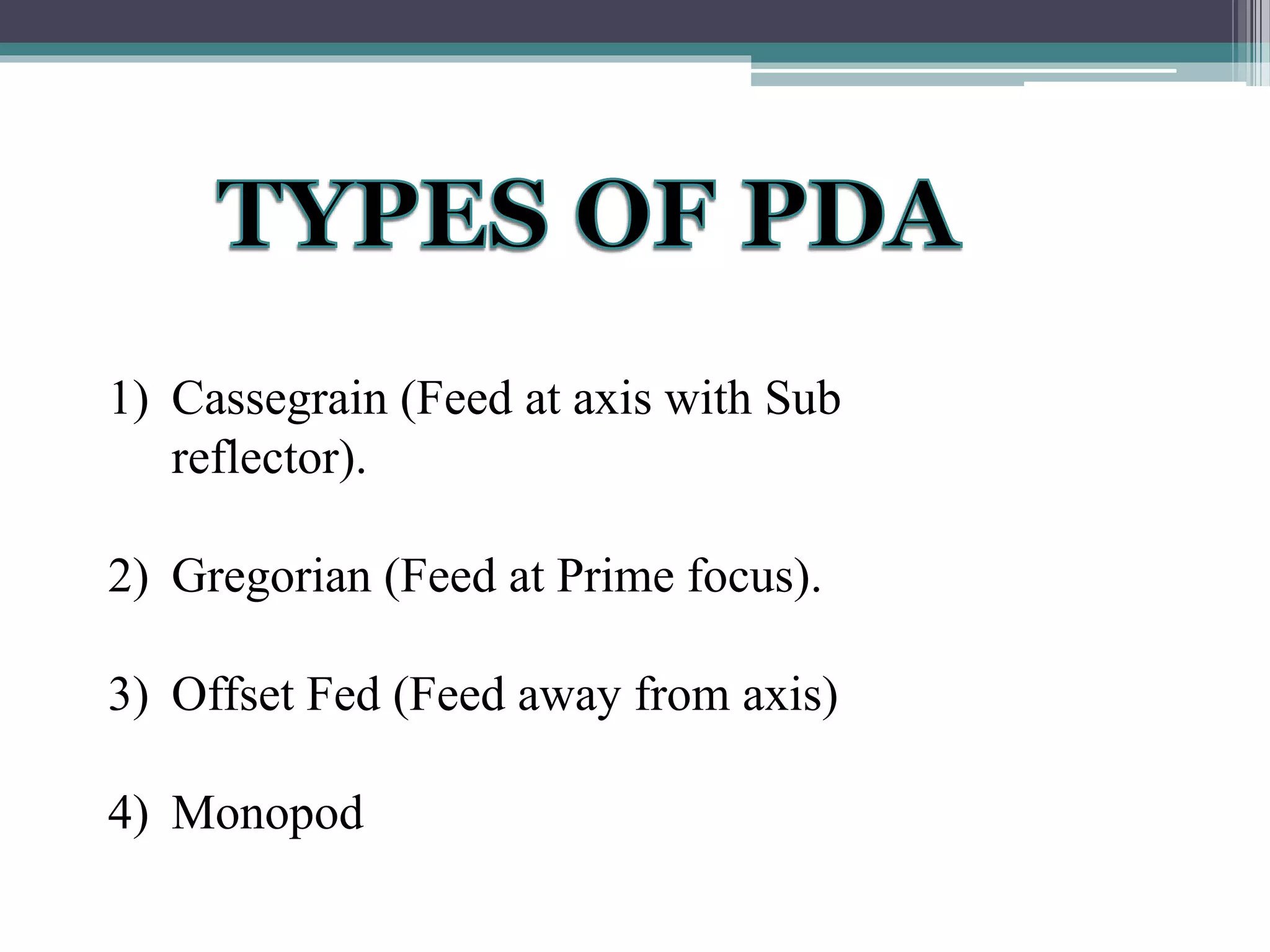
This document discusses satellite communications, including a brief history and overview of key concepts. It describes how satellites are used to transmit radio signals for telecommunications by redirecting electromagnetic waves that are obstructed by the curvature of the Earth. The document outlines different types of satellite orbits and antenna designs used for communication. It notes advantages like providing connectivity over long distances uniformly, and disadvantages such as high costs and signal propagation delays.