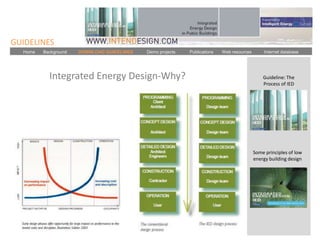
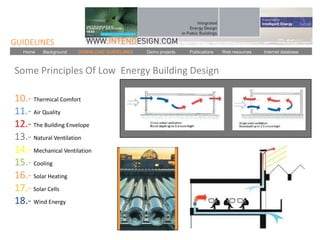
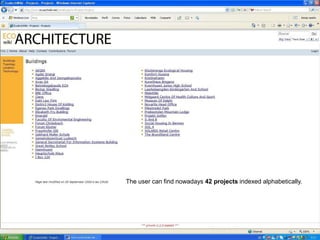
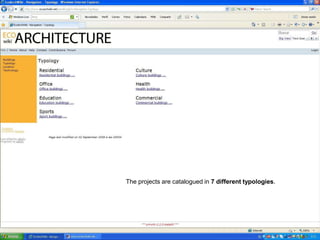
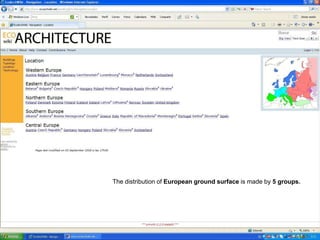
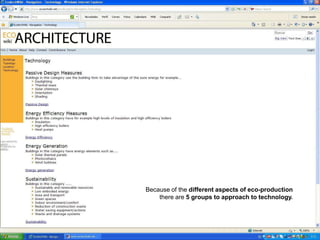
The document discusses an event called the "BIM STORM" where 133 individuals used building information modeling (BIM) to design 420 buildings covering over 54 million square feet of space in Los Angeles over the course of 24 hours. The event required real-time collaboration over the internet with no lag time and used open data standards. It involved participation from four companies focused on BIM and design software. The event demonstrates how BIM can radically transform the design process in the architecture and construction industries.