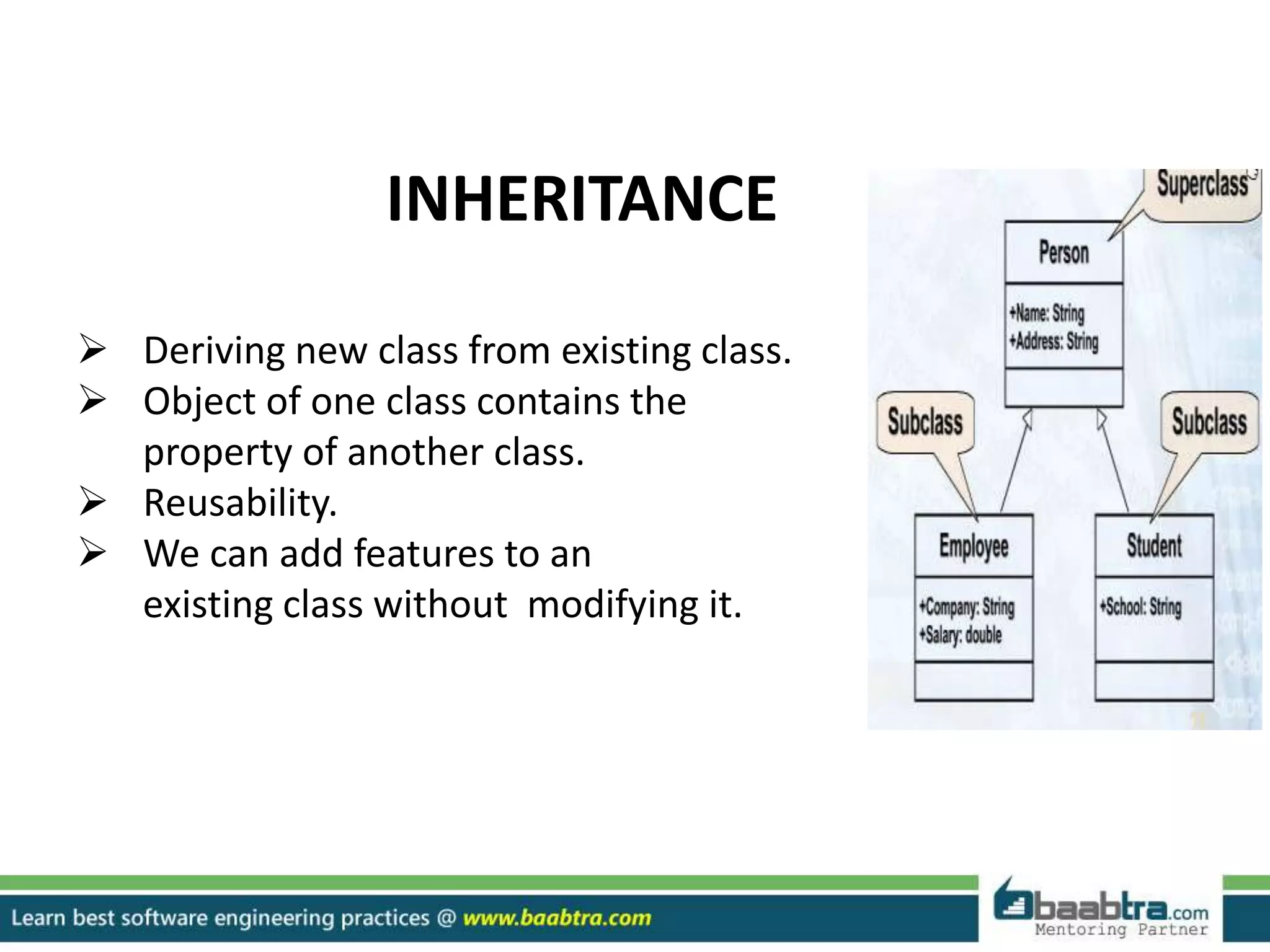
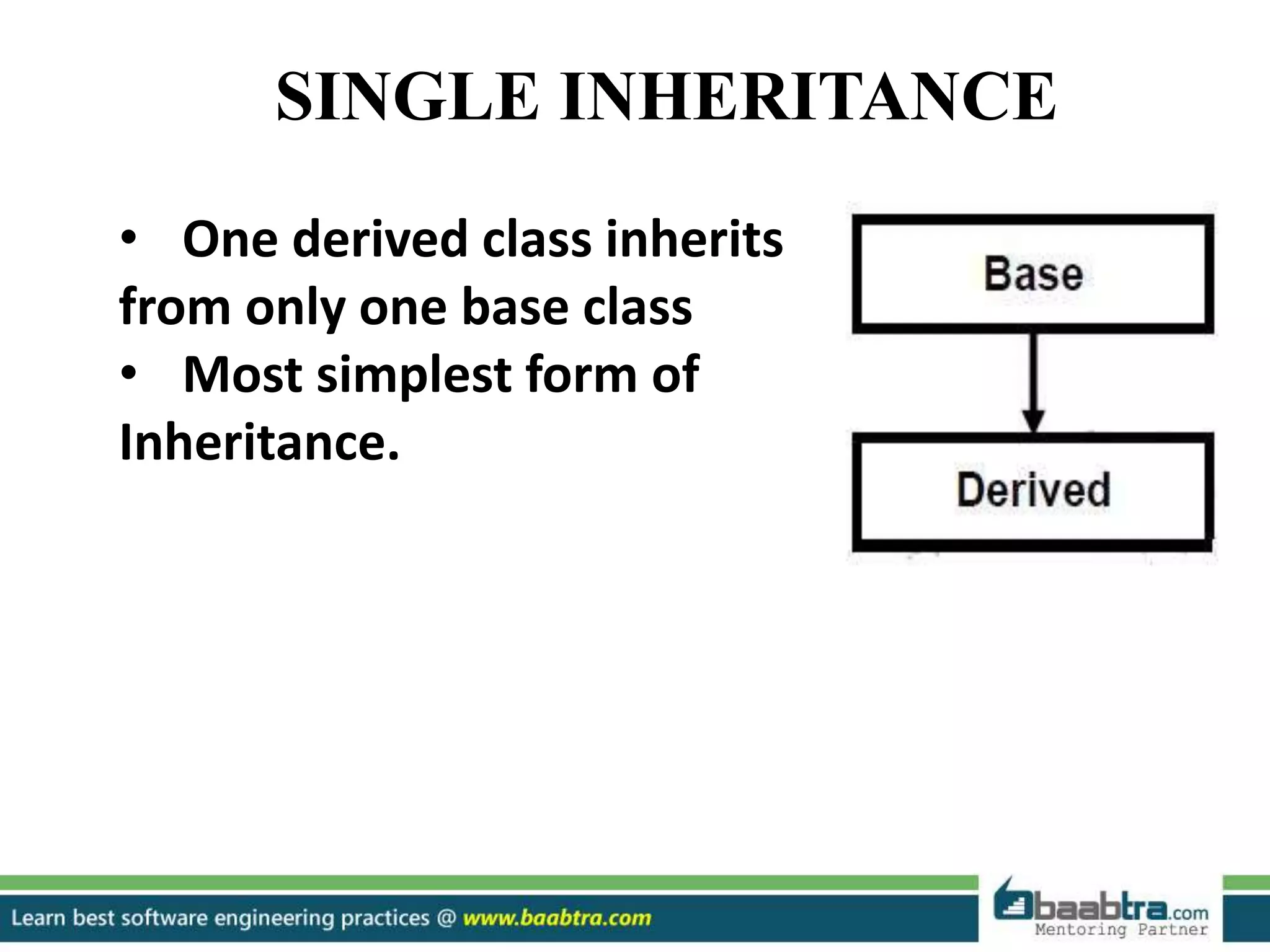
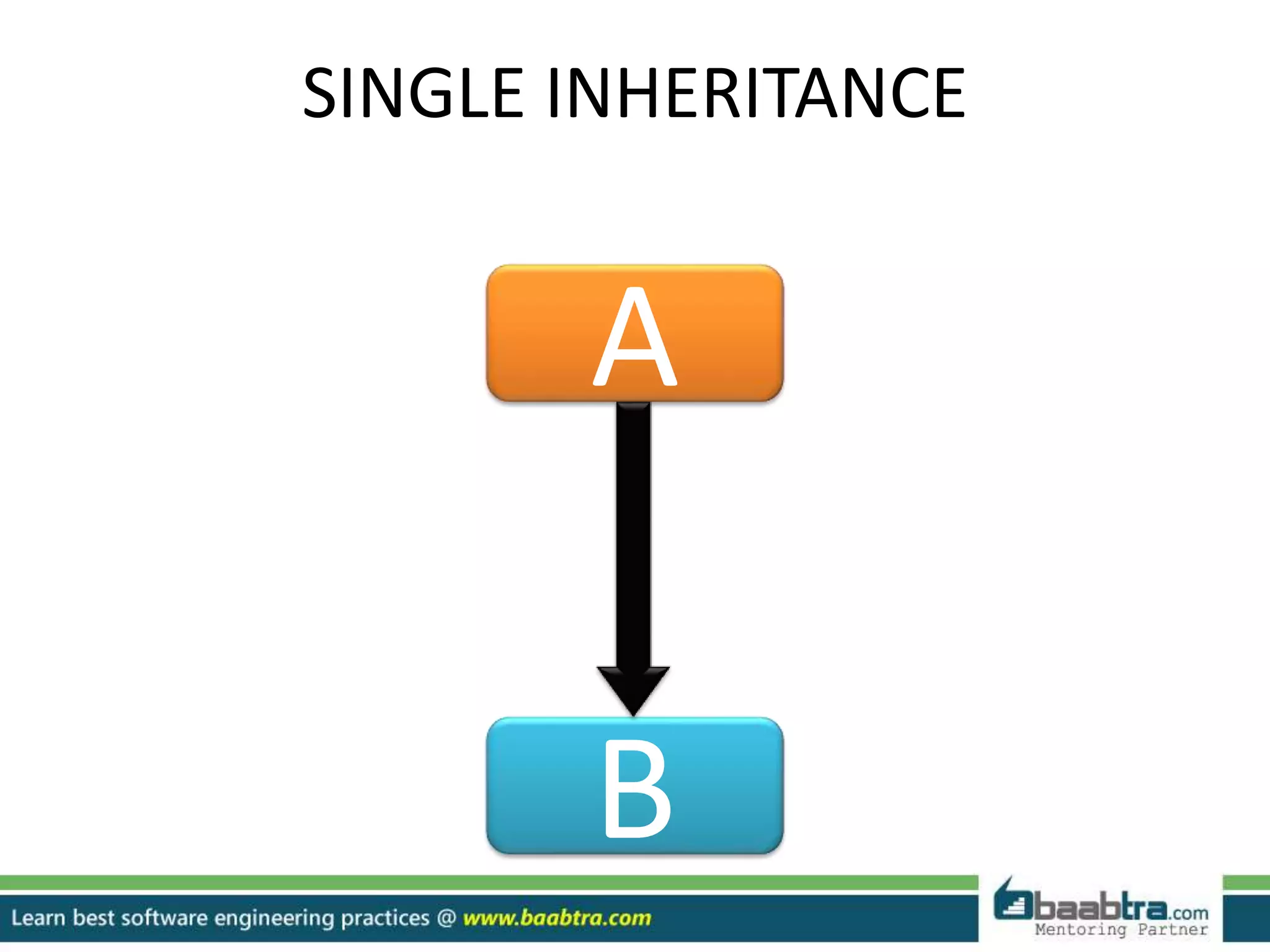
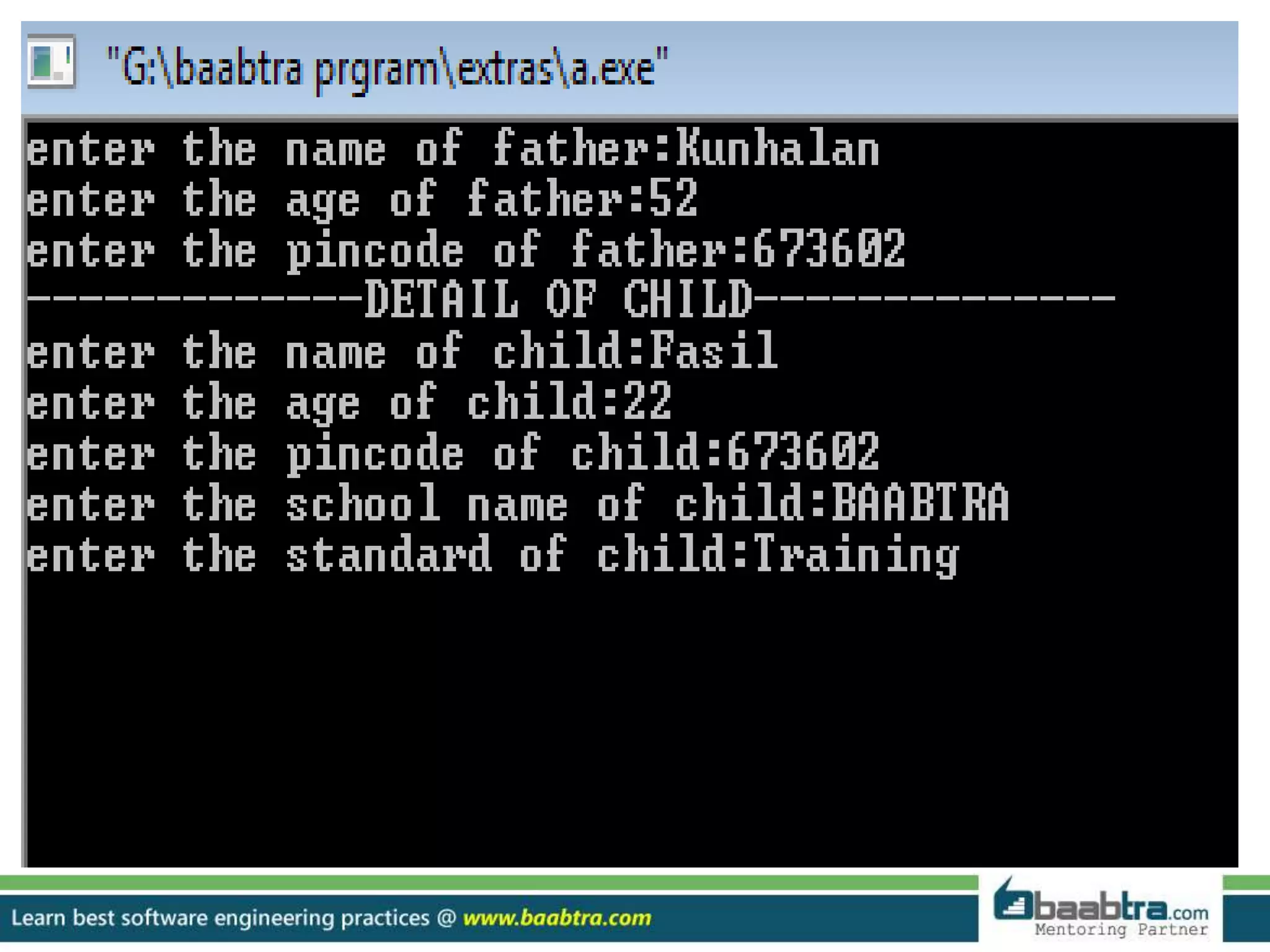
