely liquidated.
• NCLT to pass an order dissolving the corporate debtor from the date of such order
• Copy of such order to be forwarded to the RoC within 14 days from the date of order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-19-320.jpg)
![Insolvency resolution process costs & liquidation costs
Secured creditors, if security has
been relinquished as specified in
section 52
Workmen’s dues (past 24
months)
Employees’ wages (past 12 months)
Financial debts to unsecured creditors
Government dues
Secured creditors
(residual amt. if the
creditor enforces his
securities)
Other remaining debts
Preference Shareholders
Equity Shareholders
or partners
LIQUIDATION WATERFALL [S. 53]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-interpretingibc-180626185700/85/Interpreting-Insolvency-and-Bankruptcy-Code-2016-20-320.jpg)