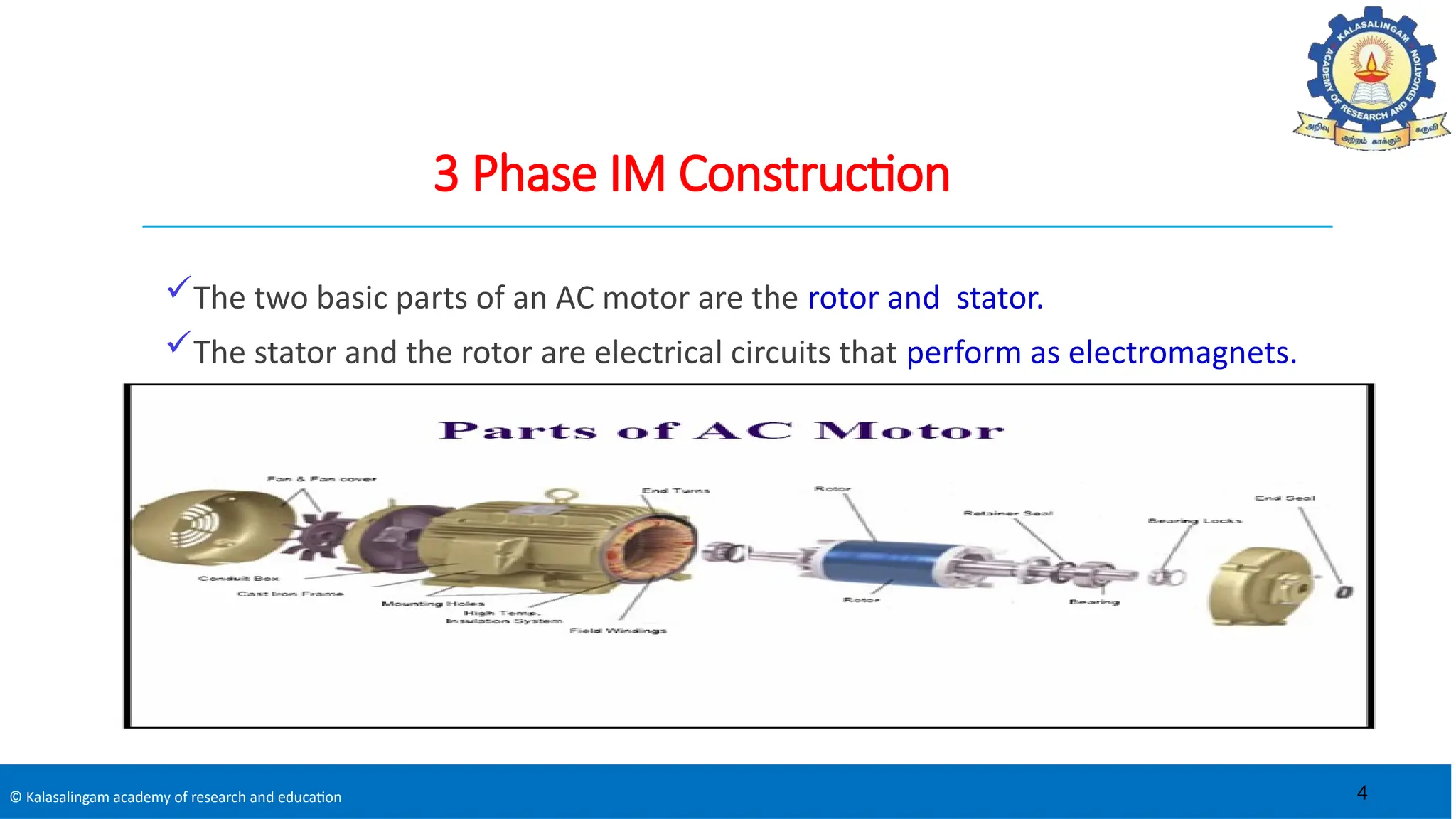
