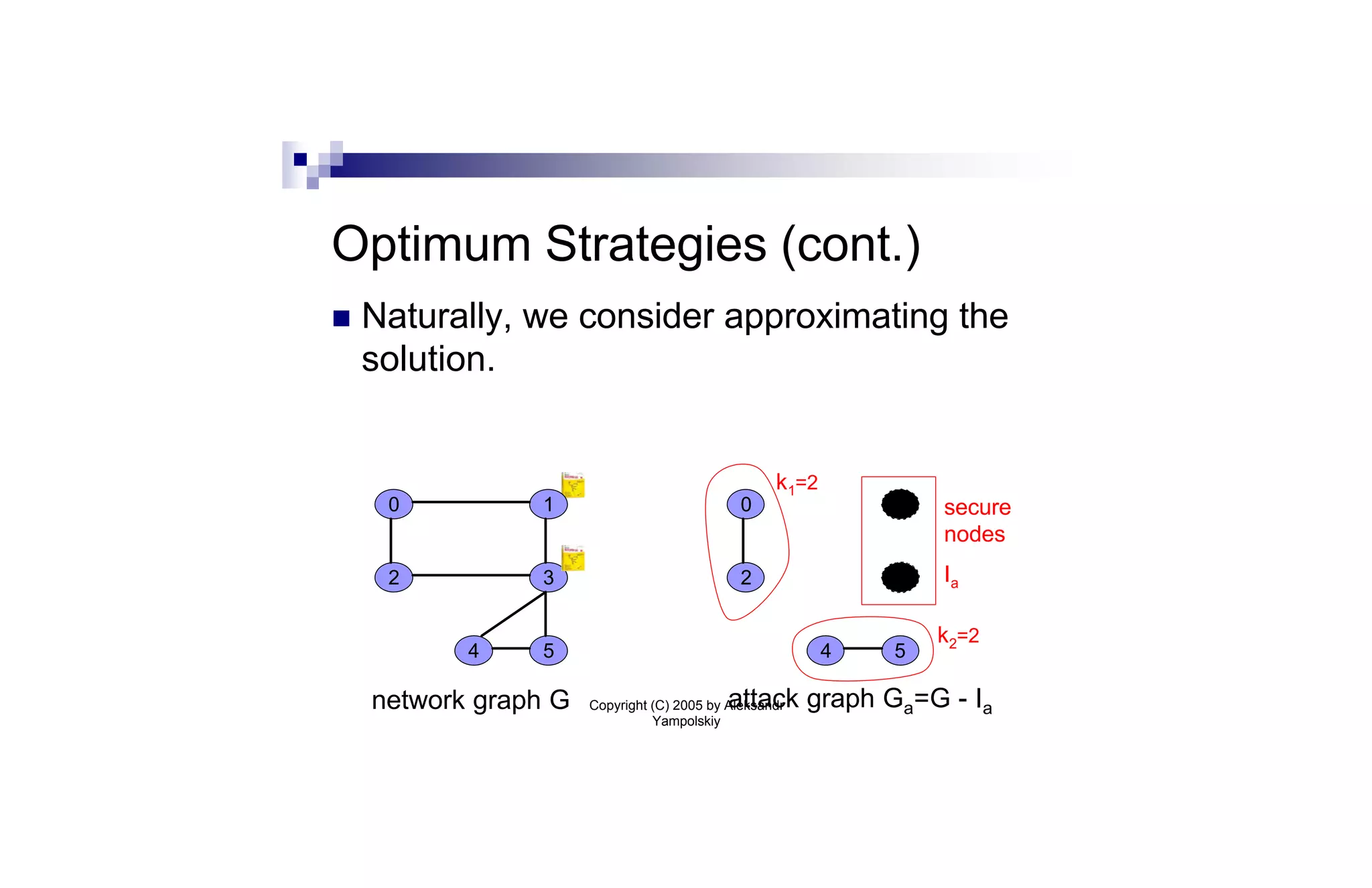
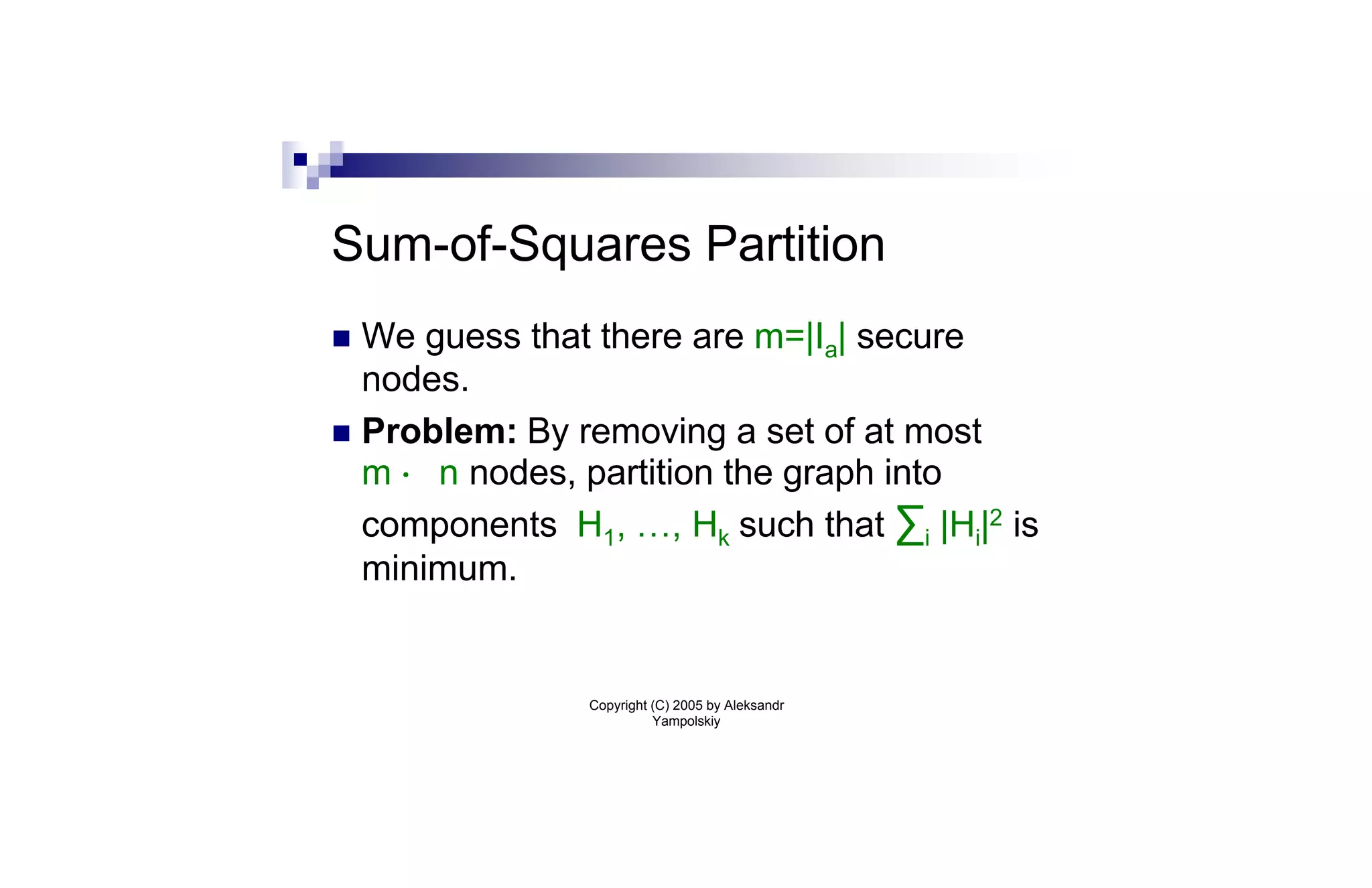
This document discusses strategies for containing computer viruses in a network. It presents a game theoretic model where nodes choose whether to install antivirus software. Nash equilibria are characterized but can be inefficient. Computing the optimal strategy that minimizes total infection risk is NP-hard. Approximating this solution can be reduced to the sum-of-squares partition problem, allowing for a near-optimal deployment. Open problems consider extensions like taxation mechanisms and strategic behavior.








