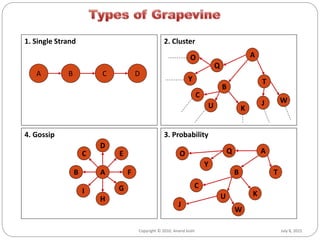
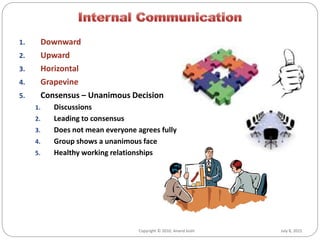
This document discusses effective communication techniques for business. It covers topics like the definition of communication, types of communication channels, barriers to communication, and principles for clear communication. Some key points include:
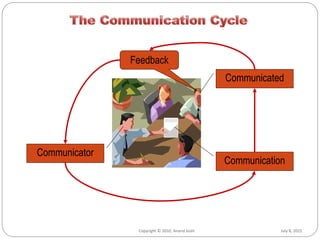
- Communication is sending and receiving ideas or thoughts from one person to another so the message is understood as intended.
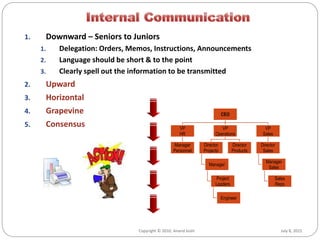
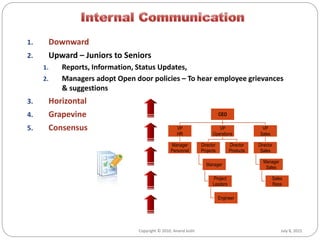
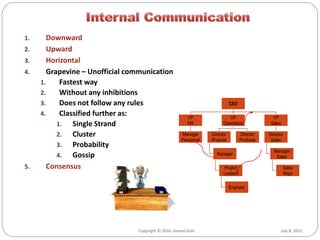
- There are various channels of communication including verbal, written, and nonverbal forms. Barriers can occur due to issues with the medium, noise, cultural differences, and more.
- Effective business communication is clear, concise, and follows principles like courtesy, sincerity, and avoiding bias. It provides all relevant details and makes the purpose and expected response apparent.