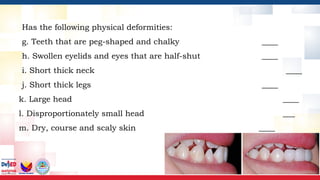
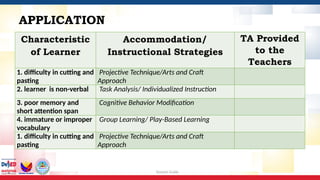
The document outlines a training session for education leaders focusing on strategies and accommodations for learners with difficulties in remembering and concentrating, scheduled for June 25-28, 2024. Participants will learn to identify characteristics of these learners, use multi-sensory instructional materials, and develop technical assistance plans to better support these students. Various activities, instructional strategies, and accommodations are suggested to enhance learning for individuals with special educational needs.