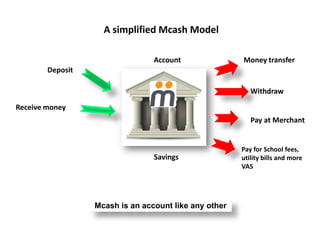
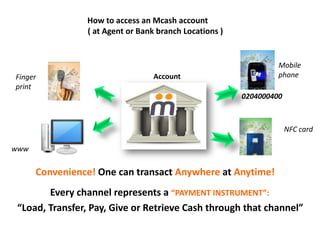
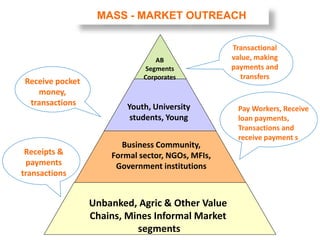
The document discusses the significance of information communication and technology (ICT) in fostering development in Uganda across various sectors such as health, agriculture, business, and education. It highlights the role of scientific research and innovative technologies in improving health outcomes, enhancing business operations, and facilitating access to education through online platforms. Additionally, it addresses the challenges related to ICT implementation, including security concerns and infrastructure limitations, while emphasizing the potential of ICT to drive sustainable growth and development.