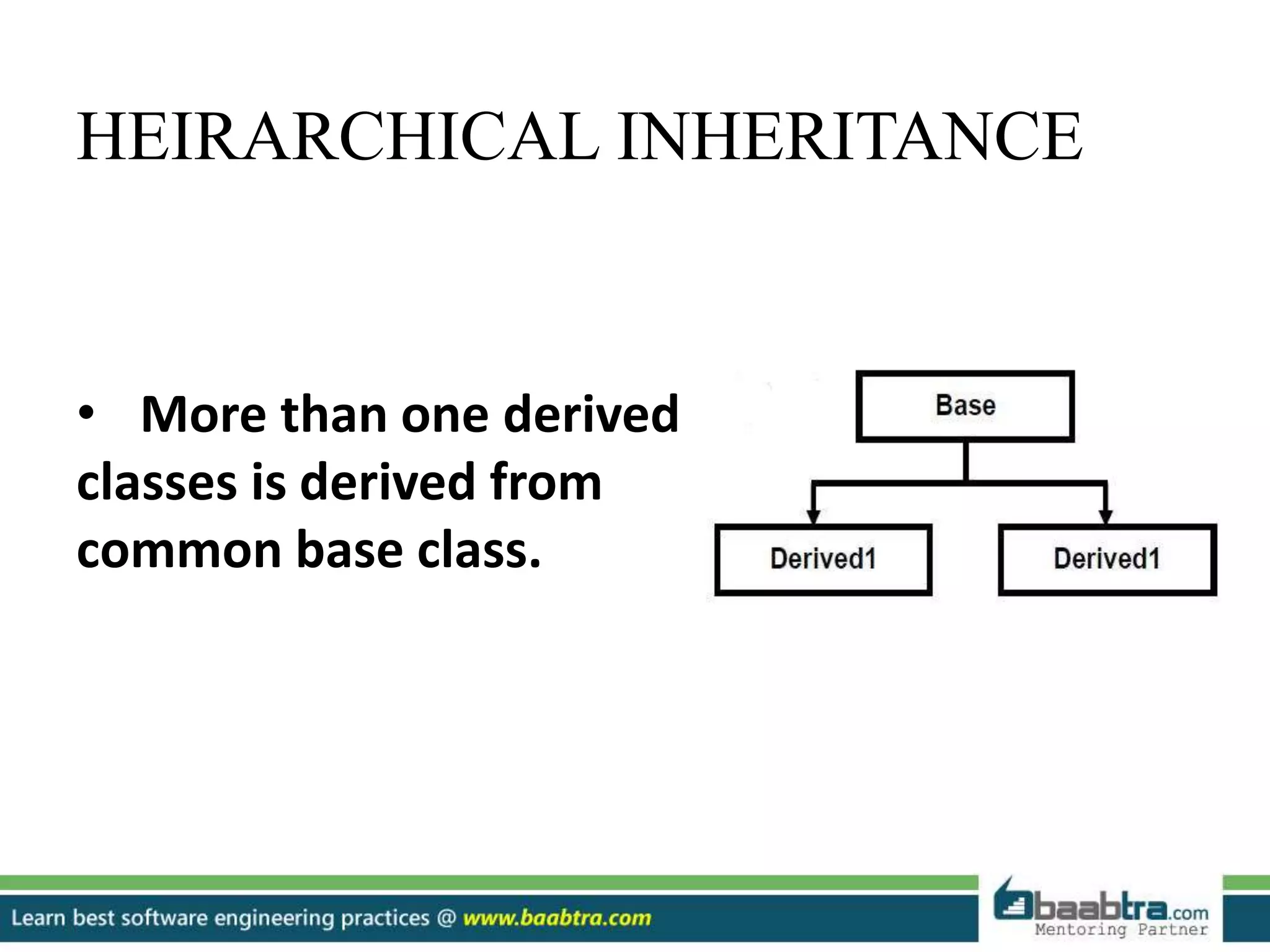
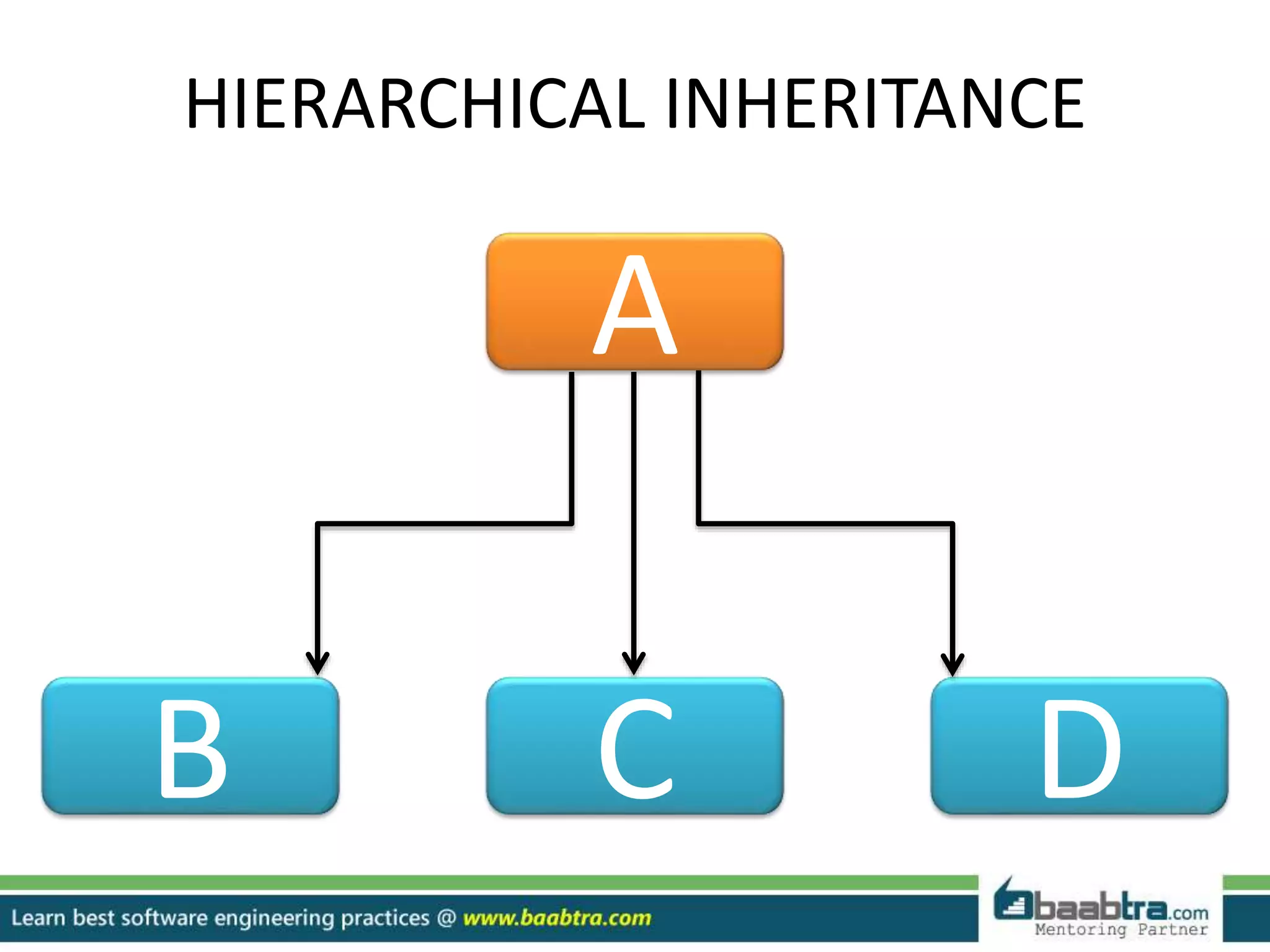
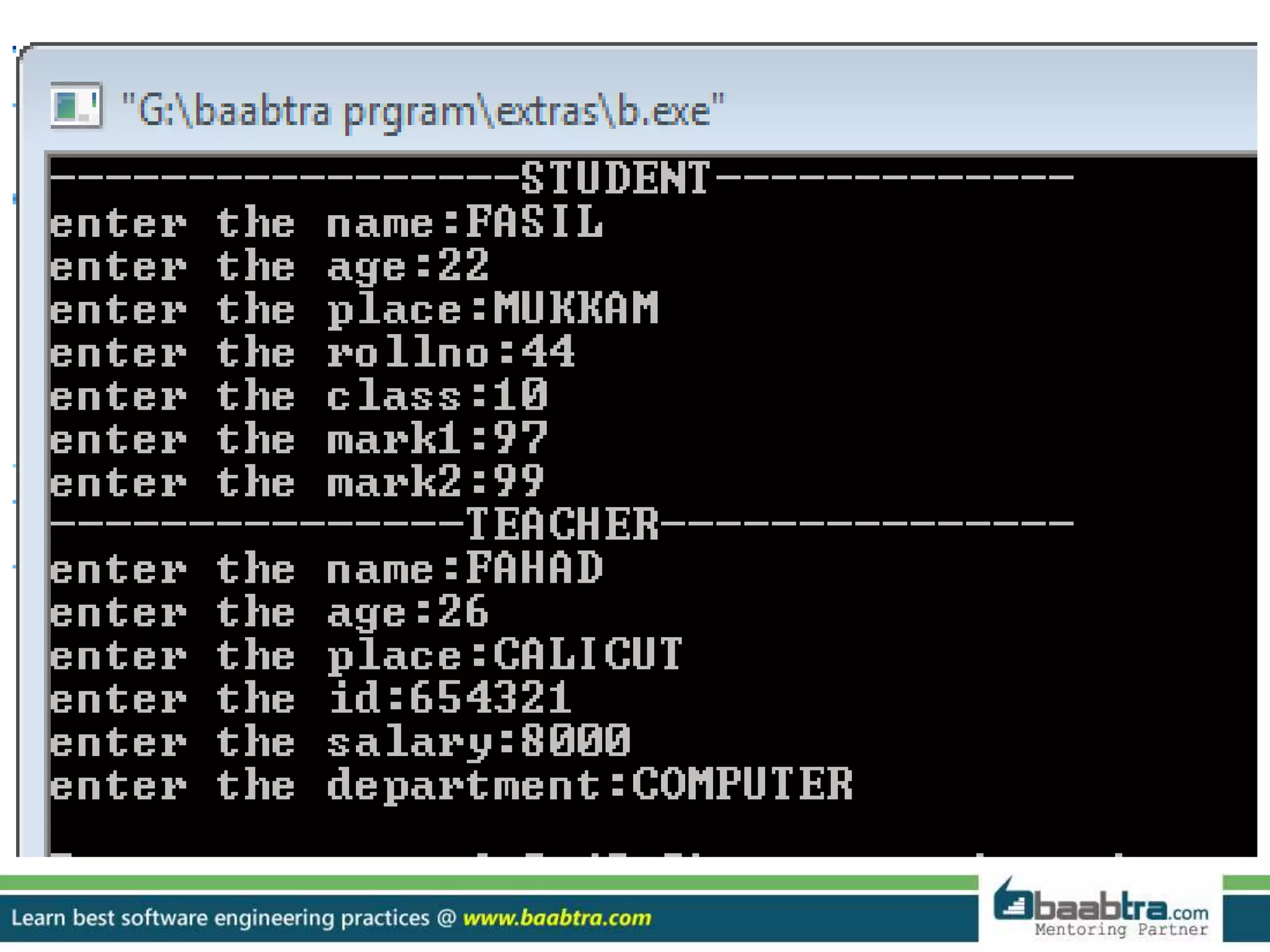
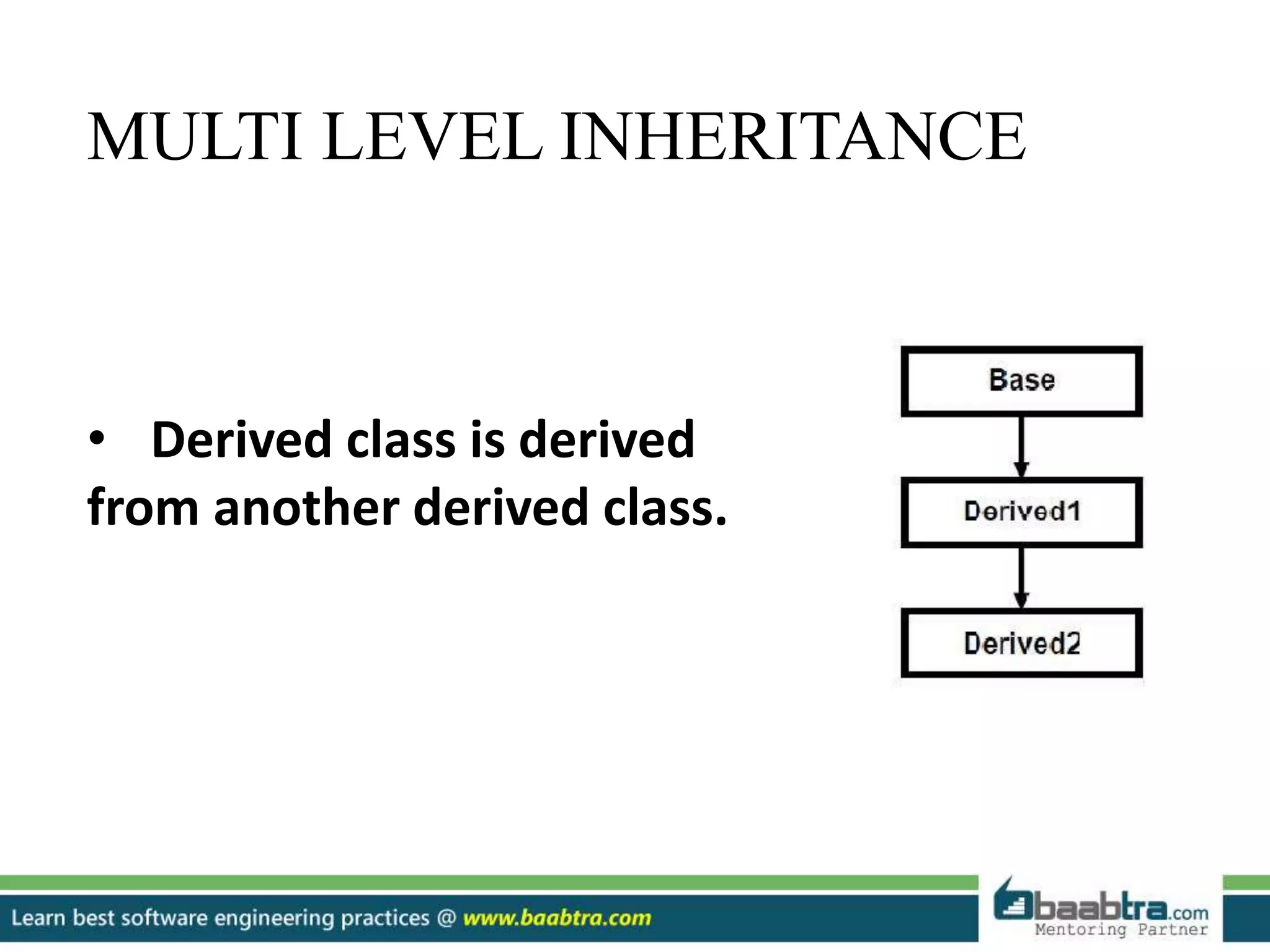
