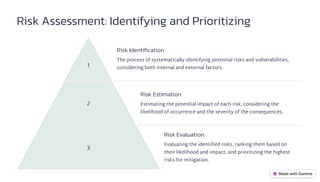
This document serves as a practical guide to IT risk management, outlining essential steps for IT professionals including risk definition, assessment, mitigation, and communication. Key components of the risk management process involve establishing context, identifying threats and vulnerabilities, and continuous monitoring. Effective roles such as senior management and security officers are crucial for implementing and sustaining risk management strategies.