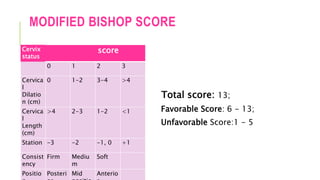
Induction of labor is the artificial initiation of uterine contractions to achieve vaginal delivery within 24 to 48 hours. Indications include prelabor rupture of membranes, hypertensive disorders, and fetal growth restriction, while contraindications include placenta previa and previous uterine rupture. Various methods for induction include prostaglandins, oxytocin infusion, amniotomy, and mechanical methods like the Foley catheter, with careful monitoring for complications such as uterine hyperstimulation and failed induction.