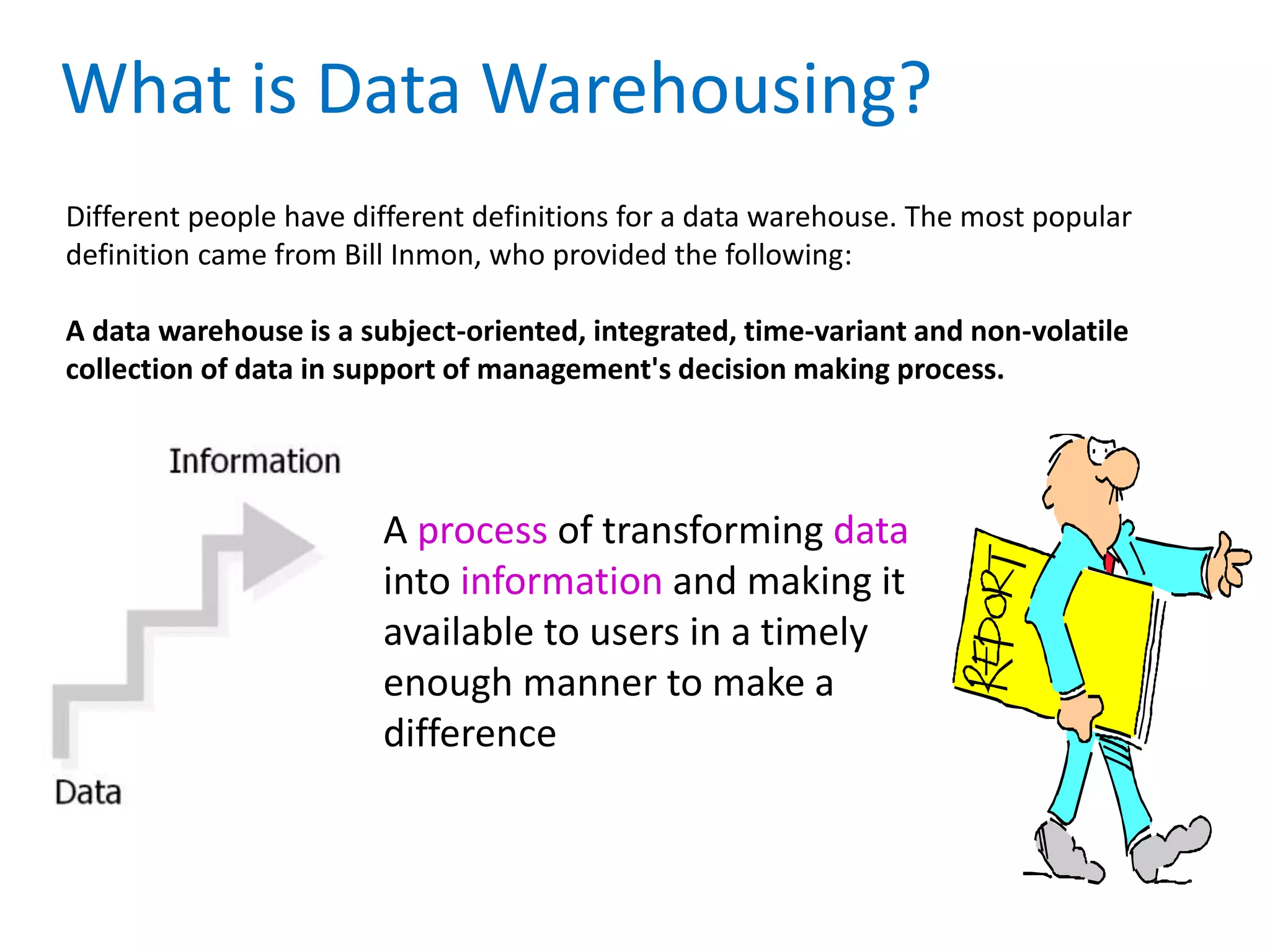
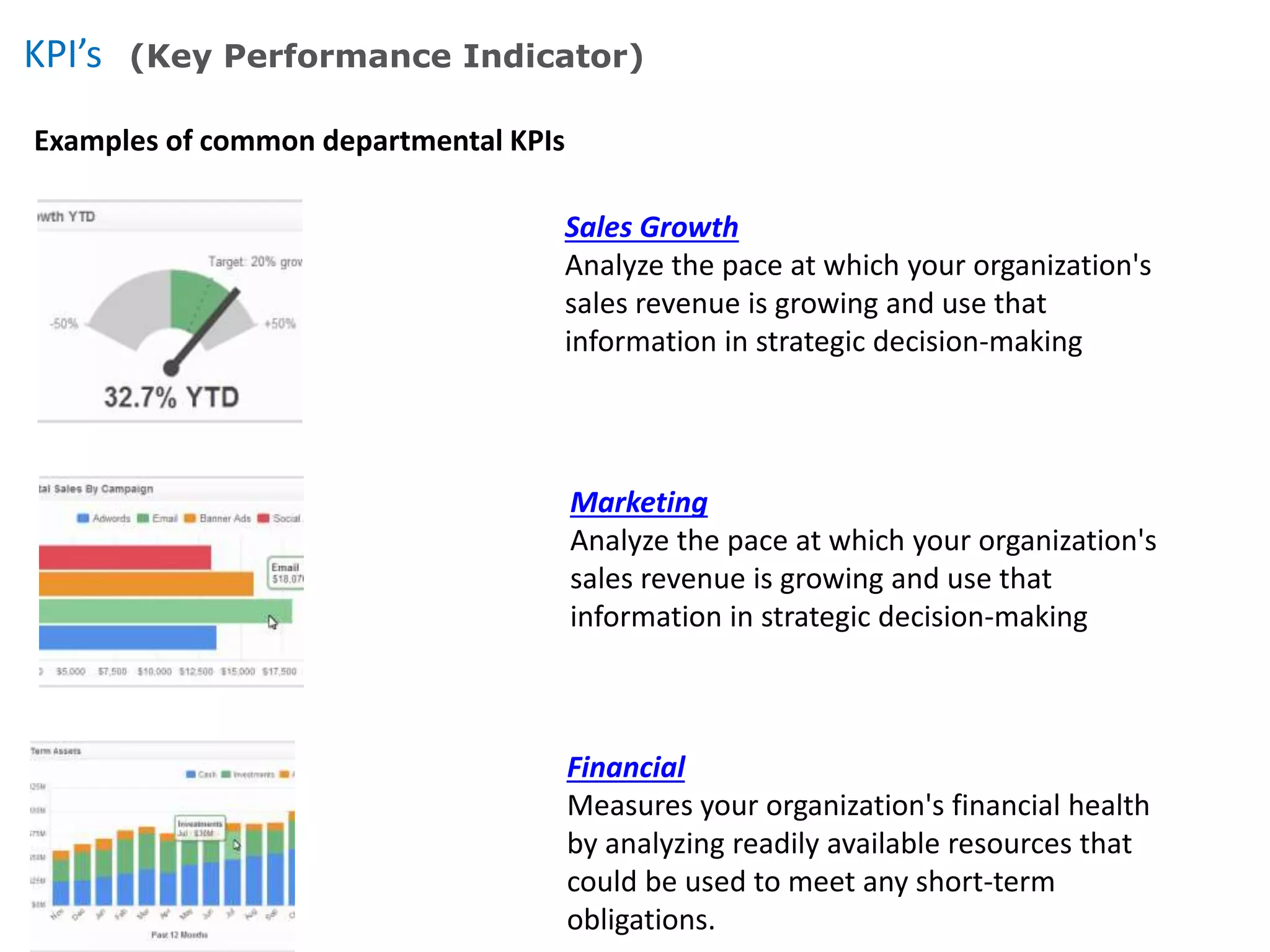
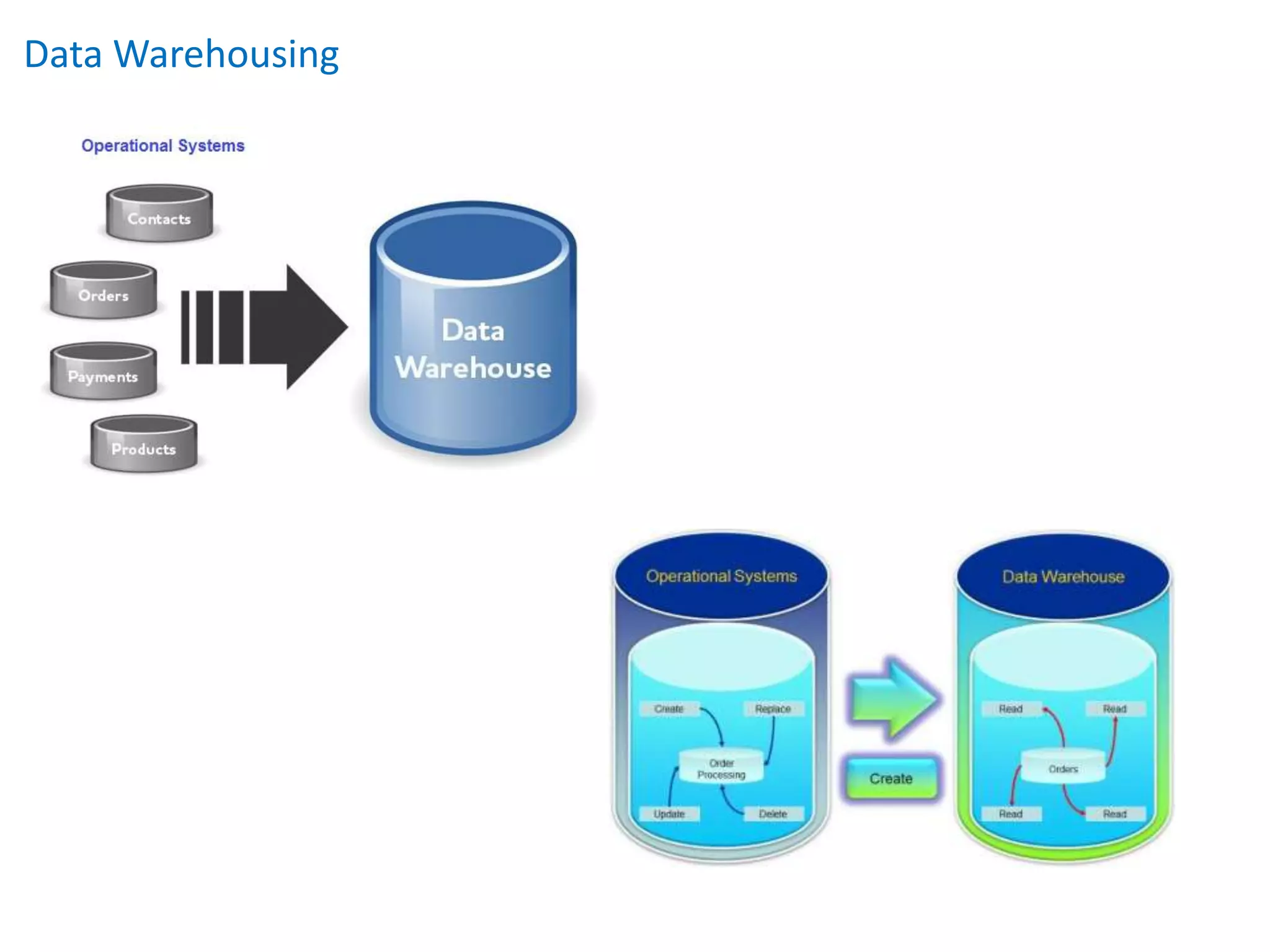
