Recommended
PPTX
Interpolation and its applications
PPTX
Interpolation-and-Approximation-Bridging-Data-Gaps-and-Modelling-Reality.pptx
PDF
PDF
PDF
$$$ Cheap breville bta630 xl
PDF
$$$ Cheap breville bta630 xl
PDF
PPTX
AShikj.pptx Image Tampering Detectionjl bbbbbb
PPTX
PPTX
Application of interpolation in CSE
PDF
Interpolation with unequal interval
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
Interpolation and-its-application
PPTX
PPTX
22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 16 Interpolations and Basic Functions.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
interpolation-and-its-application-180107160107.pptx
PDF
Data fitting in Scilab - Tutorial
PDF
Numerical Analysis: Interpolation: Forward, Backward, Lagrange's and Linear I...
PDF
PPTX
Spline interpolation numerical methods presentation
PPTX
Numerical method (curve fitting)
PDF
PDF
Intro. to computational Physics ch2.pdf
PPTX
Approximation of functions and data2.pptx
PDF
Lecture about interpolation
PDF
Khan Traders Fish Meal – MSDS Material Safety Data Sheet
DOCX
Data Analyst Training Course | Advanced Data Analytics Certification | GVT Ac...
More Related Content
PPTX
Interpolation and its applications
PPTX
Interpolation-and-Approximation-Bridging-Data-Gaps-and-Modelling-Reality.pptx
PDF
PDF
PDF
$$$ Cheap breville bta630 xl
PDF
$$$ Cheap breville bta630 xl
PDF
PPTX
AShikj.pptx Image Tampering Detectionjl bbbbbb
Similar to Interpolation_Methods_data_analytics.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Application of interpolation in CSE
PDF
Interpolation with unequal interval
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
Interpolation and-its-application
PPTX
PPTX
22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 16 Interpolations and Basic Functions.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
interpolation-and-its-application-180107160107.pptx
PDF
Data fitting in Scilab - Tutorial
PDF
Numerical Analysis: Interpolation: Forward, Backward, Lagrange's and Linear I...
PDF
PPTX
Spline interpolation numerical methods presentation
PPTX
Numerical method (curve fitting)
PDF
PDF
Intro. to computational Physics ch2.pdf
PPTX
Approximation of functions and data2.pptx
PDF
Lecture about interpolation
Recently uploaded
PDF
Khan Traders Fish Meal – MSDS Material Safety Data Sheet
DOCX
Data Analyst Training Course | Advanced Data Analytics Certification | GVT Ac...
PPTX
Query Parsing: The SEO Gatekeeper That Decides Rankings
PDF
US Digital Fan Engagement Index 2026: Benchmarking Online Demand for Sports T...
PDF
LECTURE - Overcoming the AI Failure Rate - AIG, DQM.pdf
PPTX
The Singularity Sprint (2026): Neuralink + the AI Arms Race — Ridwan Sassman
PDF
Understanding Data Analytics: Concepts, Types, and Use Cases
PPTX
inbound4709748695955476507 Deformable bodies.pptx
PPTX
GENPHYSICS-2.pptx this about general physics. Grade 11 lesson
PDF
Columbus Data and Analytics Wednesday - People Analytics 101: Making Sense of...
PPT
data collection tool ppt.ppttttdataadfttg
PDF
chapter one introduction to Probability theory.pdf
PDF
PathRAG rag pipeline PathRAG rag pipeline .pdf
PPTX
Social Media Audit of Starbucks Coffee Company.pptx
PDF
Trustworthy AI : Governance of AI through Ethics
PPTX
Lecture 14- Introduction to Hypothesis Testing.pptx
PPTX
Organizational Structure and Design Topic 4
PPTX
I need all your support to get the data for the sections like photo gallery o...
PPTX
End to End Supply Chain Management- Analytics Case Study.
PPTX
Top Institute for Data Analyst Course in Navi Mumbai
Interpolation_Methods_data_analytics.pptx 1. 2. 3. Types of Interpolation Methods
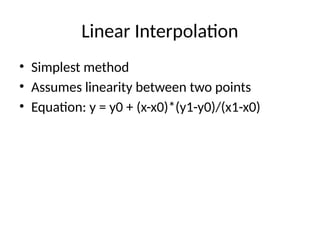
• Linear interpolation
• Polynomial interpolation
• Spline interpolation
• Lagrange interpolation
4. 5. 6. Lagrange Interpolation
• Uses Lagrange basis polynomials
• Constructs a polynomial passing through all
data points
• Widely used in numerical methods
7. 8. 9. Limitations of Interpolation
• Accuracy decreases outside data range
(extrapolation)
• High-degree polynomials may oscillate
• Requires careful method selection
10.