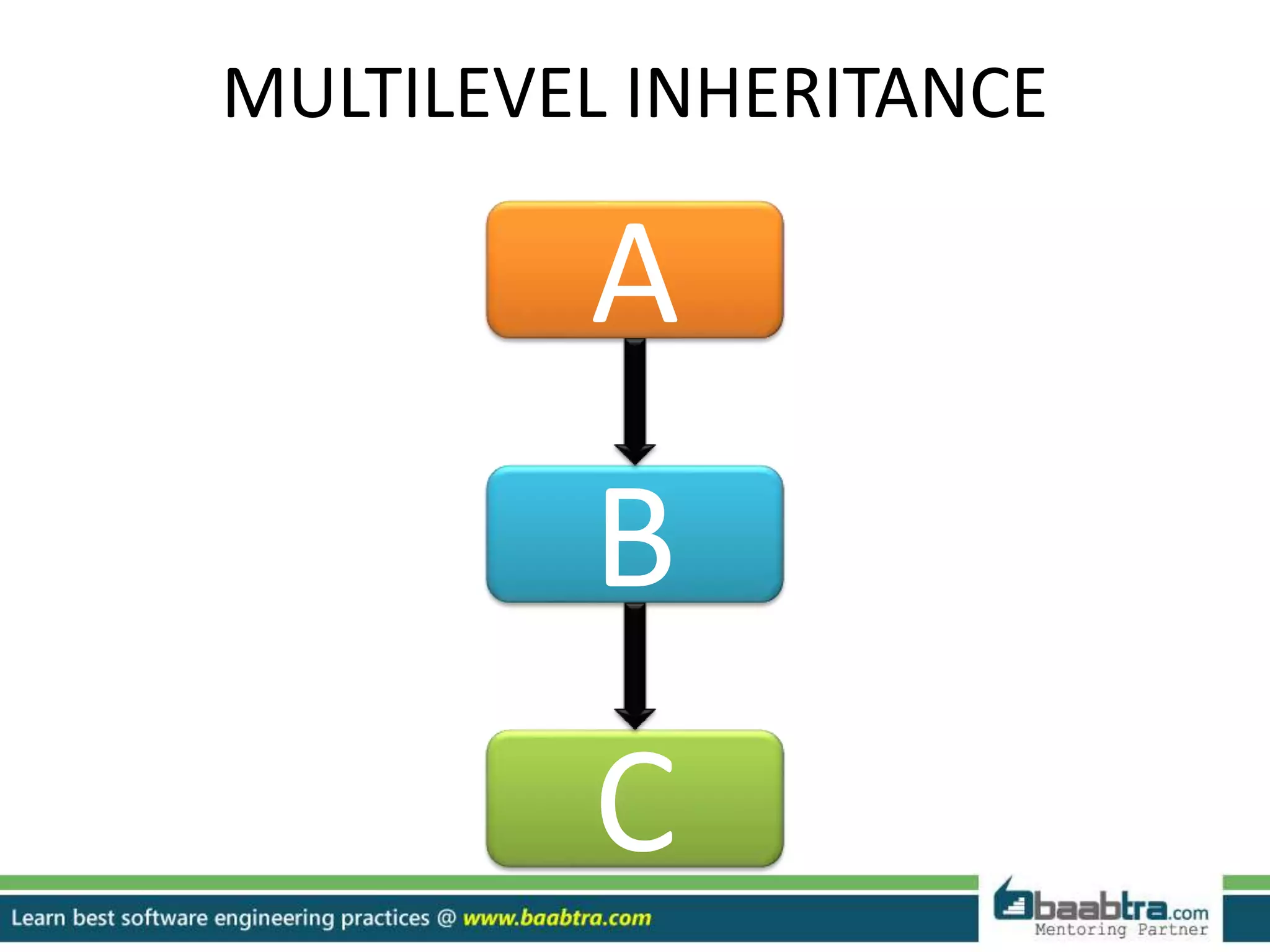
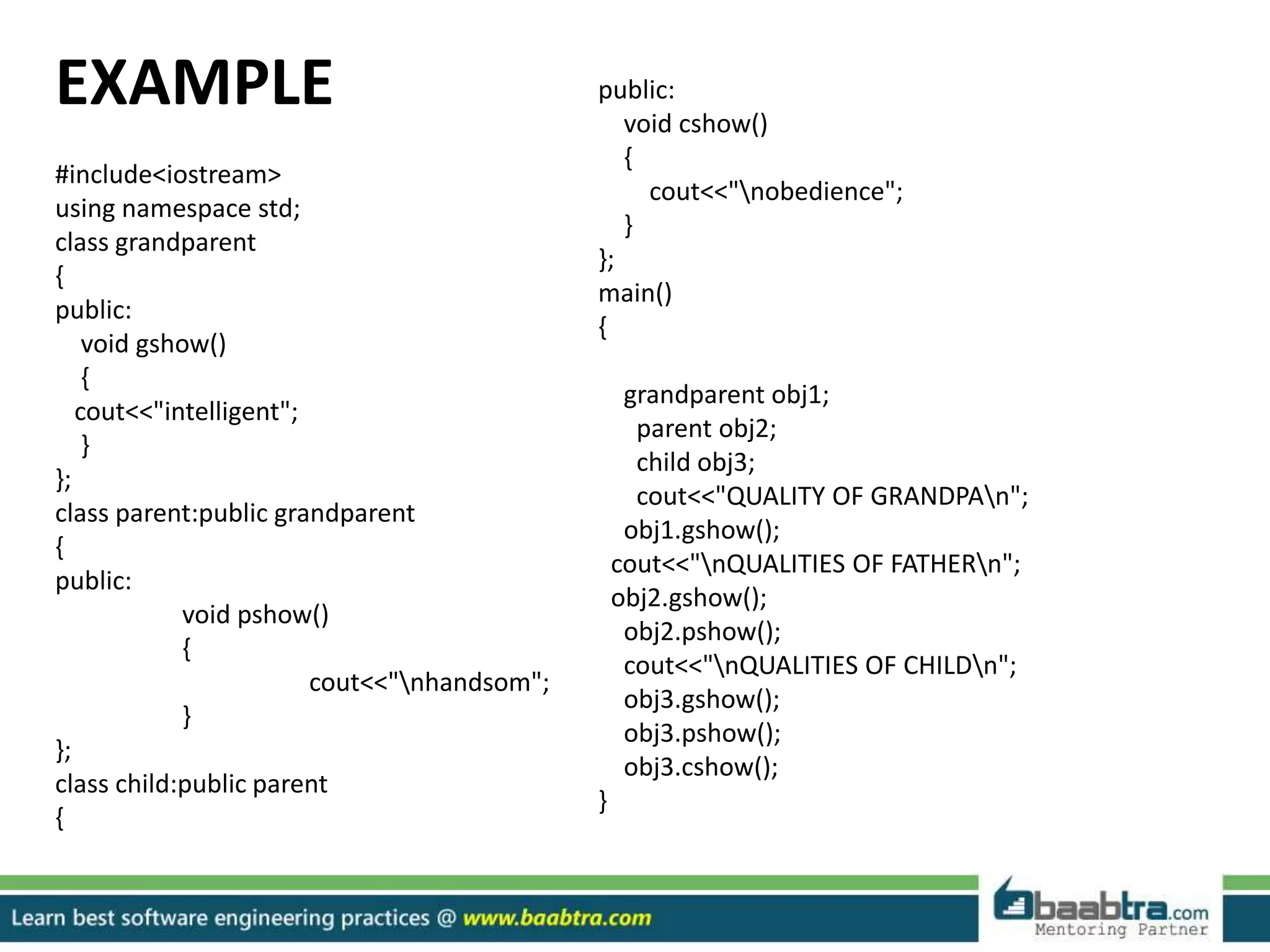
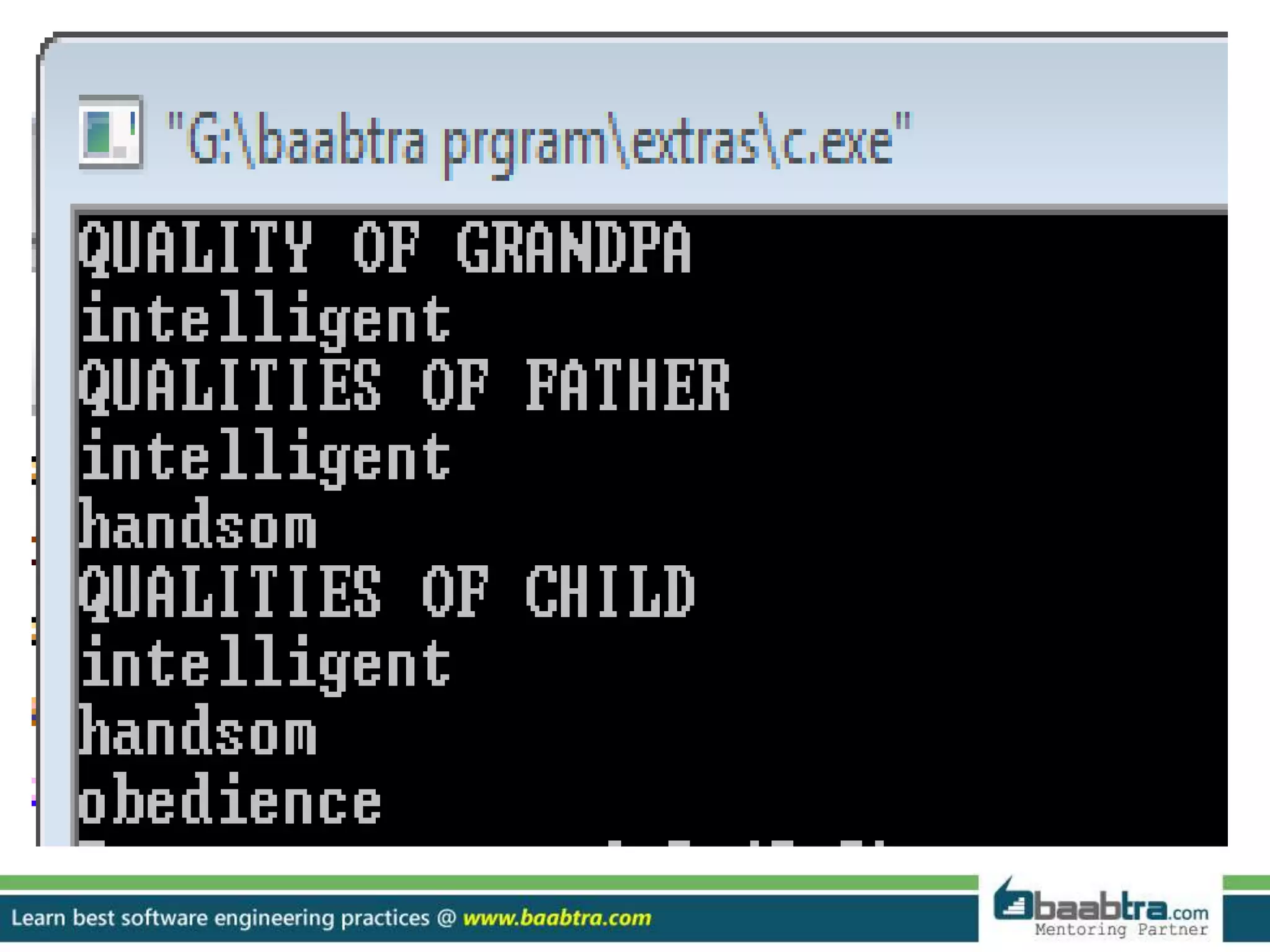
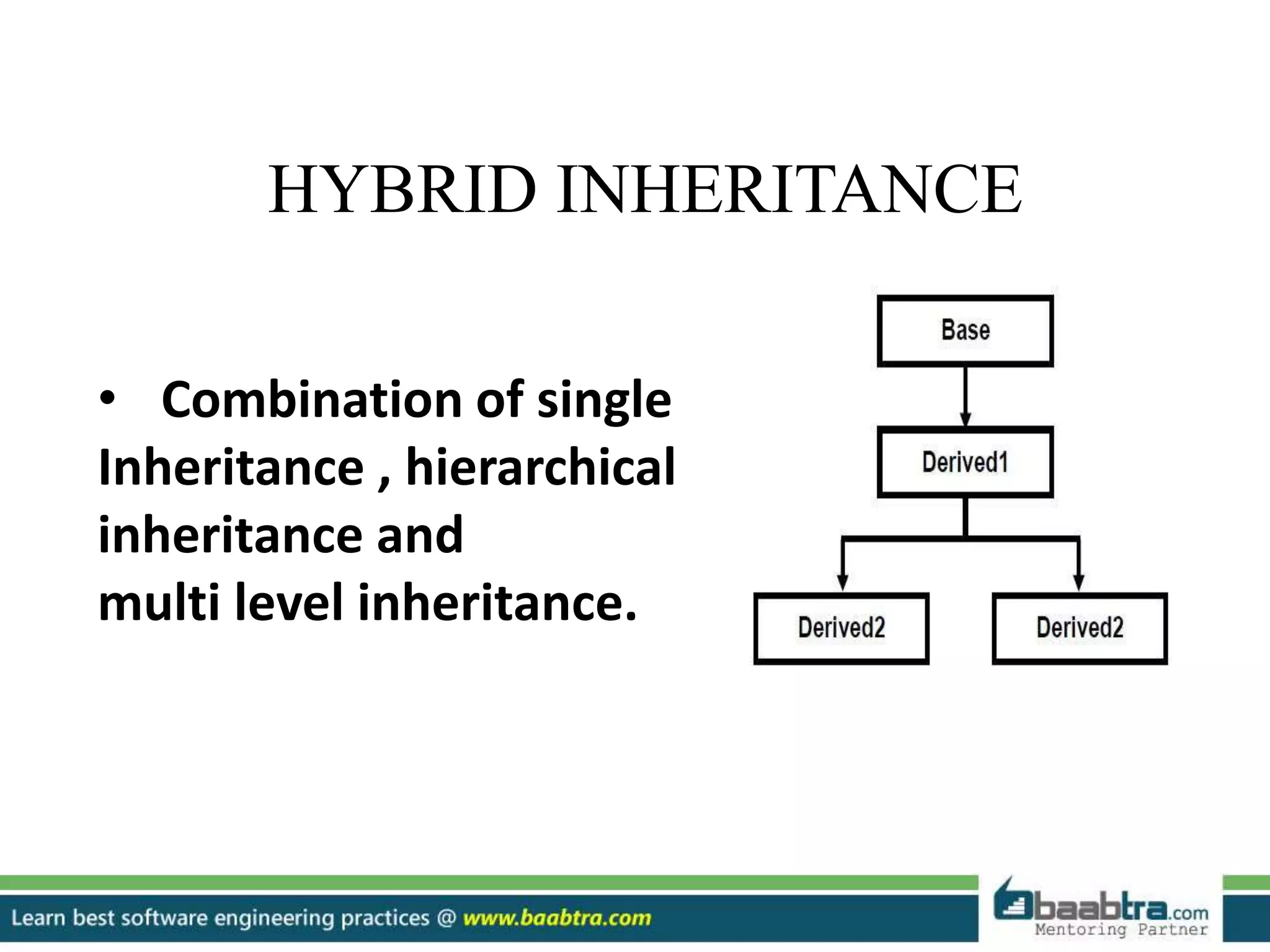