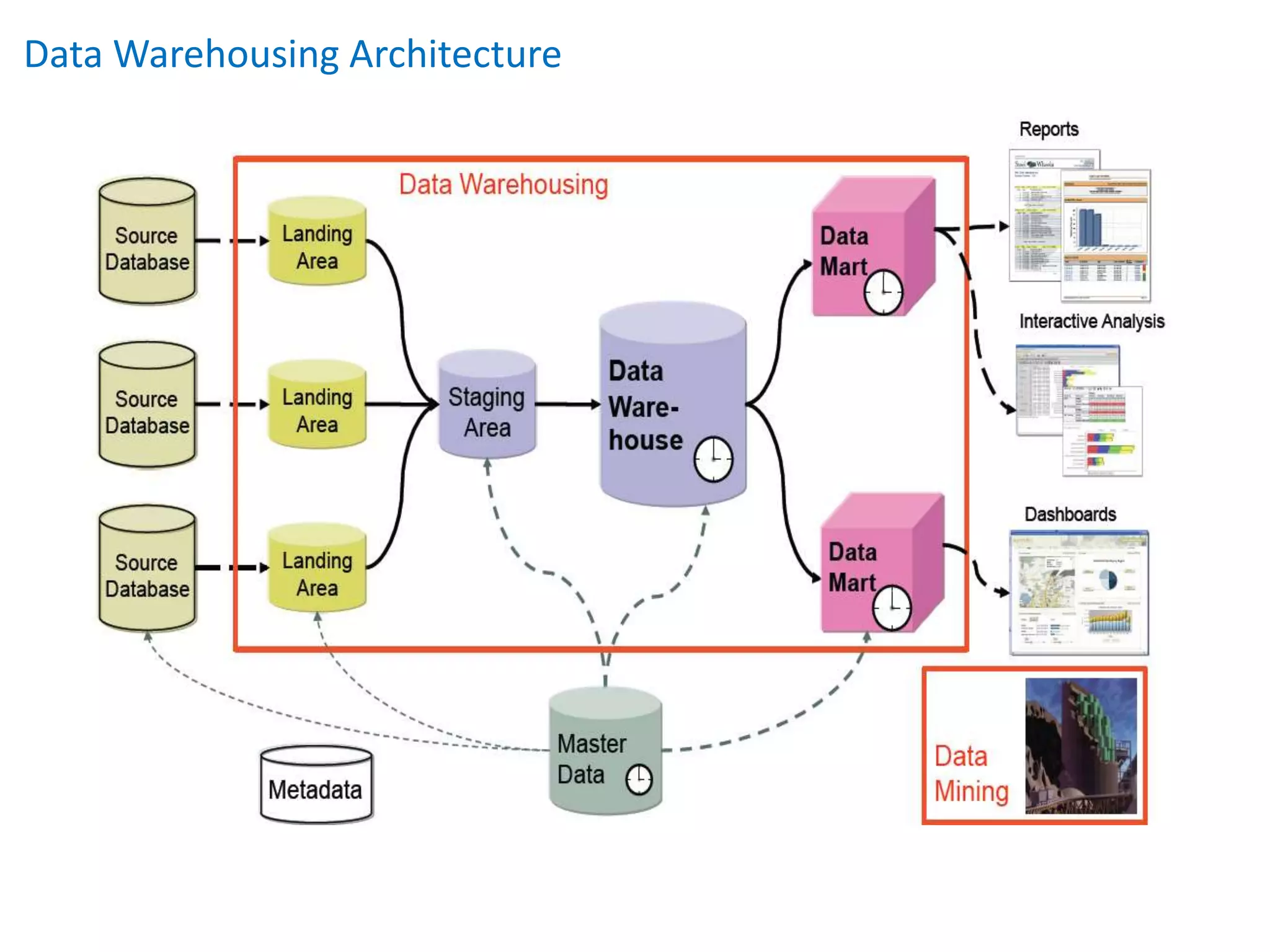
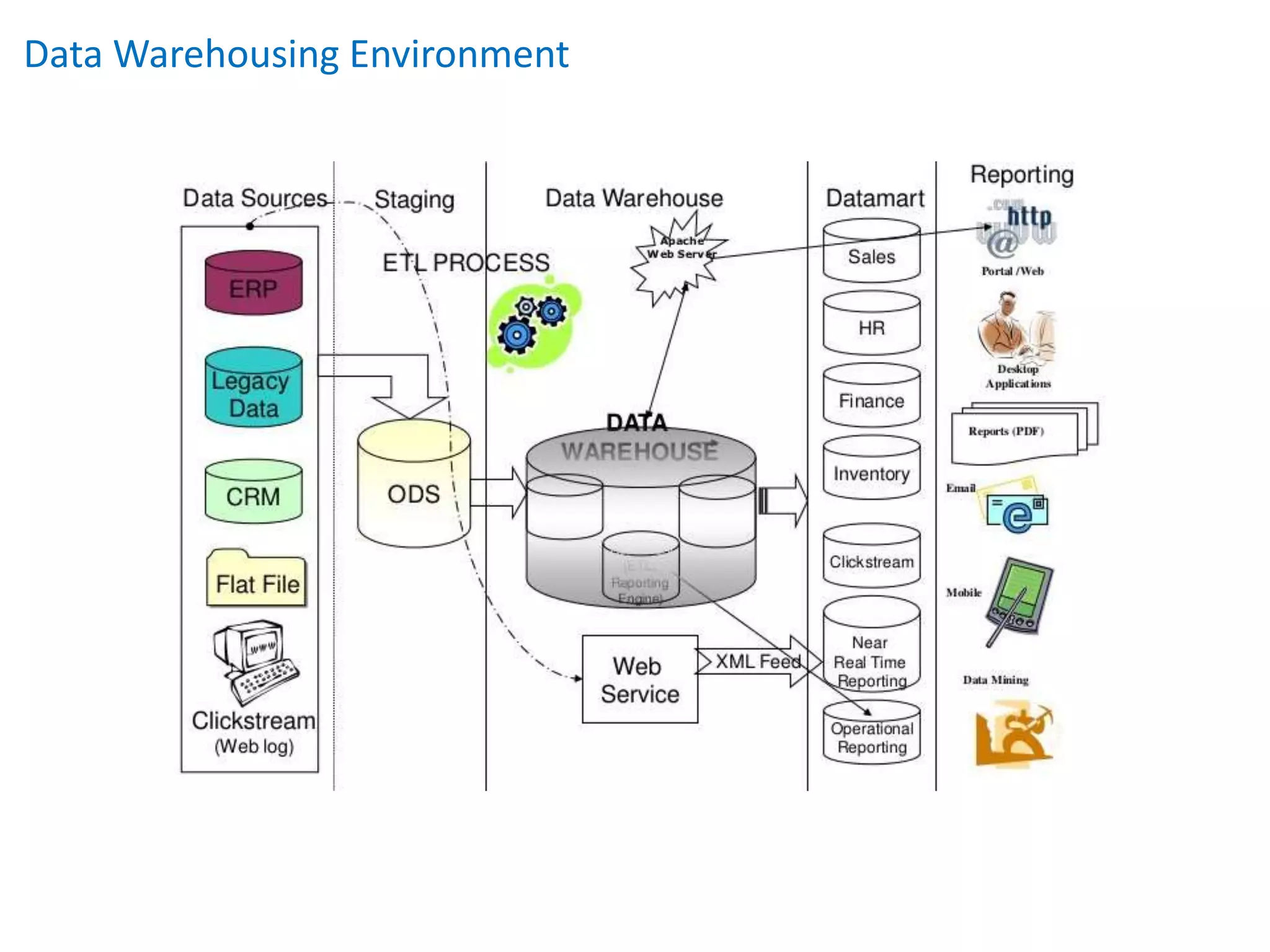
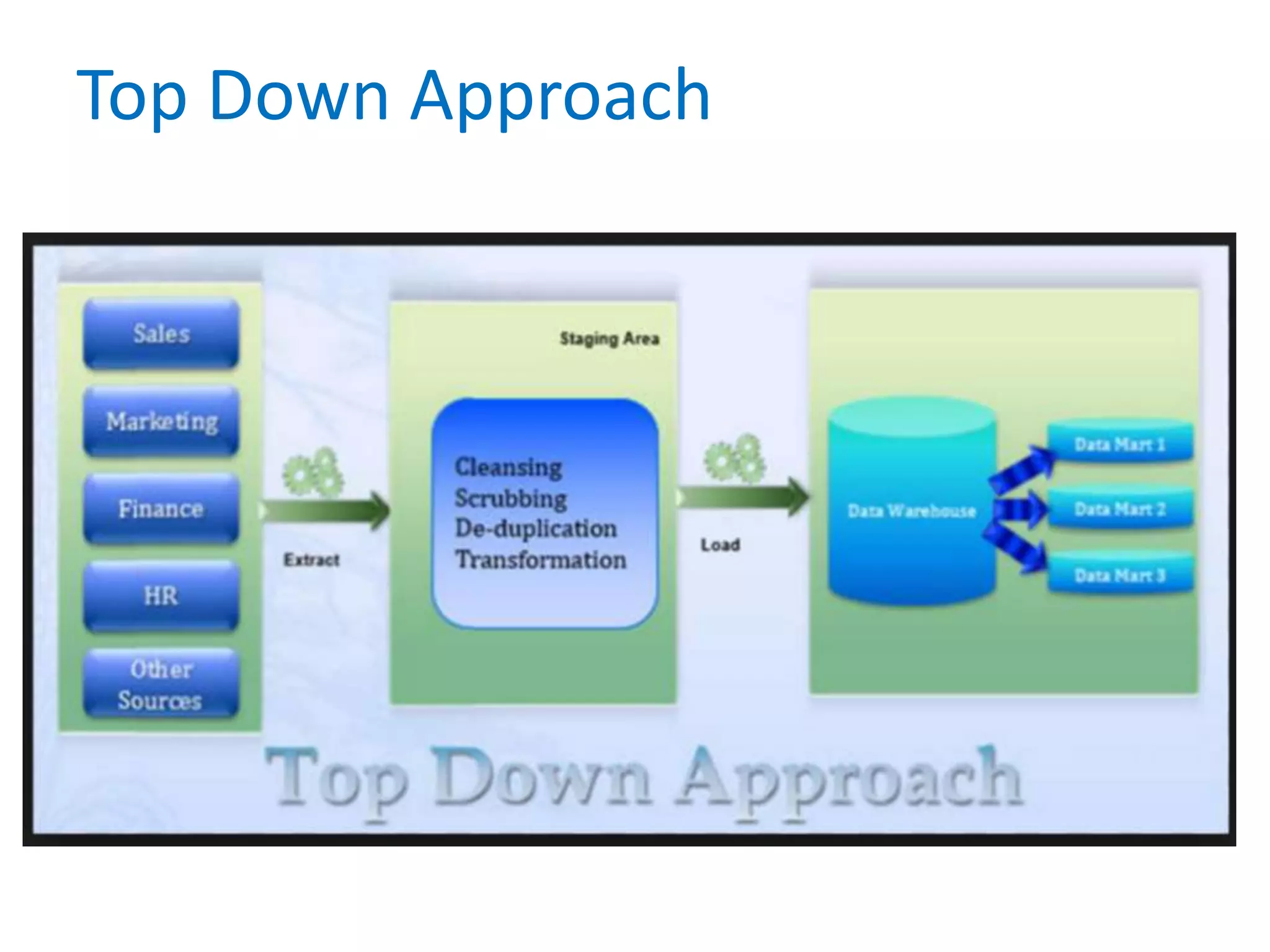
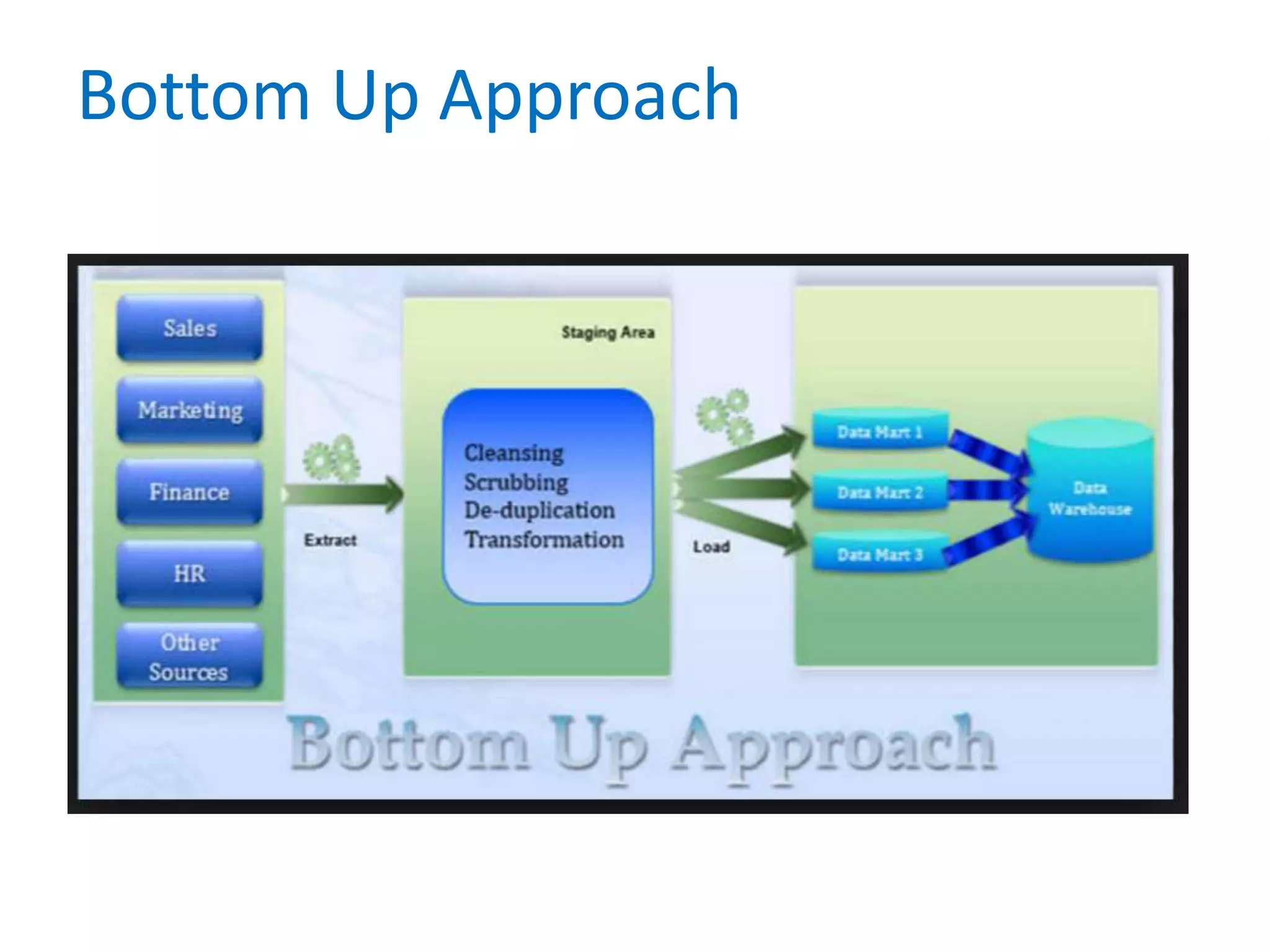