![Our Model : Individual Costs
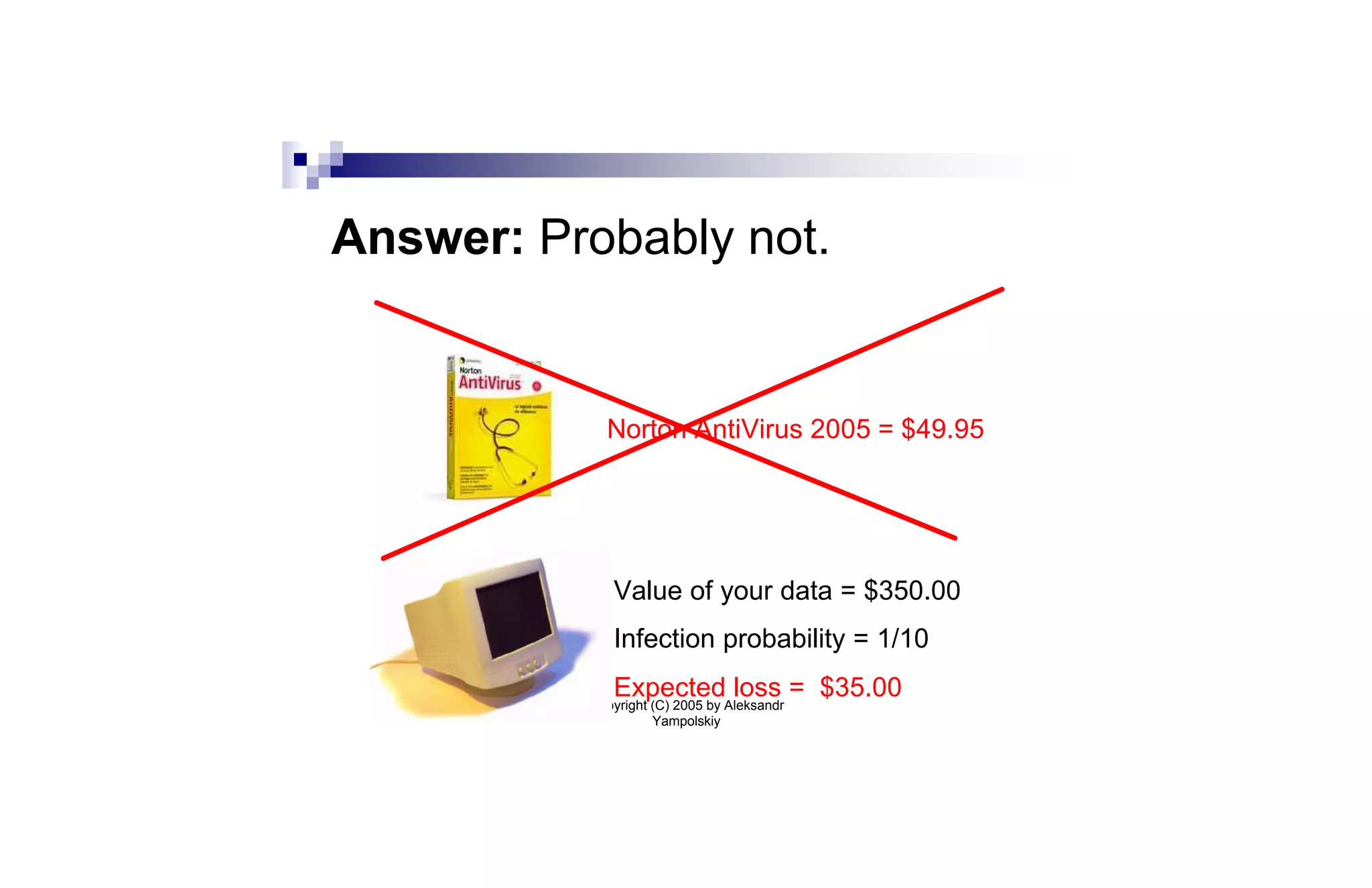
n Anti-virus software costs C. Expected loss
from virus is L.
