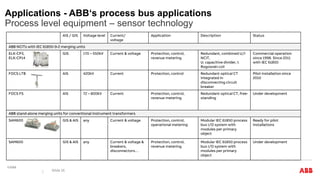
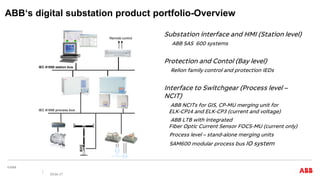
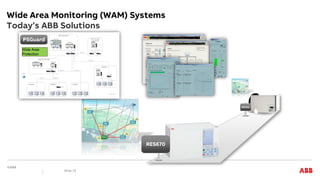
This document discusses trends and demands in modern power system protection. It notes challenges from increasing renewable energy sources, including lower inertia and decreasing frequency quality. Market demands include high availability and speed/reliability of protection systems. Main trends are improvements to conventional protection functions and integration of high-speed protection using digital technologies. Examples are provided of digital substation applications using IEC 61850 and functional consolidation in protection systems. Wide area monitoring and HVDC line protection are also discussed as important areas.