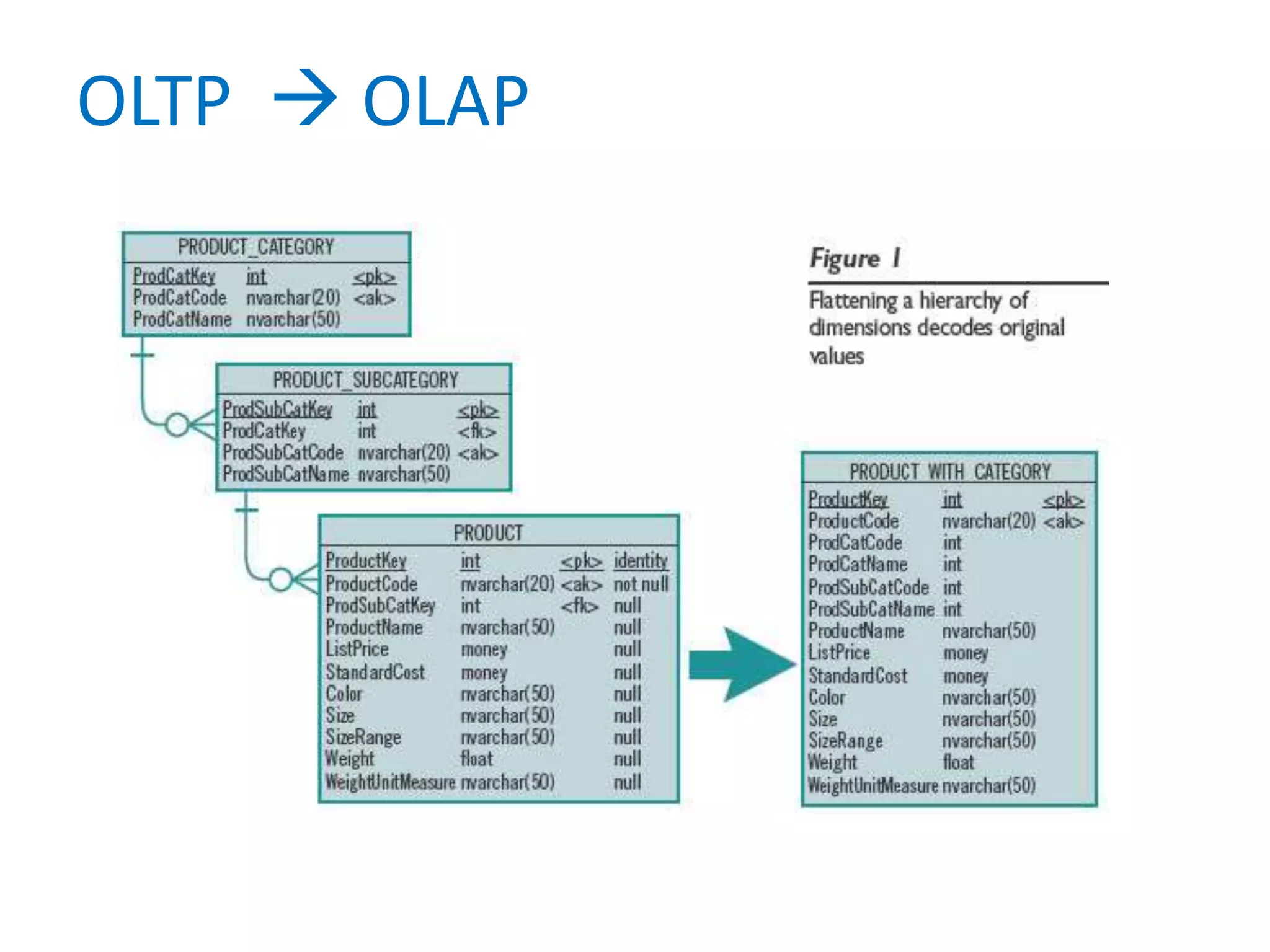
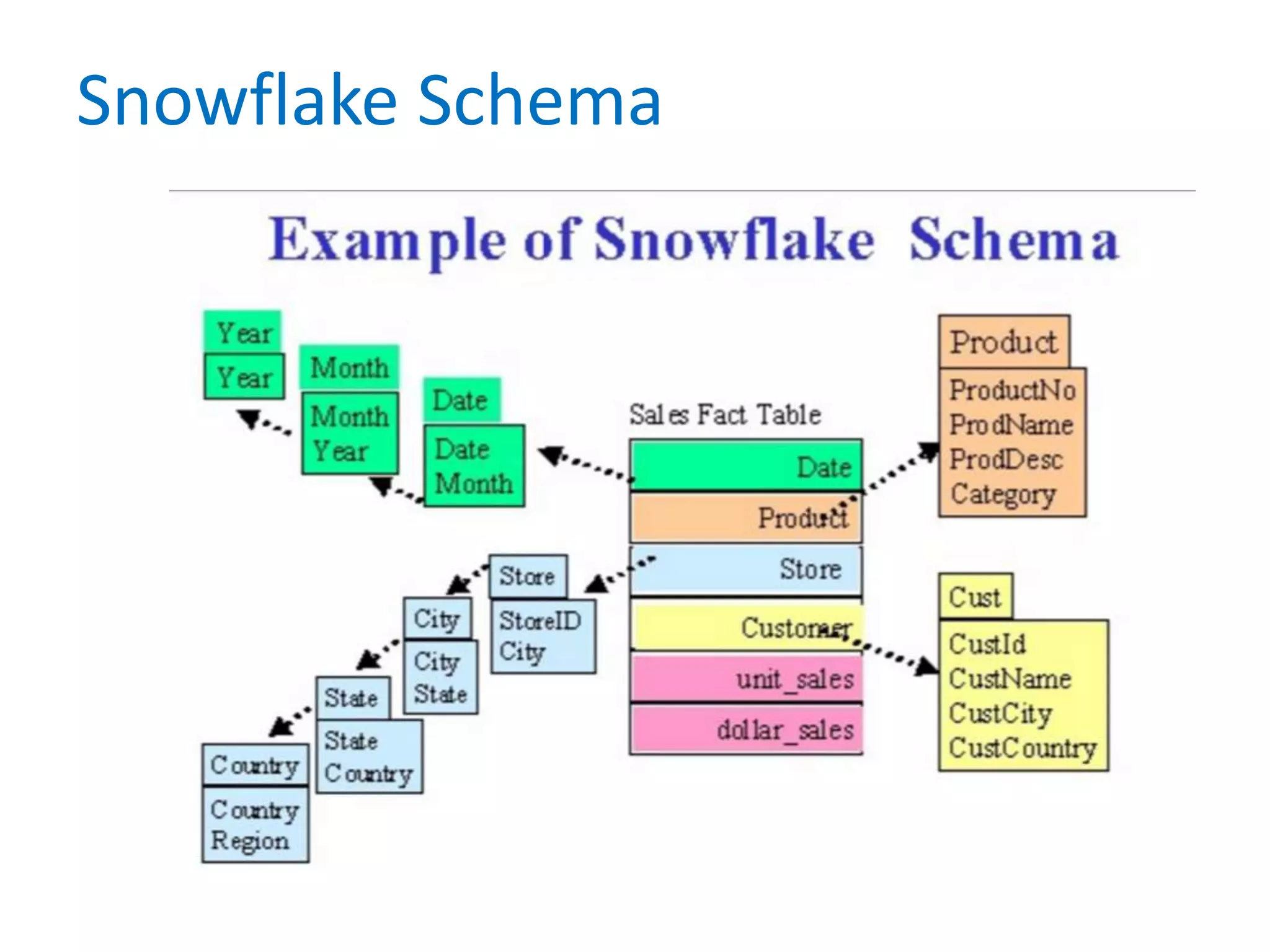
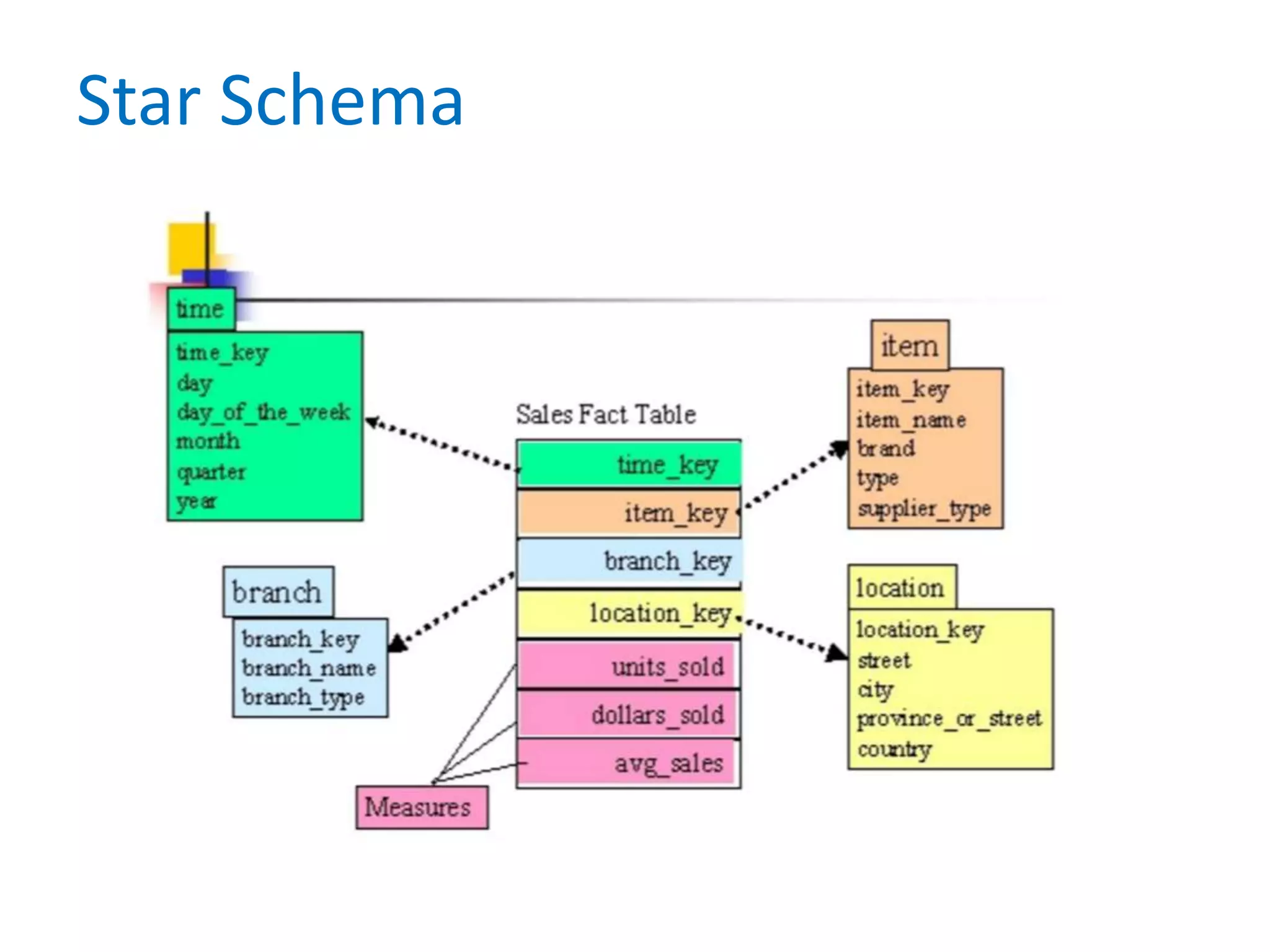
