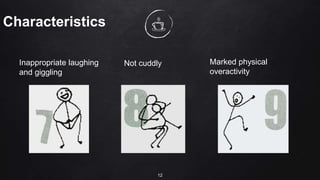
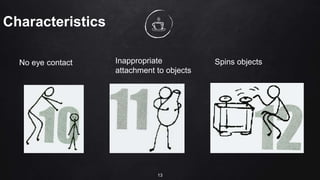
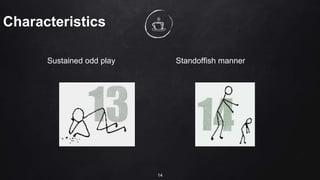
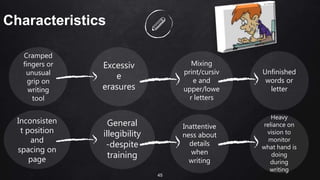
The document discusses inclusive education for learners with special education needs in the Philippines. It establishes the right of all children to education, regardless of disability, and aims to develop an education system that enables learners with disabilities to reach their full potential. The document provides background on disabilities in the Philippines and defines terms related to disability and the goals of special education services.