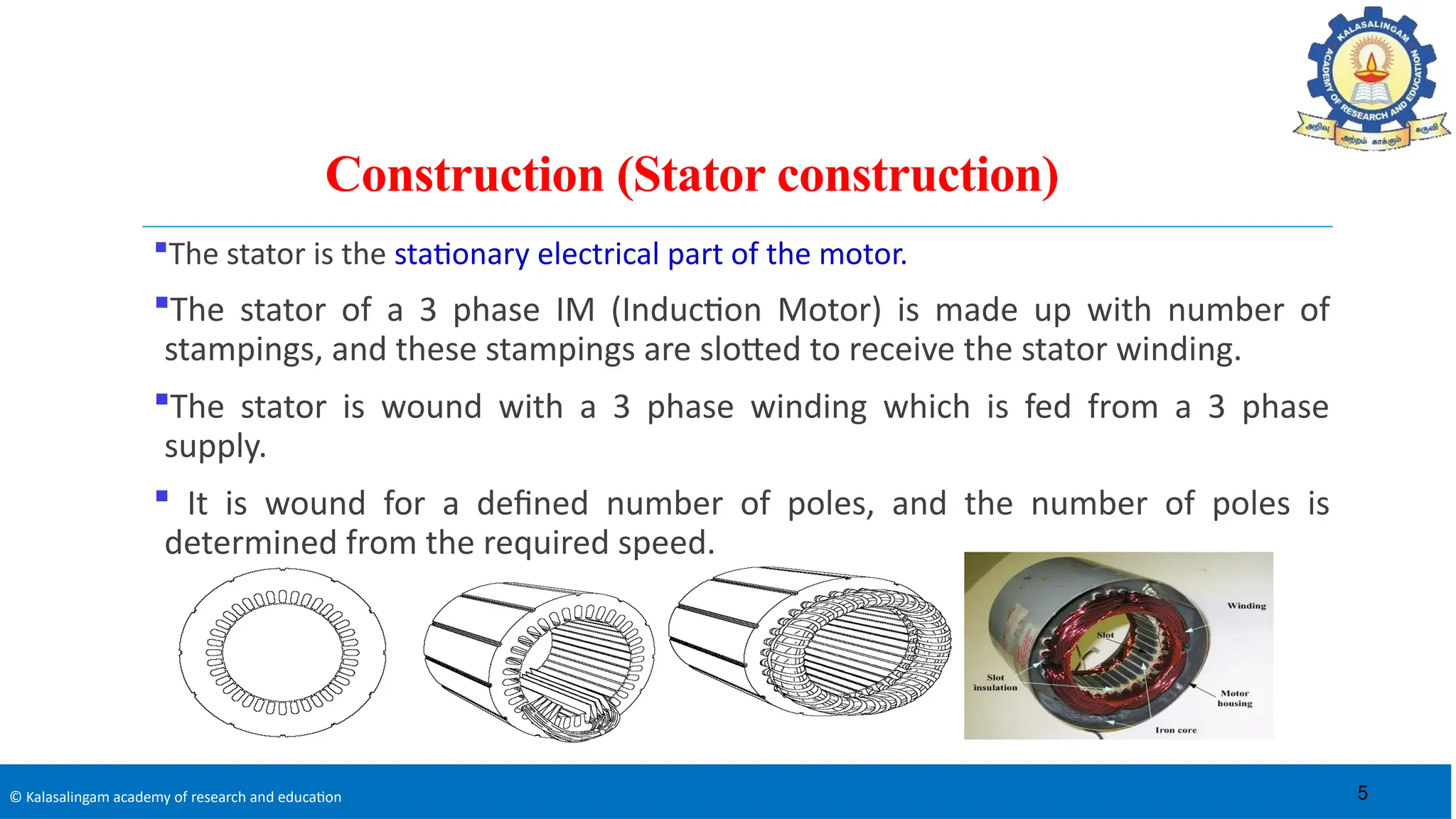