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to data warehousing including:
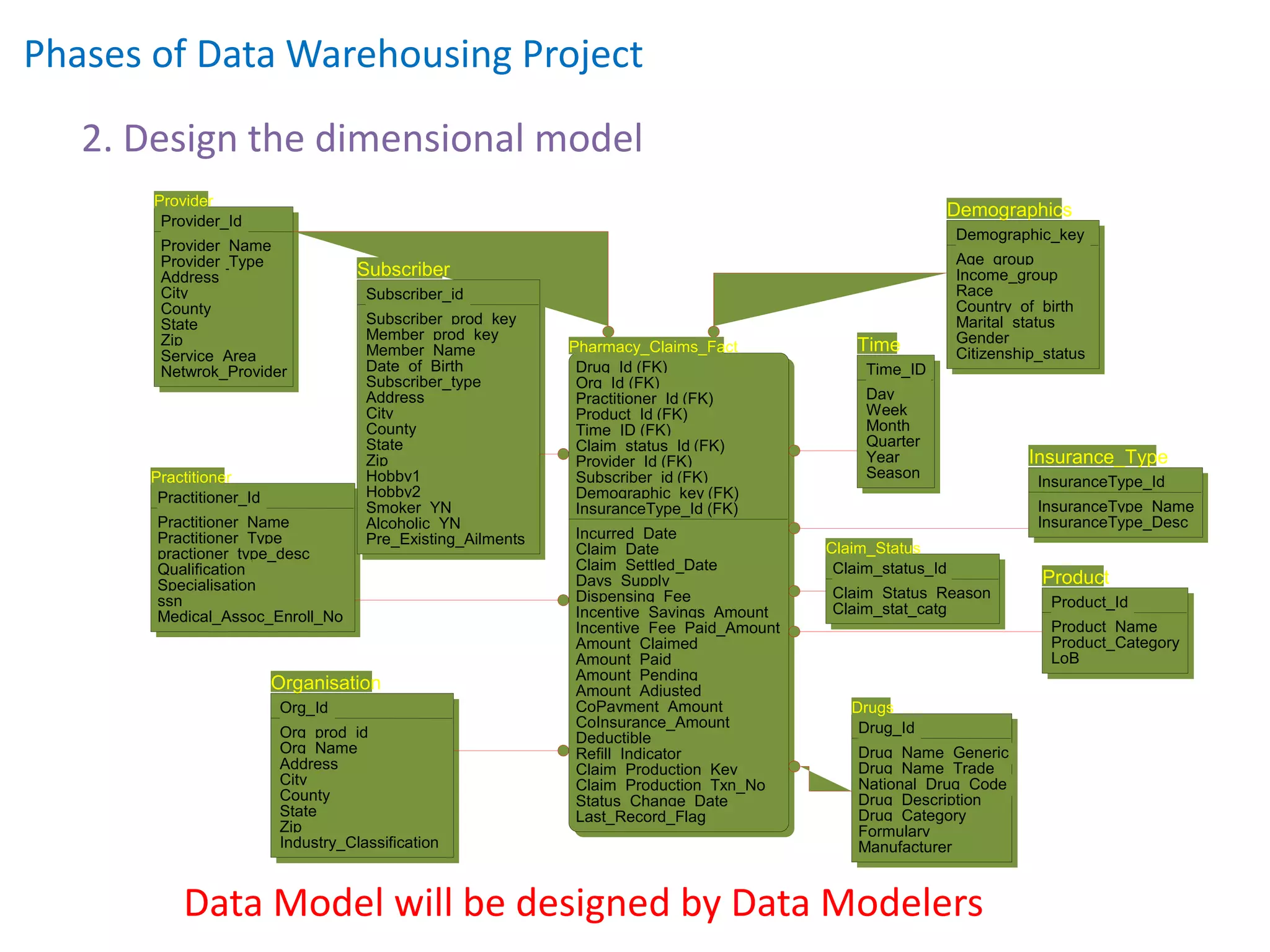
