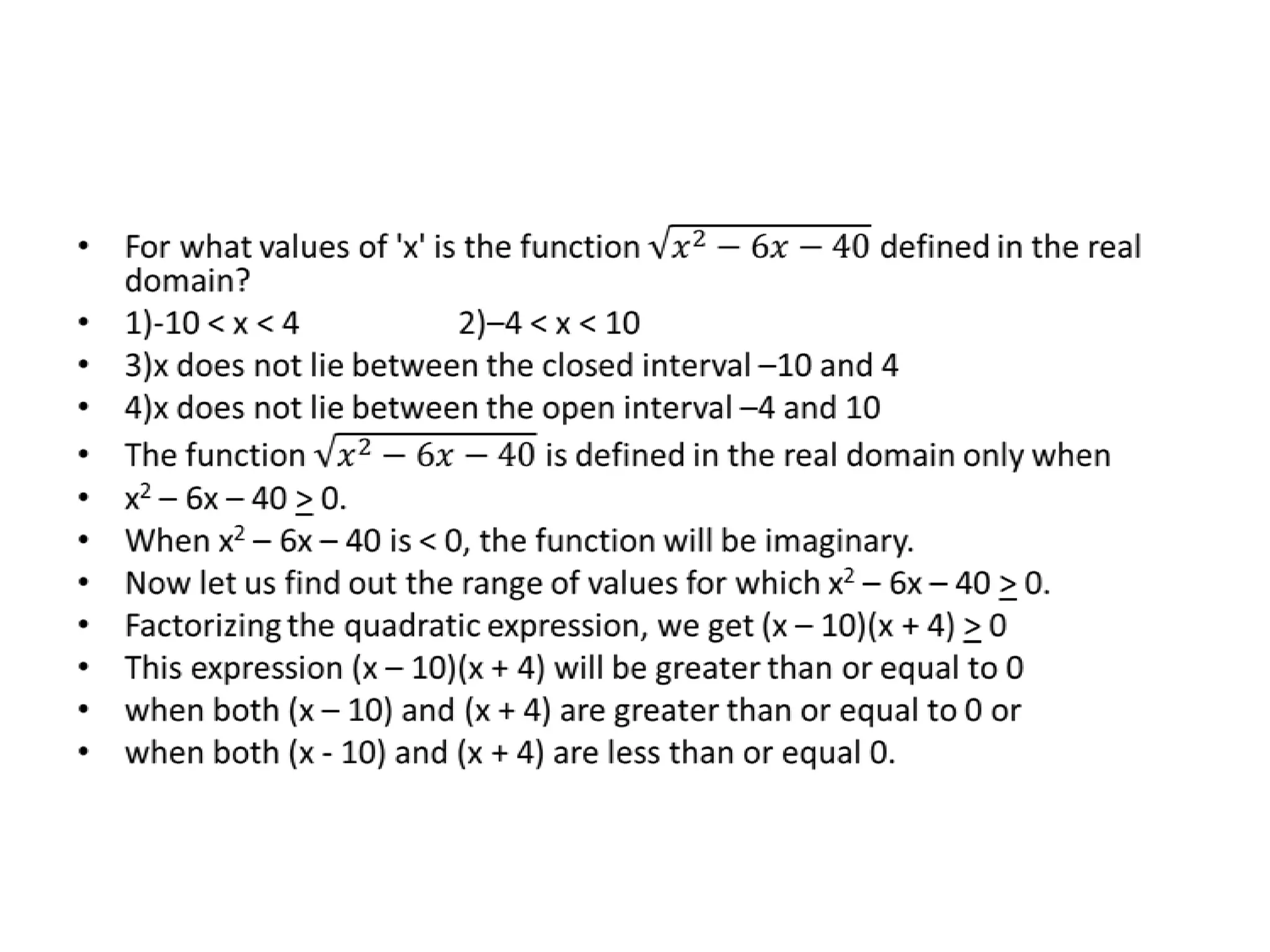
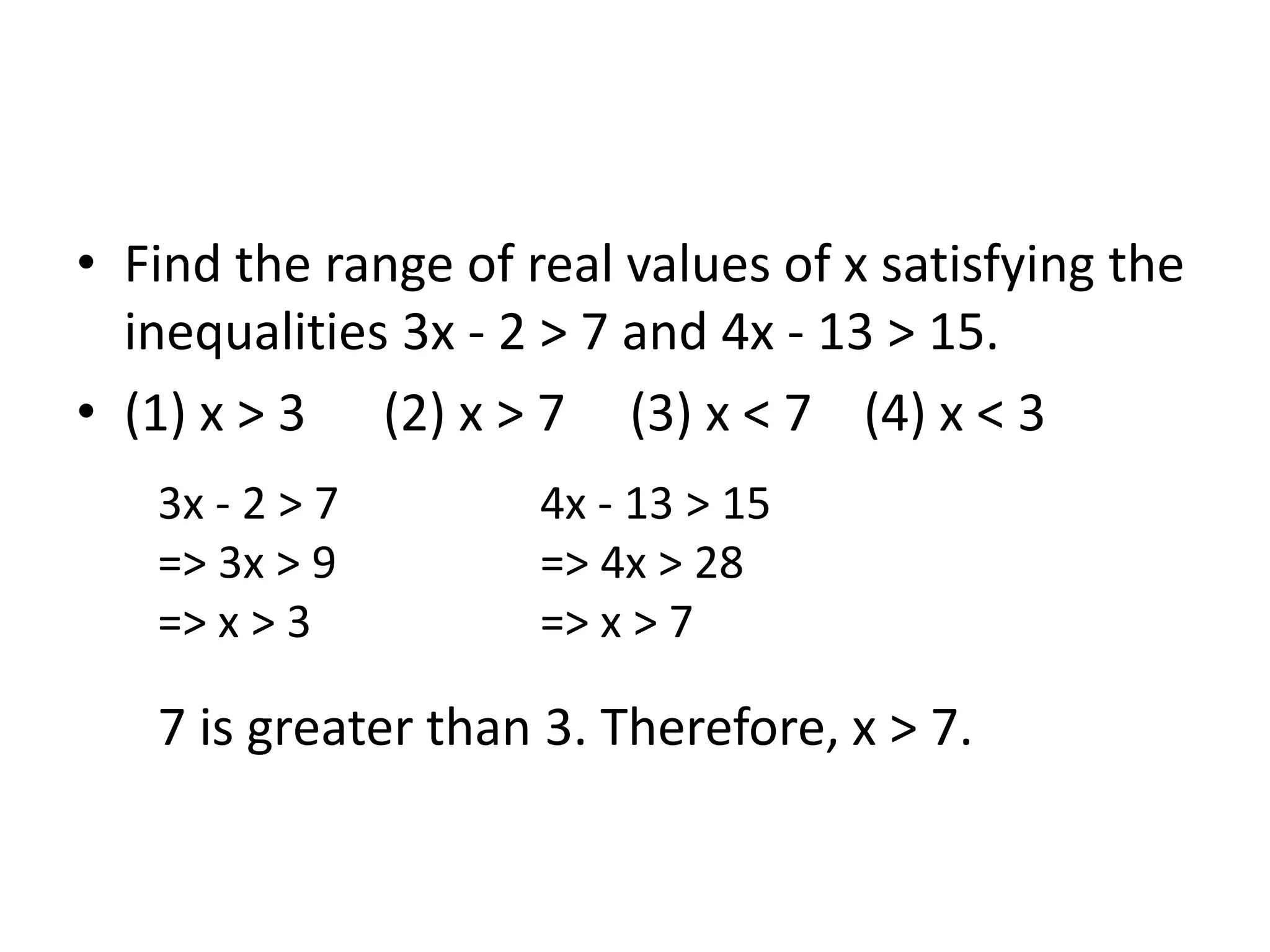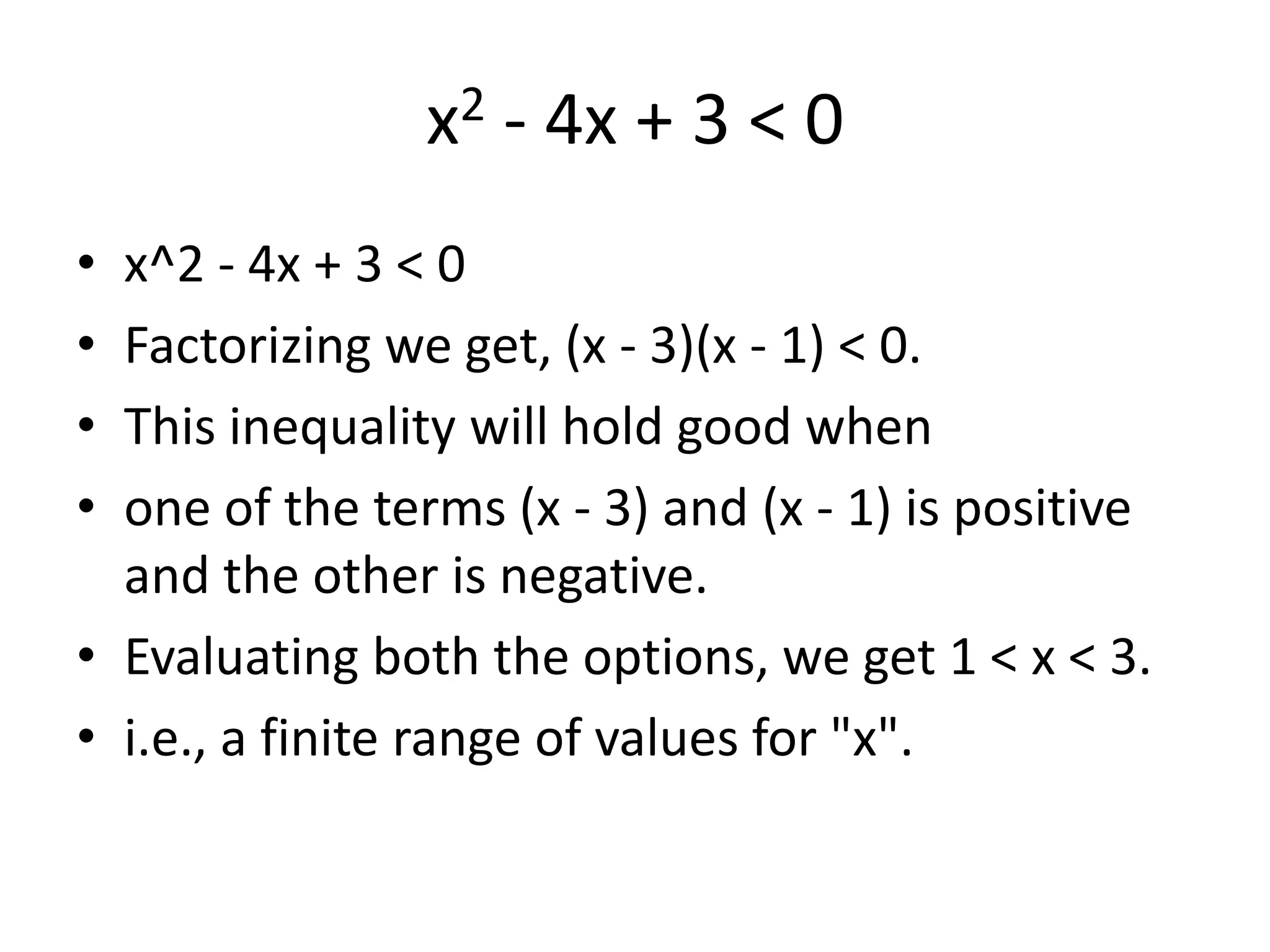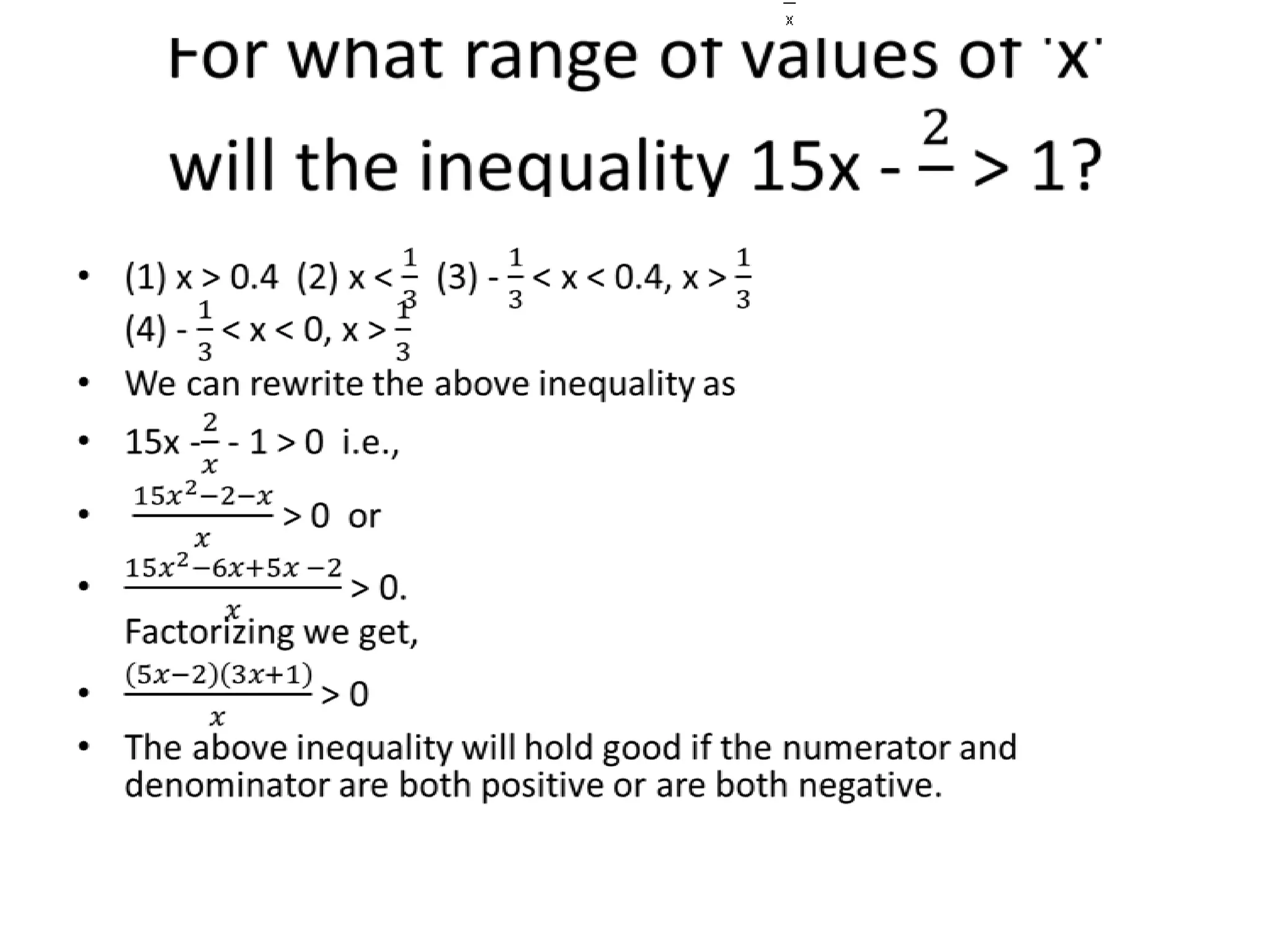The document discusses inequalities and modulus. It provides examples of determining the range of values for variables in different inequalities:
1) For the inequalities 3x - 2 > 7 and 4x - 13 > 15, the range of values is x > 7.
2) For the modulus inequality |x + 2| > 4, the range is infinite as x can be either less than -6 or greater than 2.
3) For the inequality x2 - 4x + 3 < 0, the range is finite between 1 and 3 as it is the only inequality that satisfies the condition of one term being positive and the other negative.