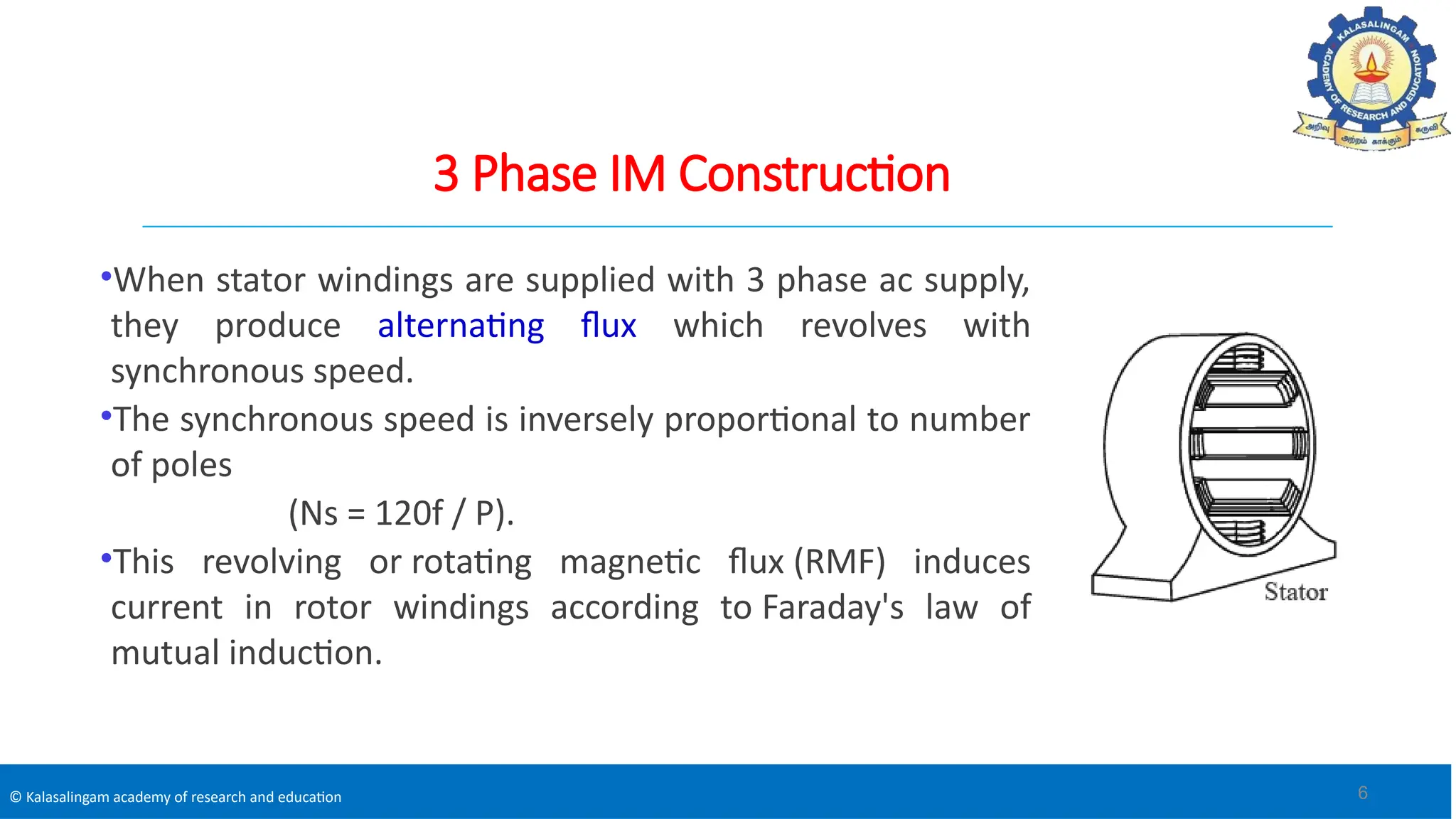