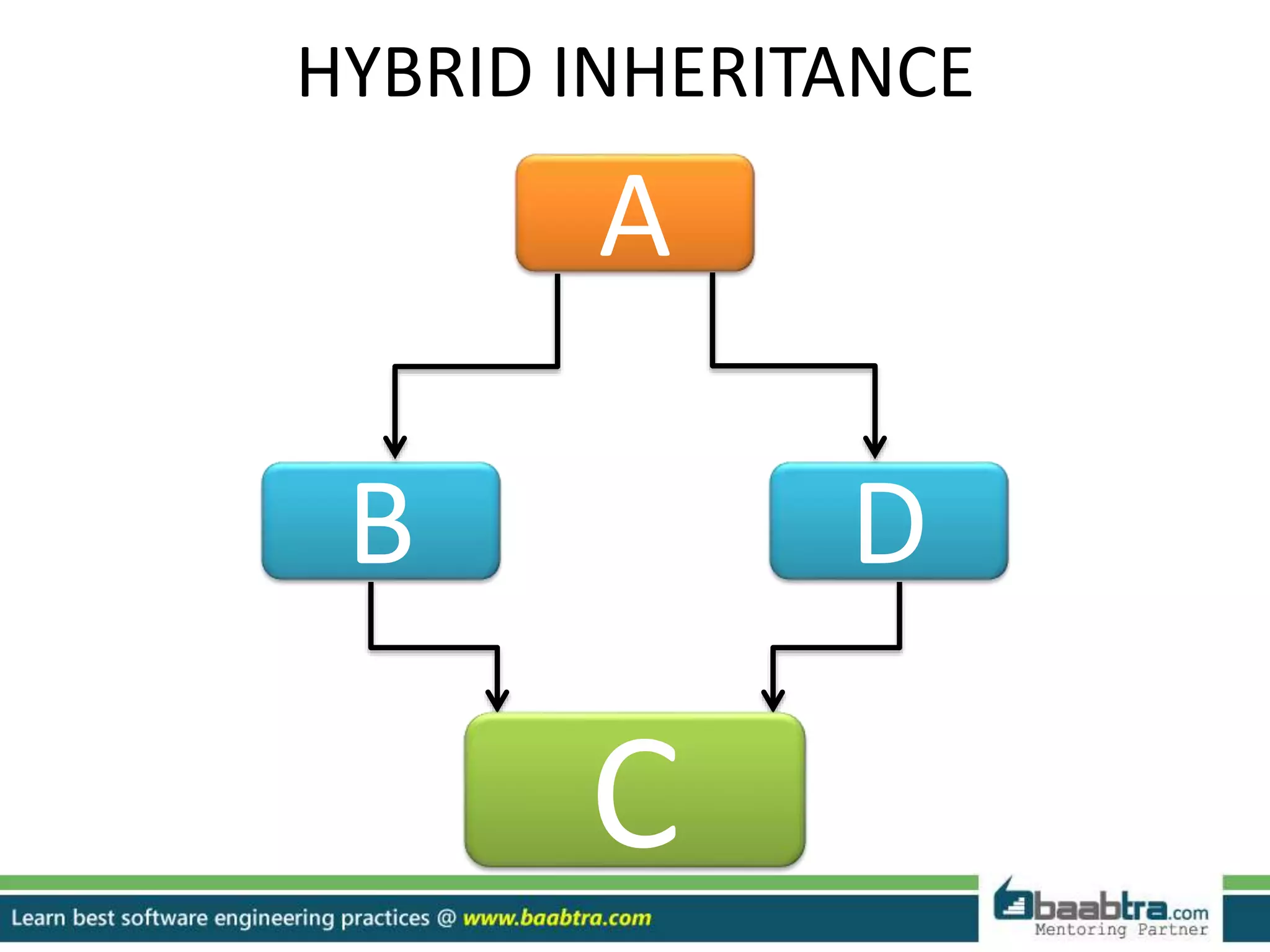
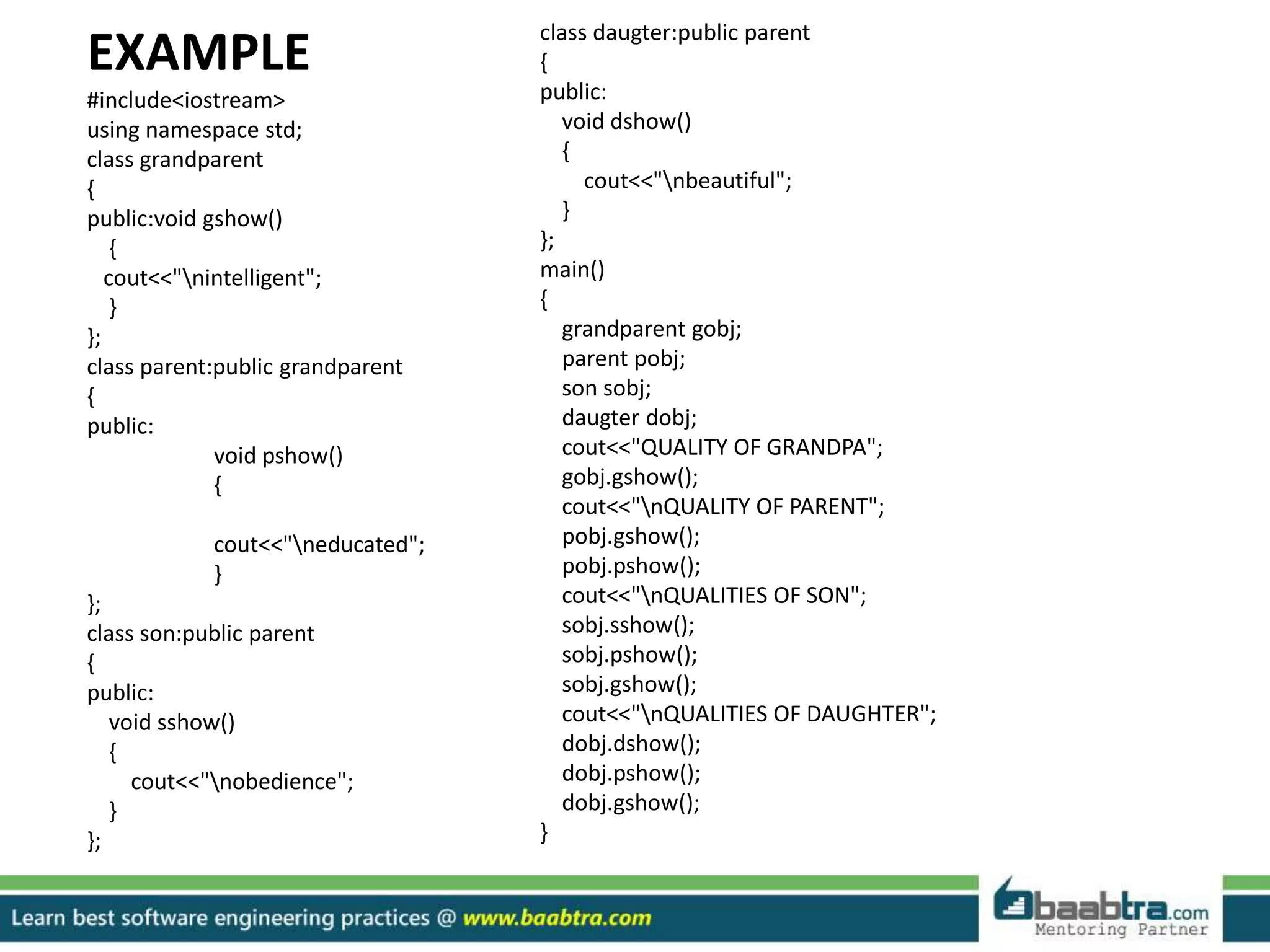
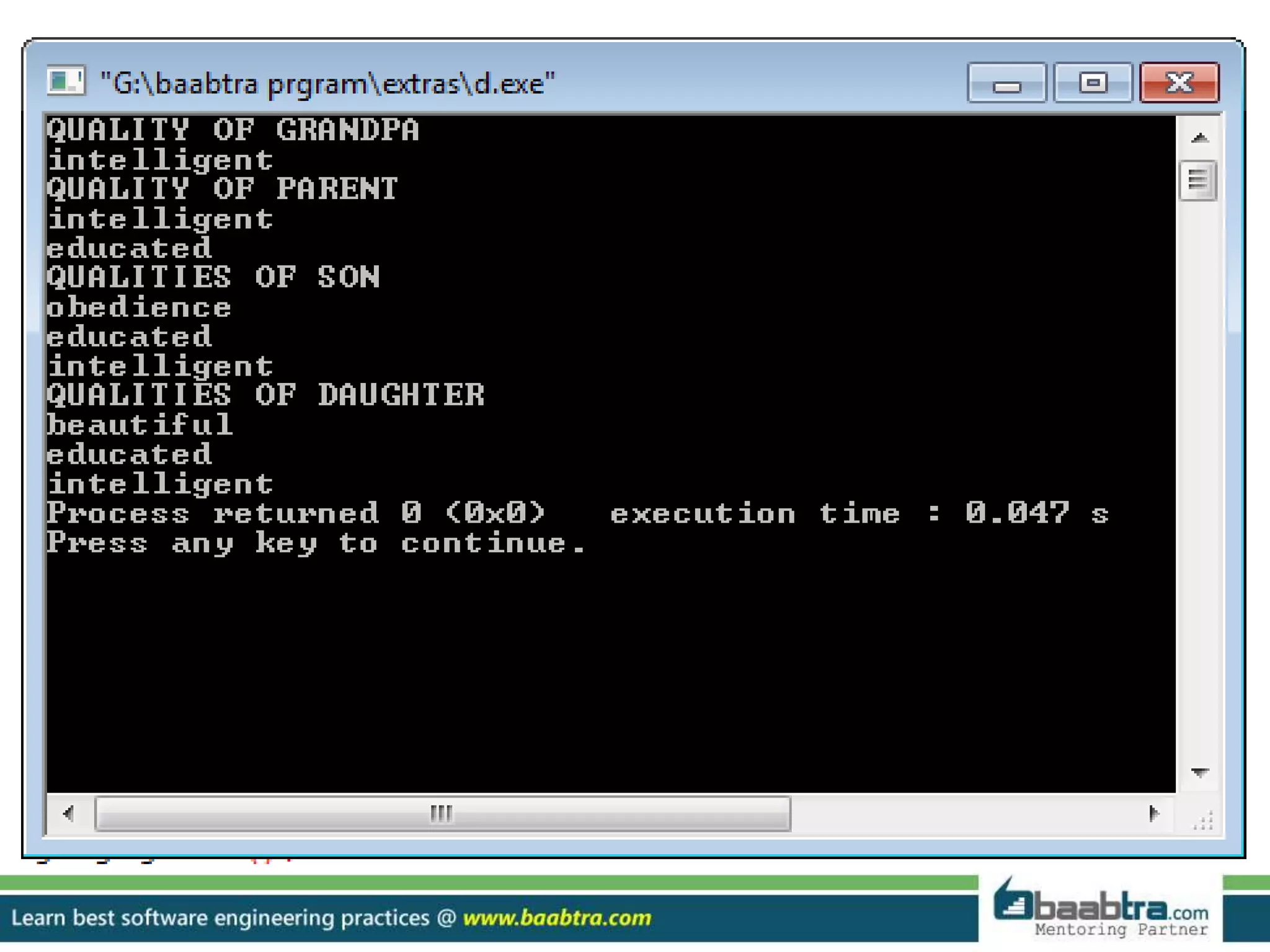
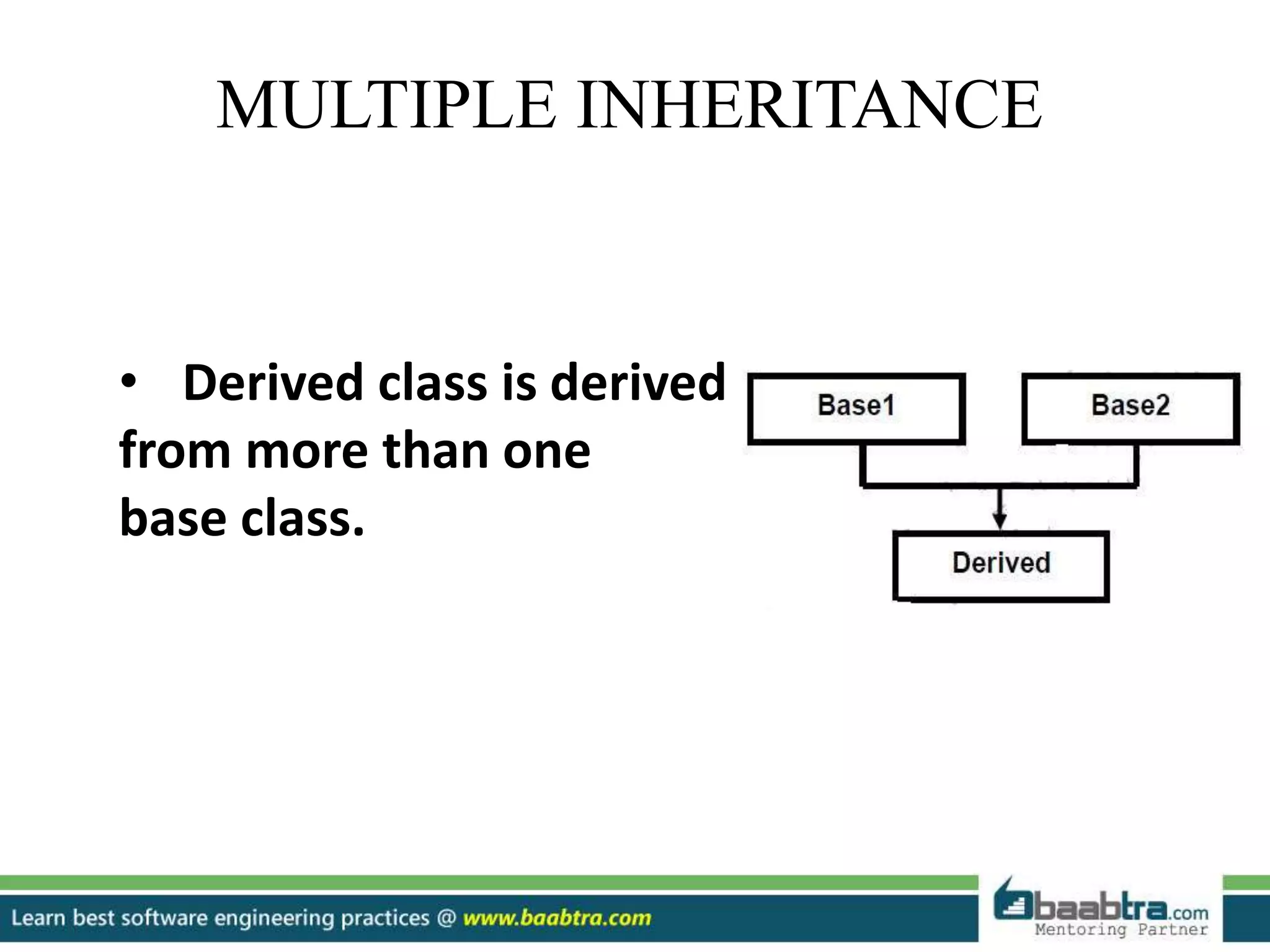
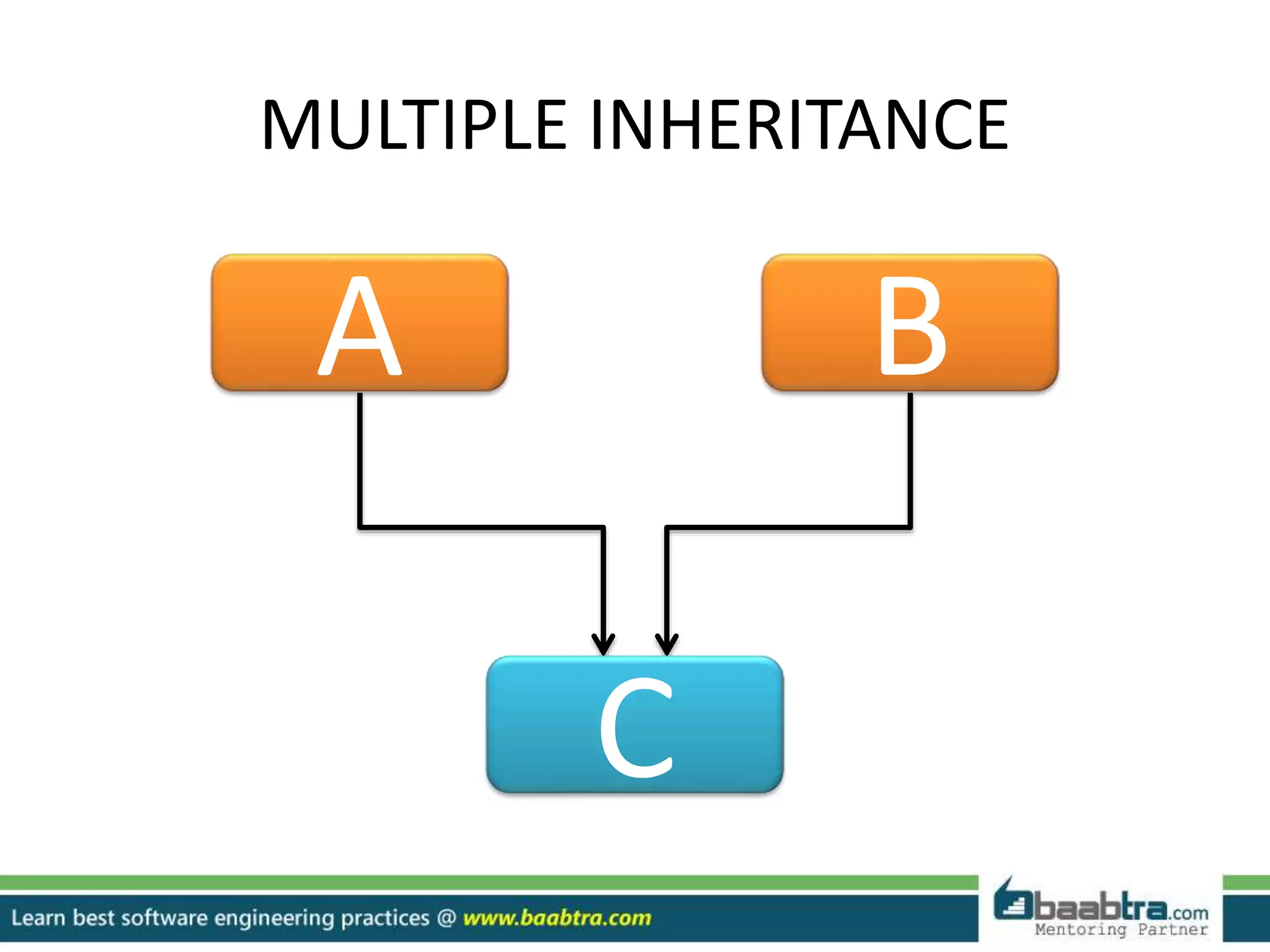