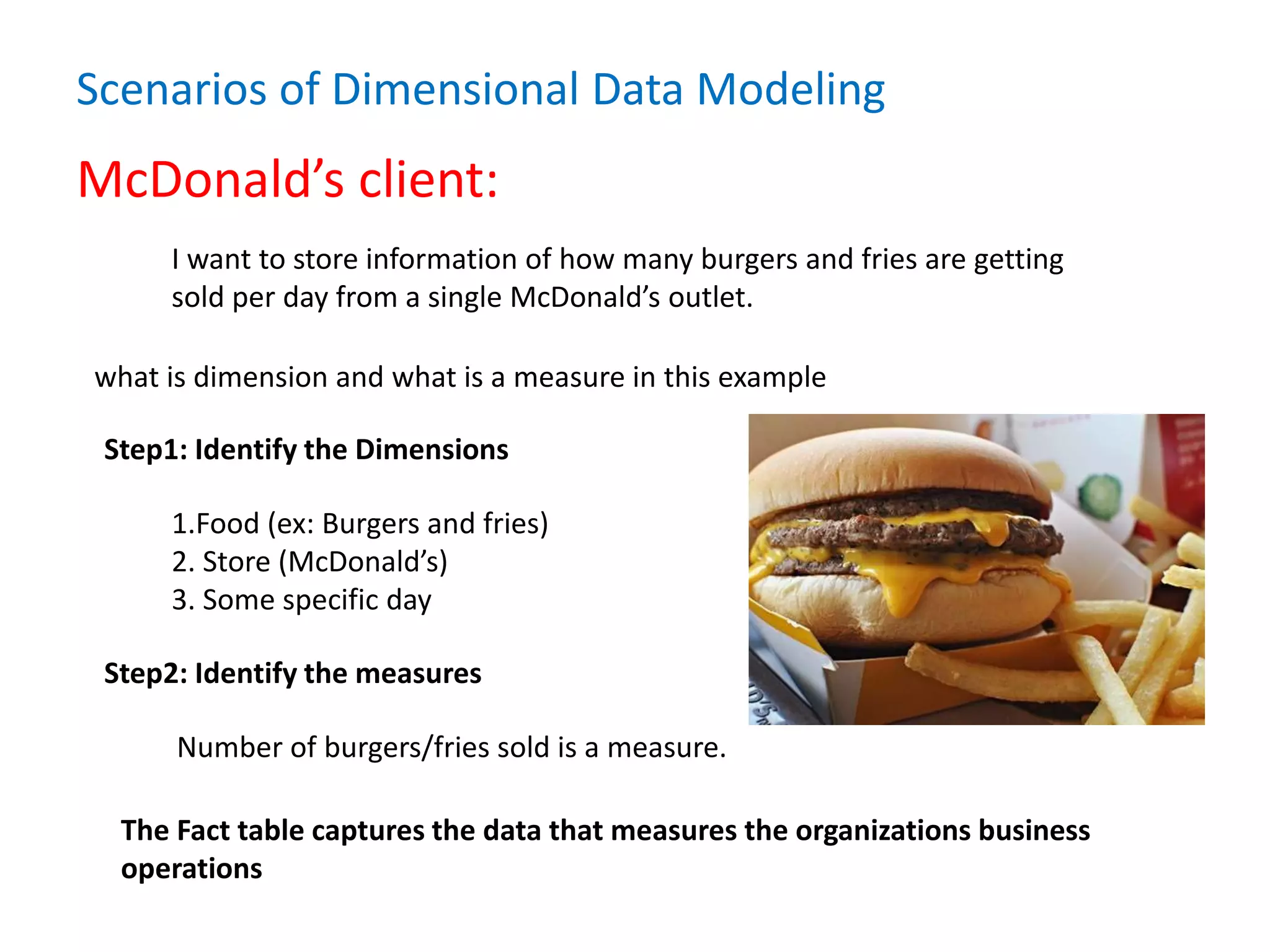
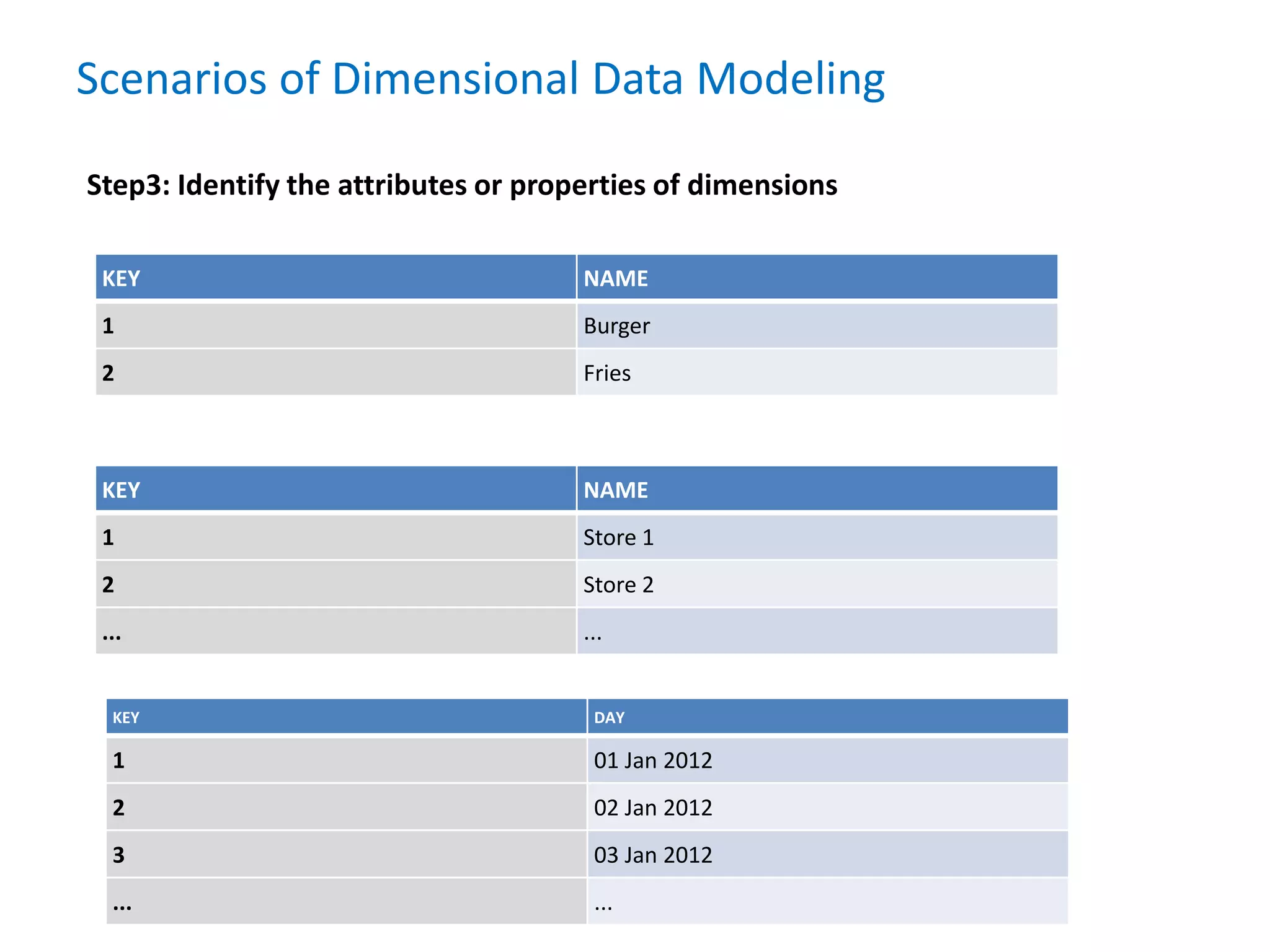
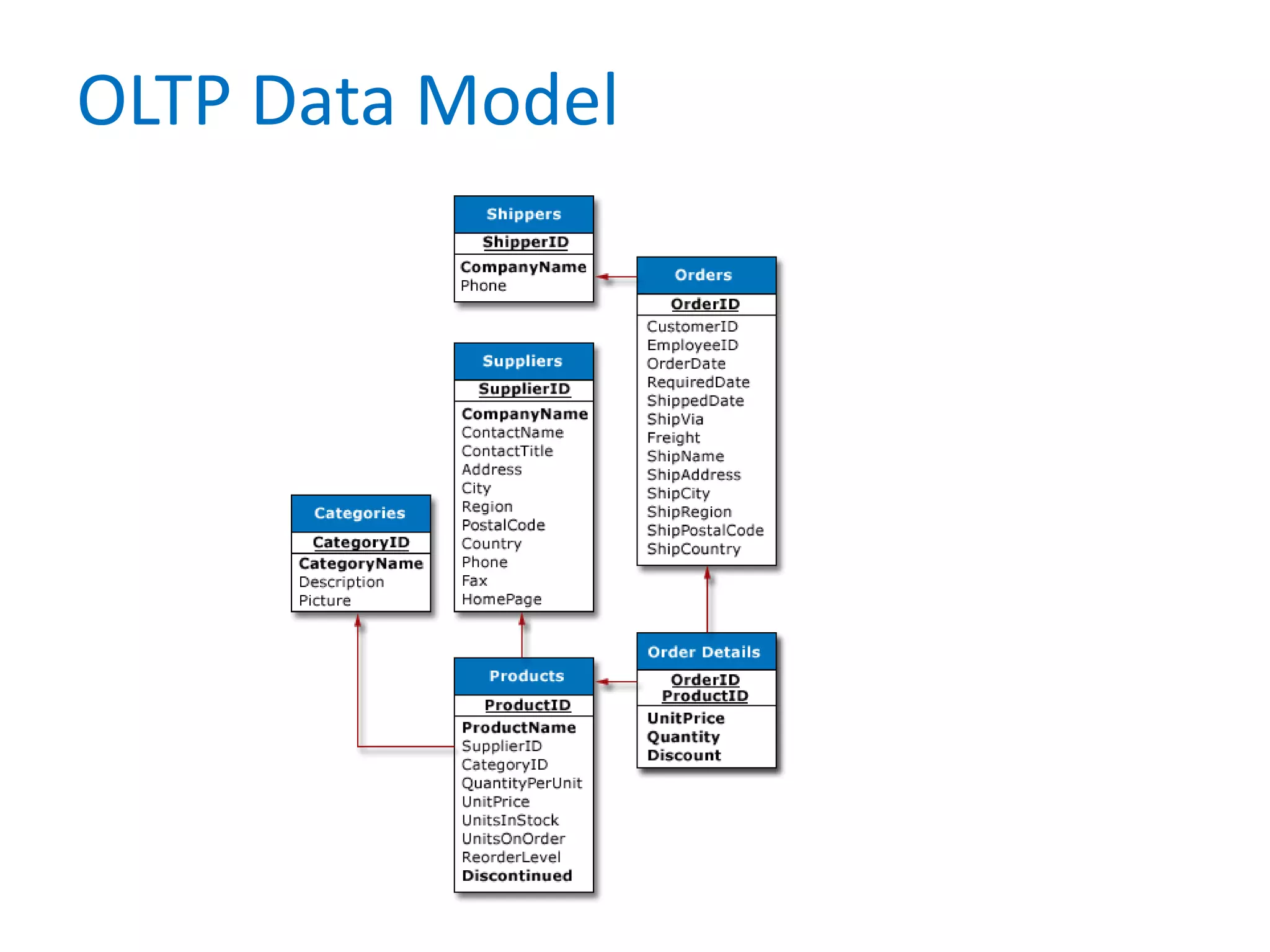
- It defines data warehousing and lists some of its key components like dimensional data modeling, star and snowflake schemas, and slowly changing dimensions.
