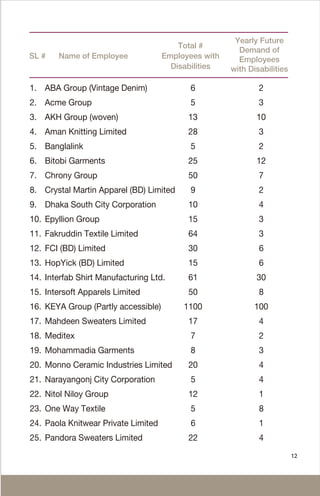
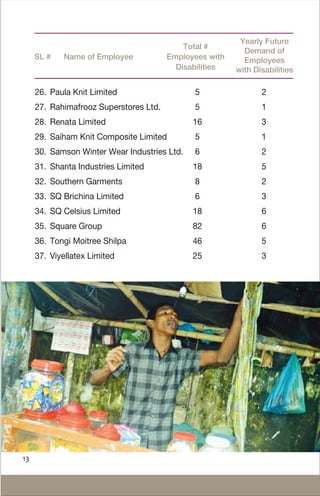
The document provides information about the employment and health rights of persons with disabilities in Bangladesh. It discusses that around 16.1 million people in Bangladesh have disabilities. While laws have been passed to protect disability rights, persons with disabilities still face barriers to accessing education, employment and healthcare. The document outlines government quotas for disability employment and lists vocational training programs to help persons with disabilities gain skills and find jobs. It provides a list of pro-disability employers in Bangladesh and their commitment to hiring persons with disabilities.