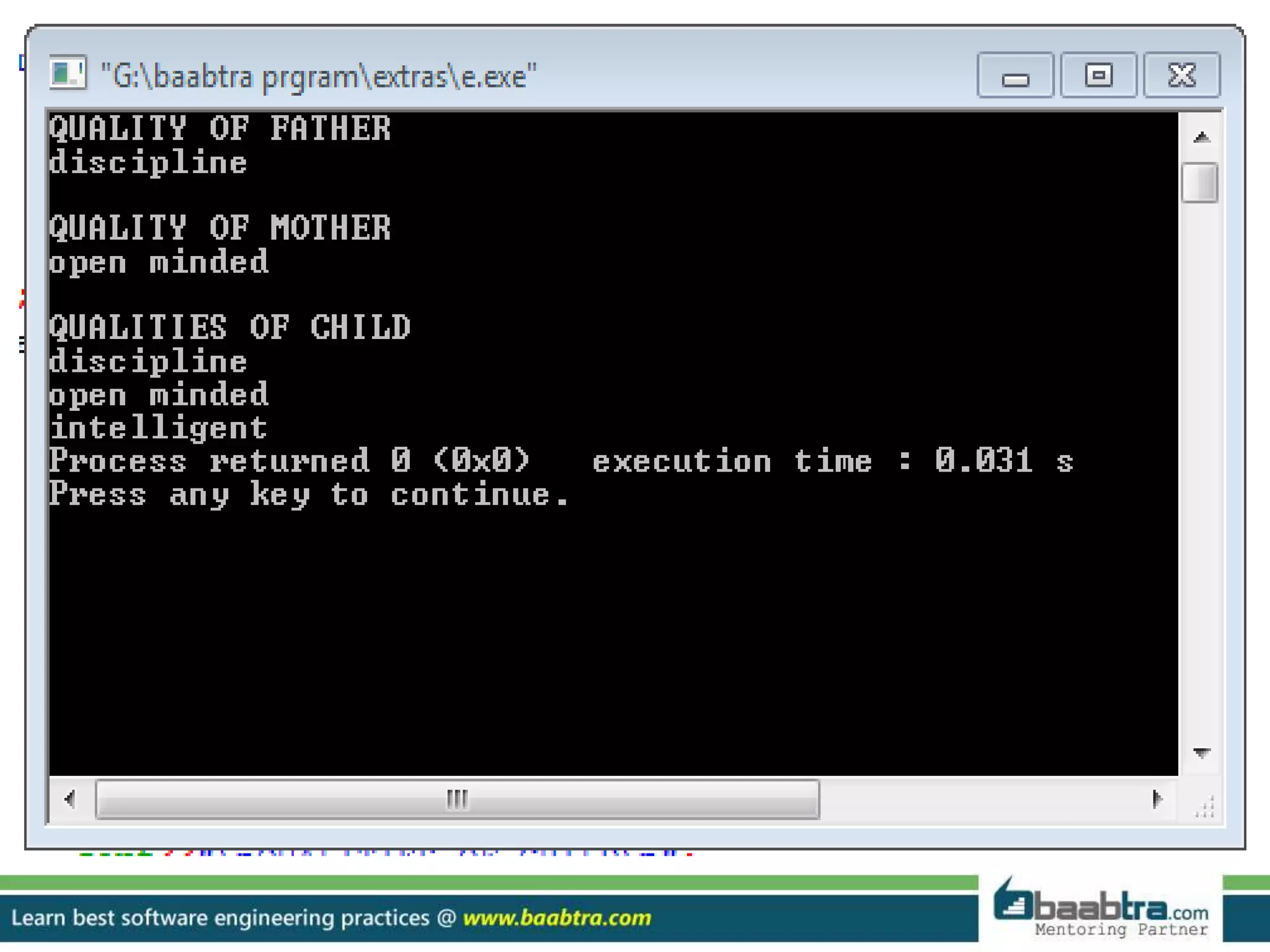
This document discusses different types of inheritance in object-oriented programming including single, multiple, hierarchical, multilevel, and hybrid inheritance. It provides examples of each type written in C++ code. Single inheritance allows a derived class to inherit from one base class. Hierarchical inheritance has more than one derived class inheriting from a common base class. Multilevel inheritance means a derived class inherits from another derived class. Hybrid inheritance combines different inheritance techniques. The document concludes that inheritance allows code reuse and extending existing classes.