n Cost of strategy to node i:
n Here, pi(a) = Pr[i is infected | i does not
install an anti-virus]
Copyright (C) 2005 by Aleksandr
Yampolskiy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talkviruses-100914155953-phpapp01/75/Inoculation-strategies-for-victims-of-viruses-13-2048.jpg)


![Nash Strategies
n Def: Strategy profile is in Nash
equilibrium if no node can improve its
payoff by switching to a different strategy:
for i = 0,...,n-1 and any x 2 [0,1],
n Fact: Nash strategies do not optimize total
social cost (cf. Prisoner’s Dilemma)
Copyright (C) 2005 by Aleksandr
Yampolskiy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talkviruses-100914155953-phpapp01/75/Inoculation-strategies-for-victims-of-viruses-16-2048.jpg)


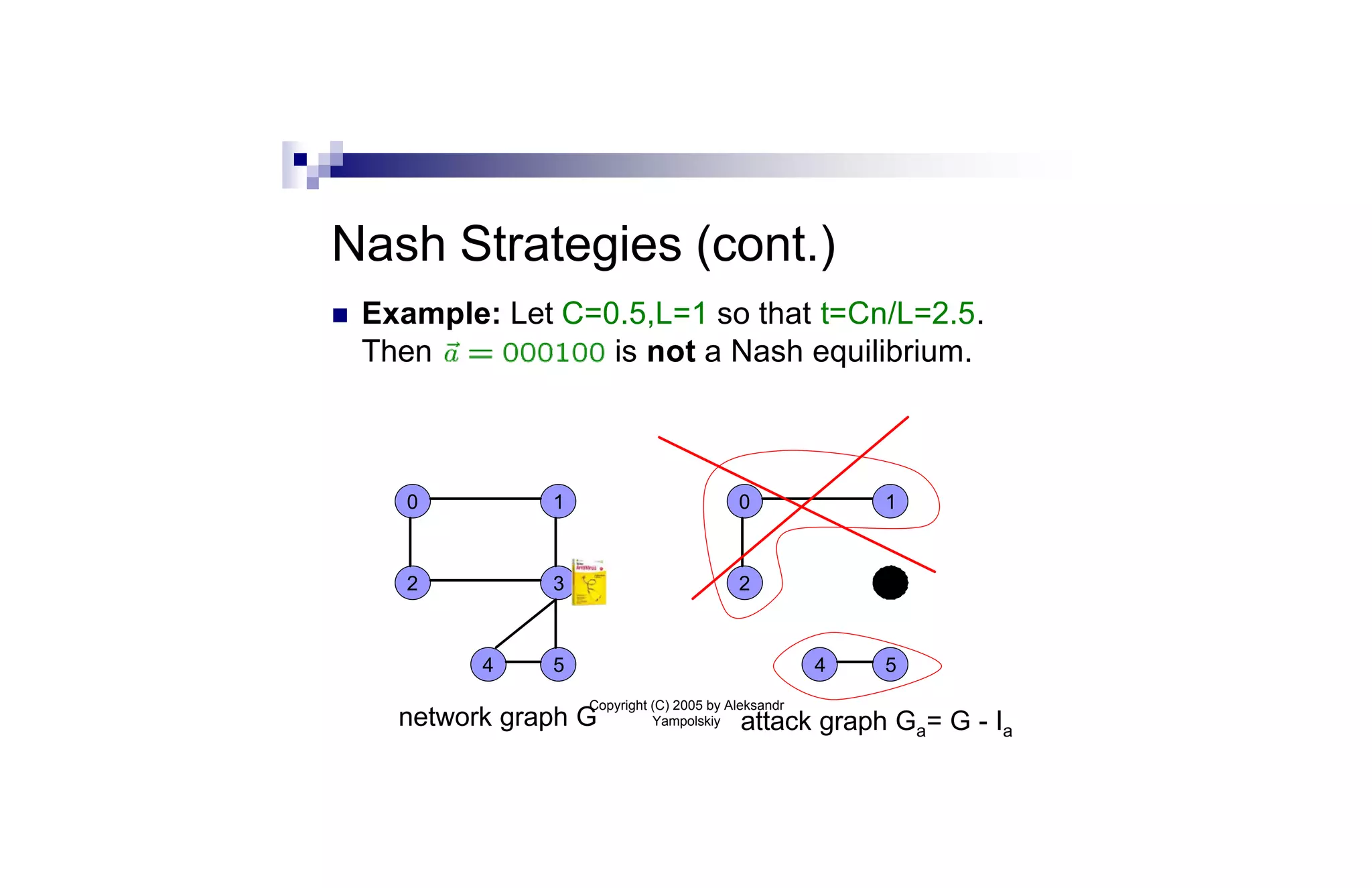




![Price of Anarchy [KP99]
n Price of anarchy measures how far away a
Nash equilibrium can be from the social
optimum
n Formally, it is the worst-case ratio between
cost of Nash equilibrium and cost of social