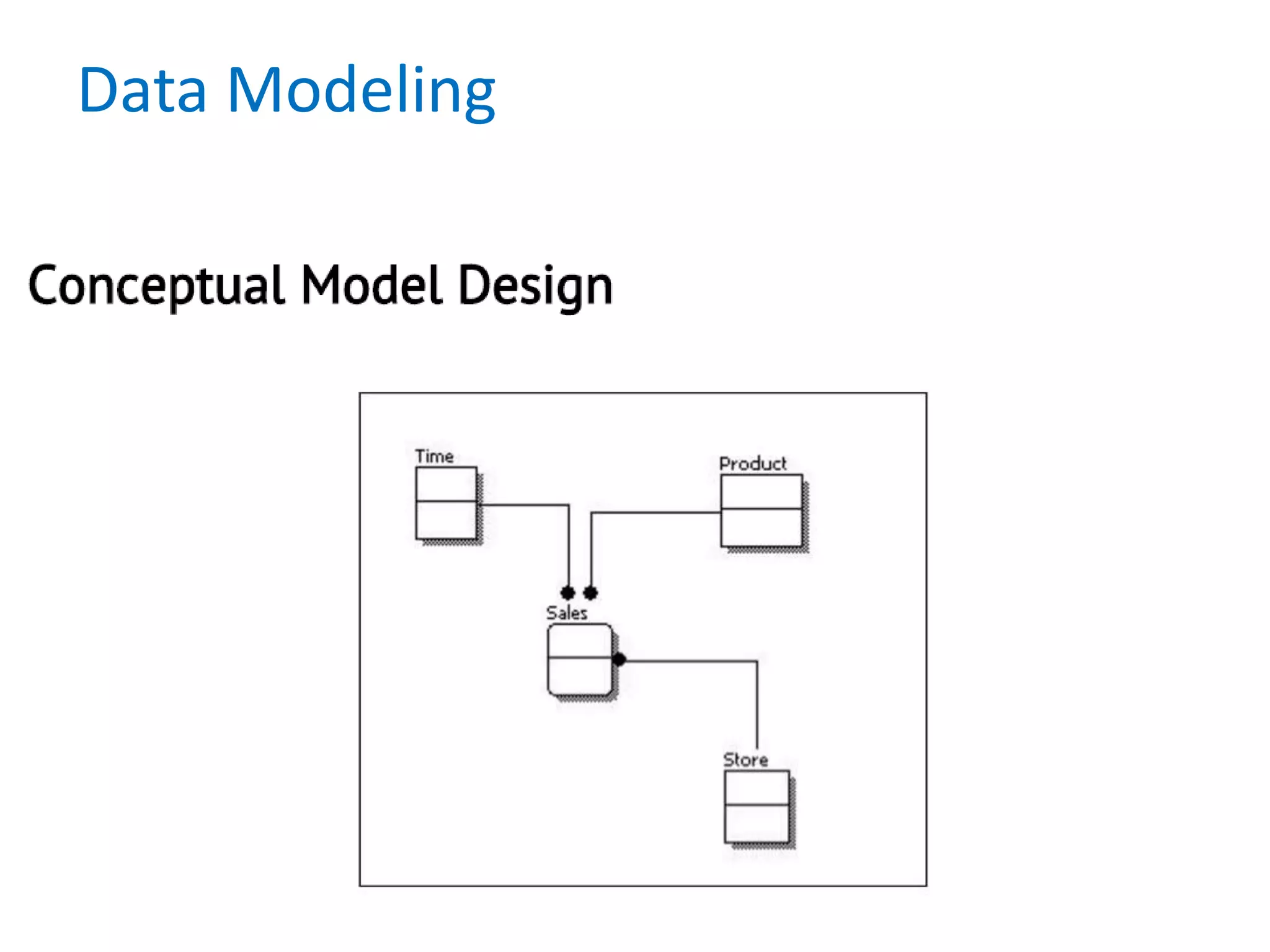
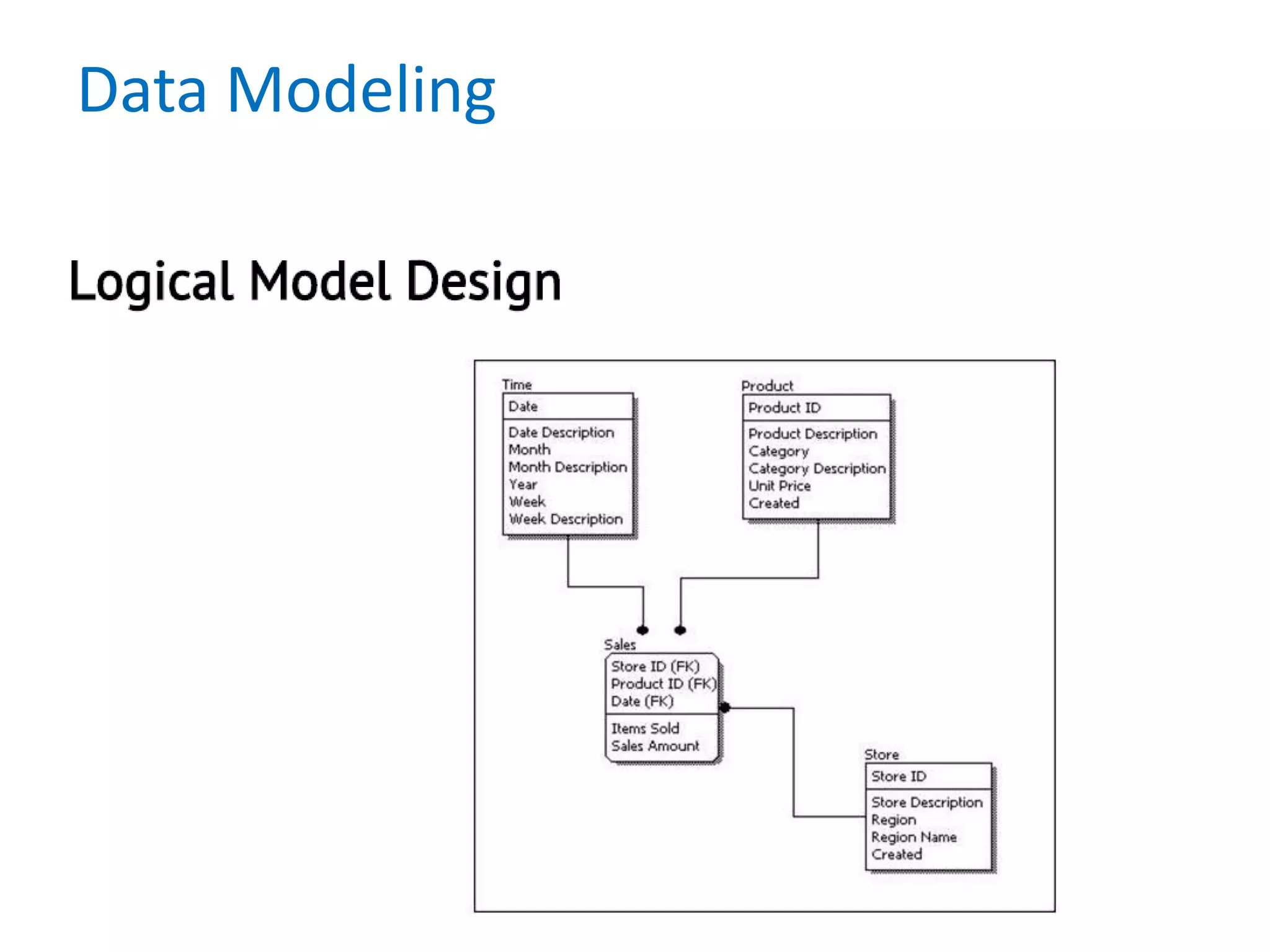
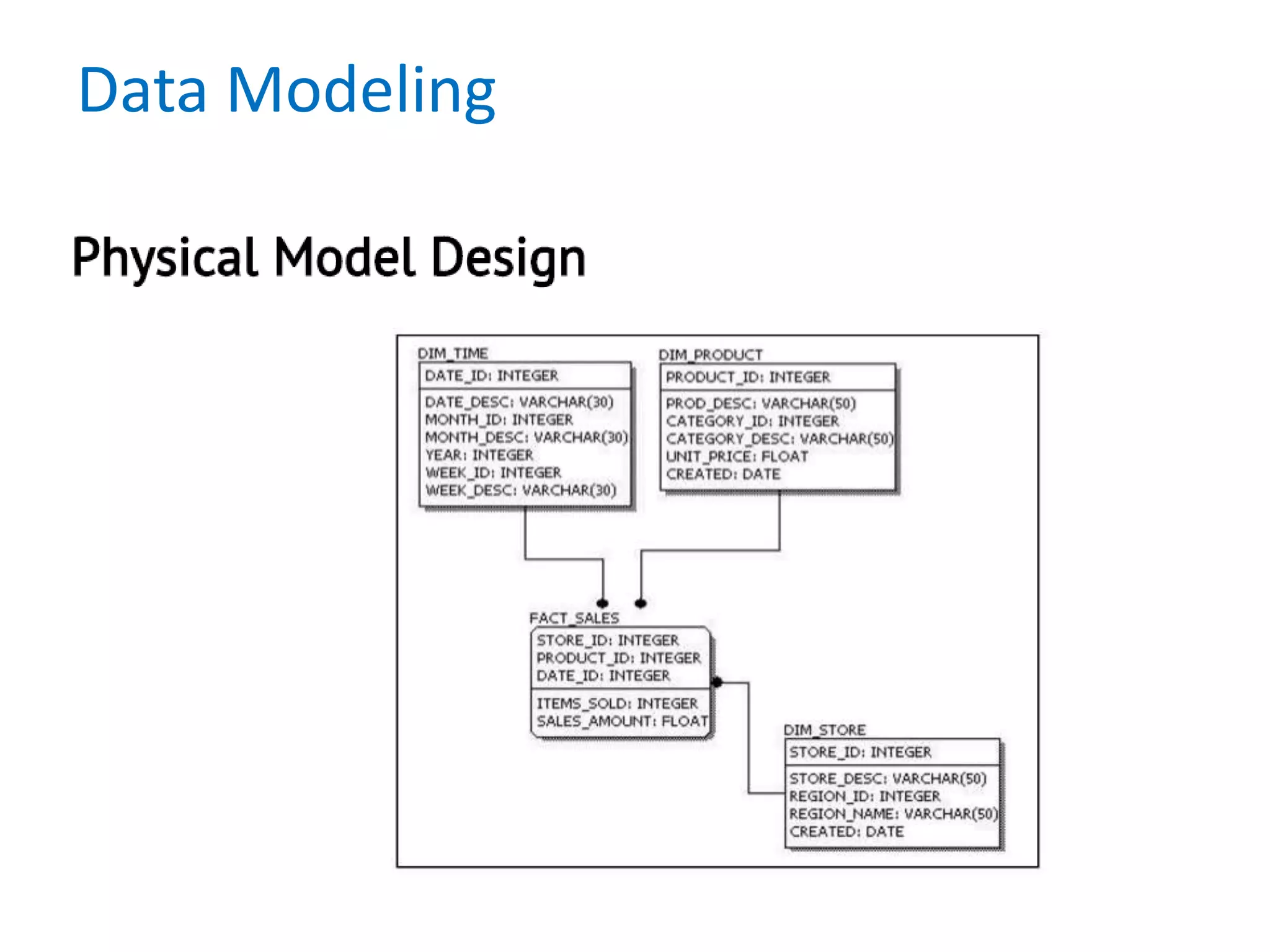
- It also discusses conceptual, logical, and physical data models and how they relate to each other.
