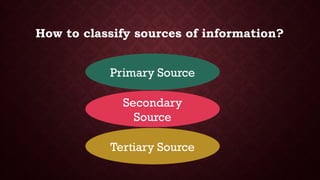
The document discusses the essential competency of using information in everyday life, detailing methods of gathering it such as listening, reading, and observation. It classifies information sources into primary, secondary, and tertiary categories, explaining the distinctions between them and providing examples for each. Additionally, it highlights various types of informative content like news reports, speeches, informative talks, and panel discussions.