optimum
n For network G and costs C, L, we denote it:
Copyright (C) 2005 by Aleksandr
Yampolskiy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talkviruses-100914155953-phpapp01/75/Inoculation-strategies-for-victims-of-viruses-24-2048.jpg)

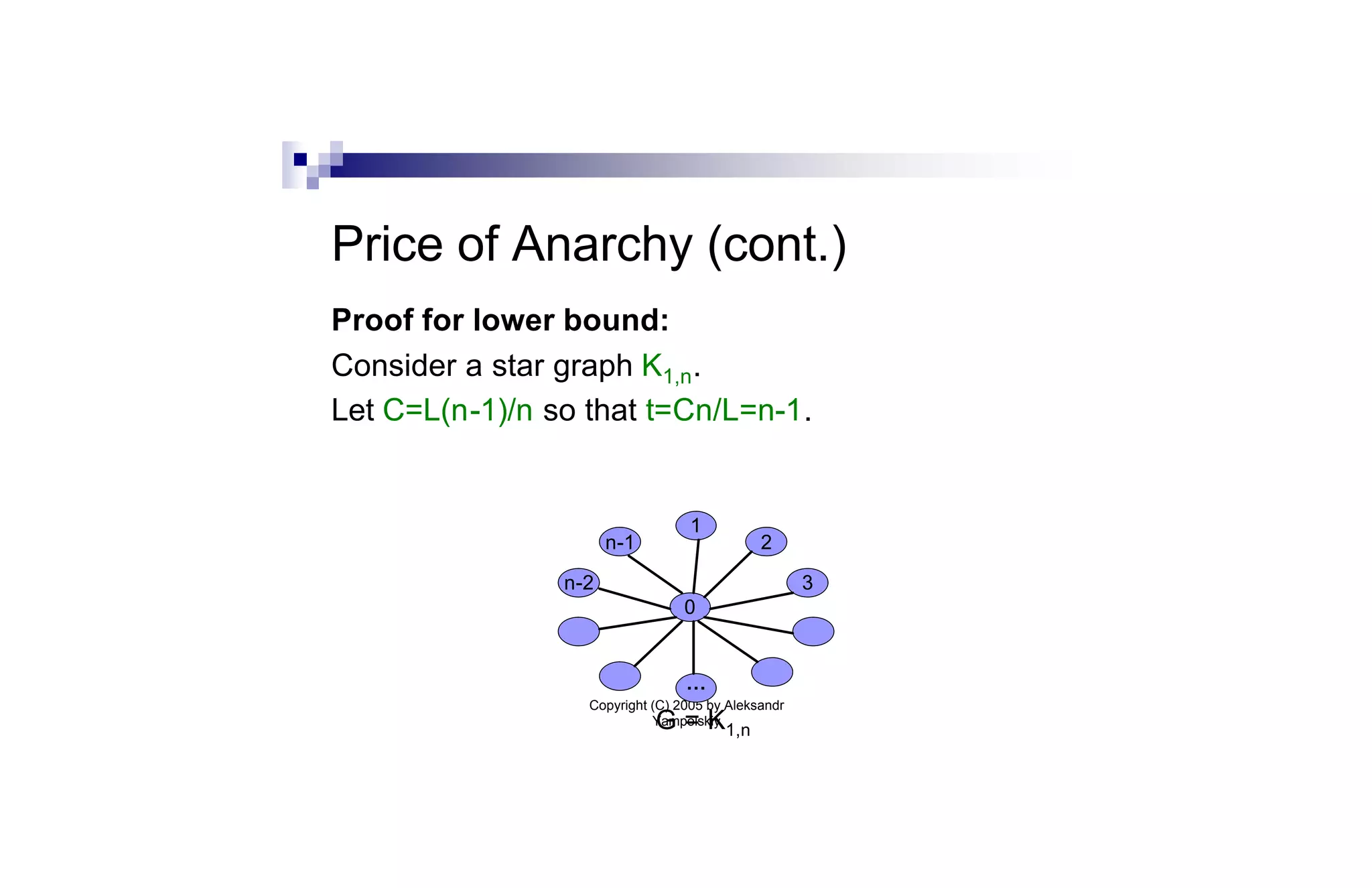
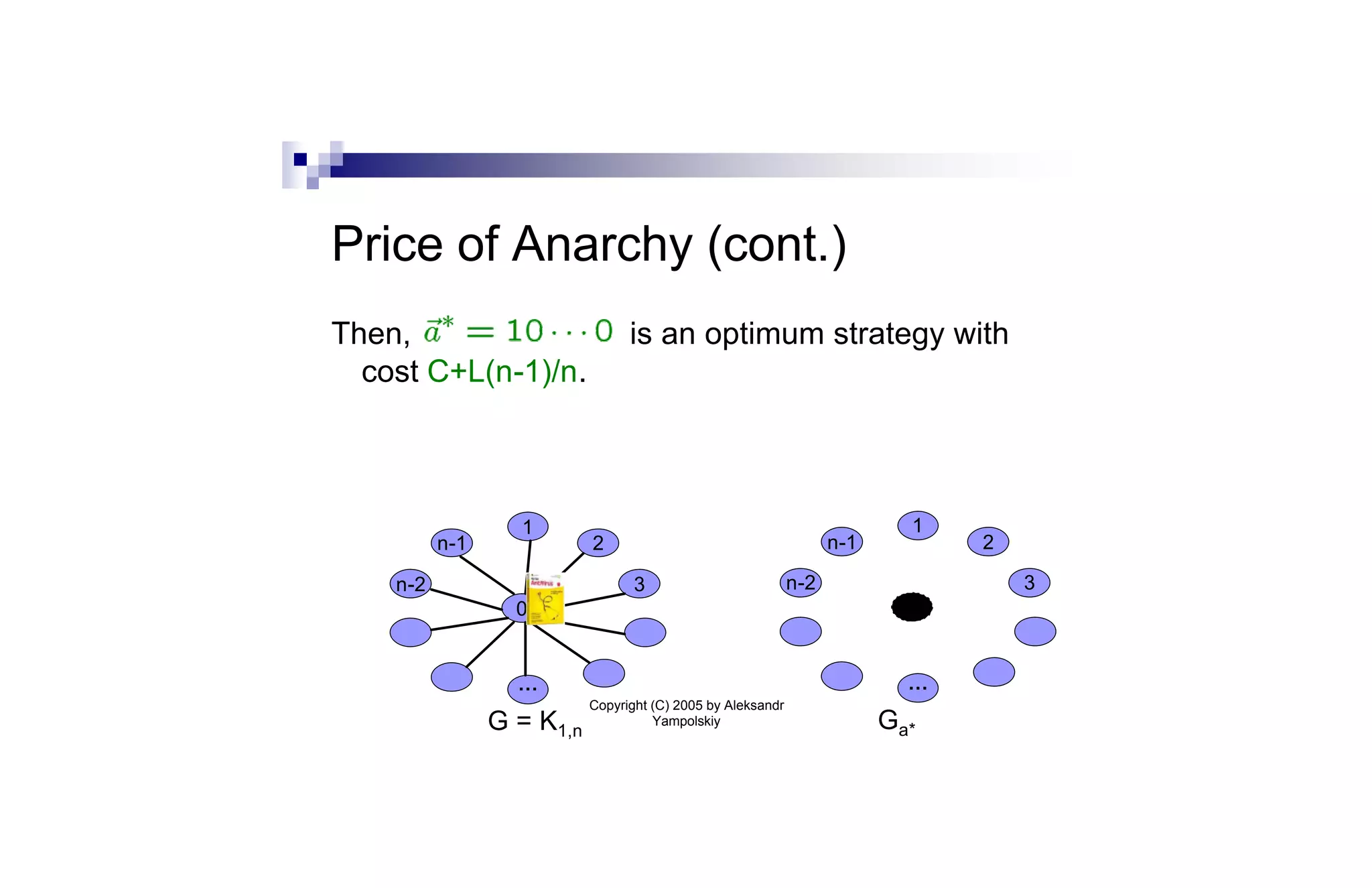
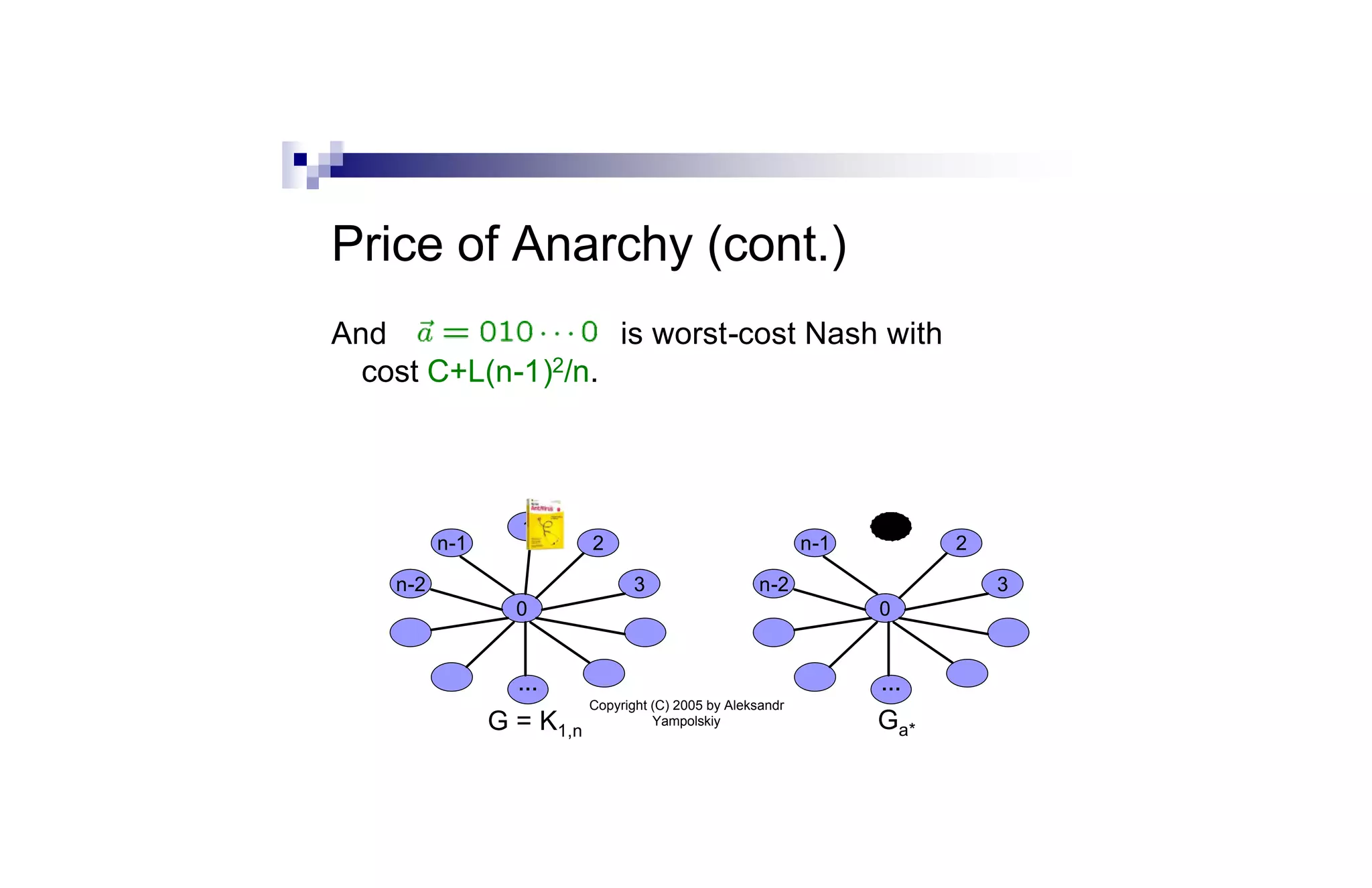






![Sum-of-Squares Partition (cont.)
Thm: We can find a set of O(log2 n)¢m nodes whose
removal partitions the graph into components
H1,…,Hk such that ∑i |Hi|2 · O(1)¢OPT.
Proof sketch: We use the Leighton-Rao sparse cut
algorithm [LR99]. The approach is similar to greedy
log n approximation algorithm for set cover. We
repeatedly remove the node cut that gives the best
per-node benefit.
Copyright (C) 2005 by Aleksandr
Yampolskiy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talkviruses-100914155953-phpapp01/75/Inoculation-strategies-for-victims-of-viruses-37-2048.jpg)