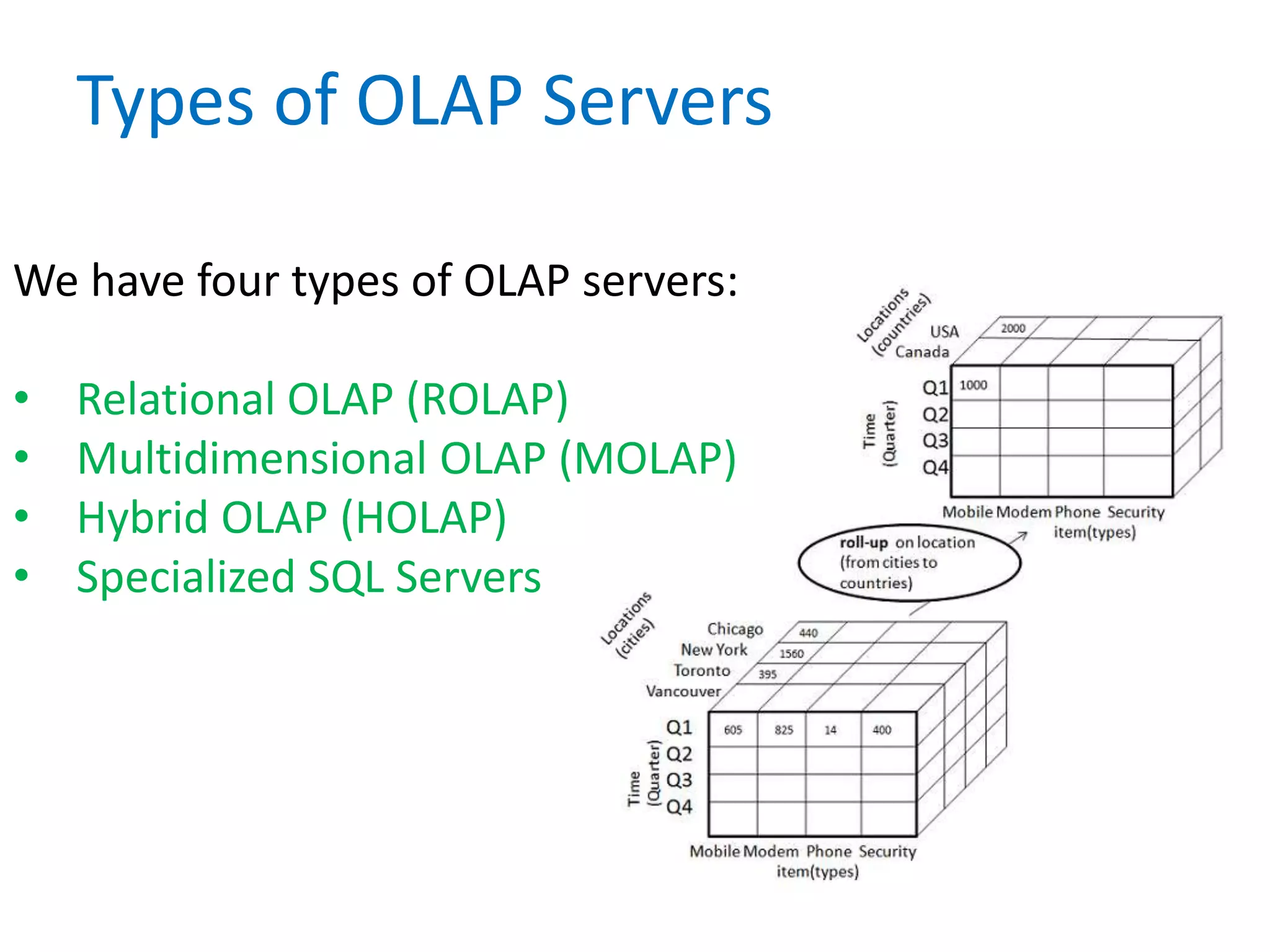
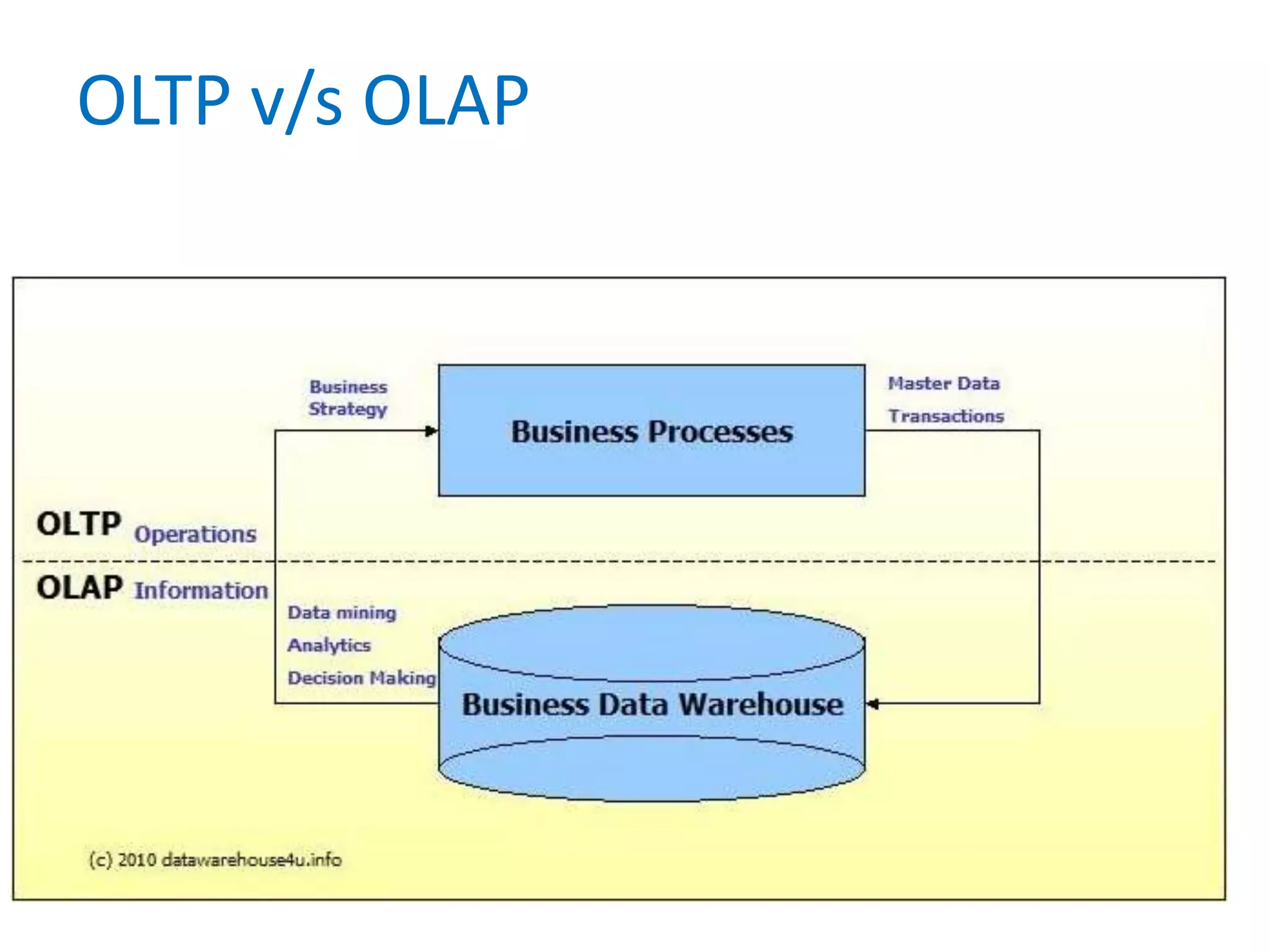
- Finally, it briefly introduces the concepts of data integrity, OLAP, and different OLAP server types like MOLAP, ROLAP, and HOLAP.