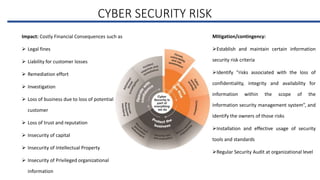
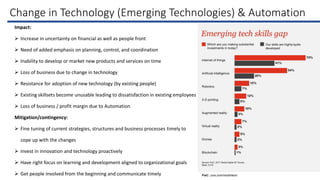
This document discusses the IT industry in India. It provides an introduction to the major components of the IT industry in India, including IT services, business process outsourcing, software products and engineering services, and hardware. It notes some of the top players in the Indian IT industry and provides revenue figures. It also discusses IT as a service (ITaaS) delivery model. The document then outlines some of the key drivers for success and risks faced by industry players, including cybersecurity risks, political and regulatory risks, risks from changes in technology and automation, and provides mitigation strategies for three of the top risks. It also discusses risk management standards and guidelines and provides an overview of the COSO enterprise risk management framework and Wipro