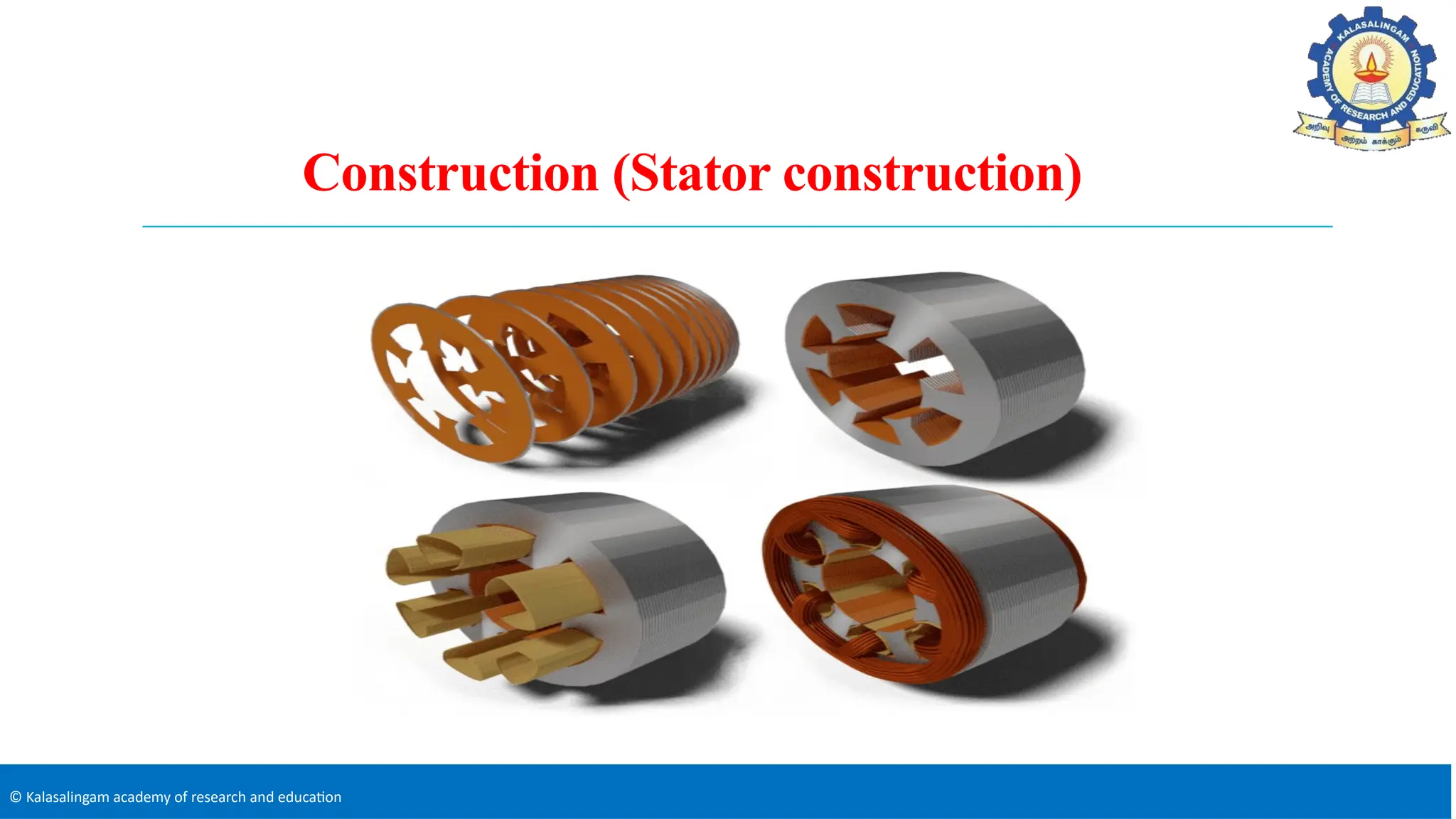
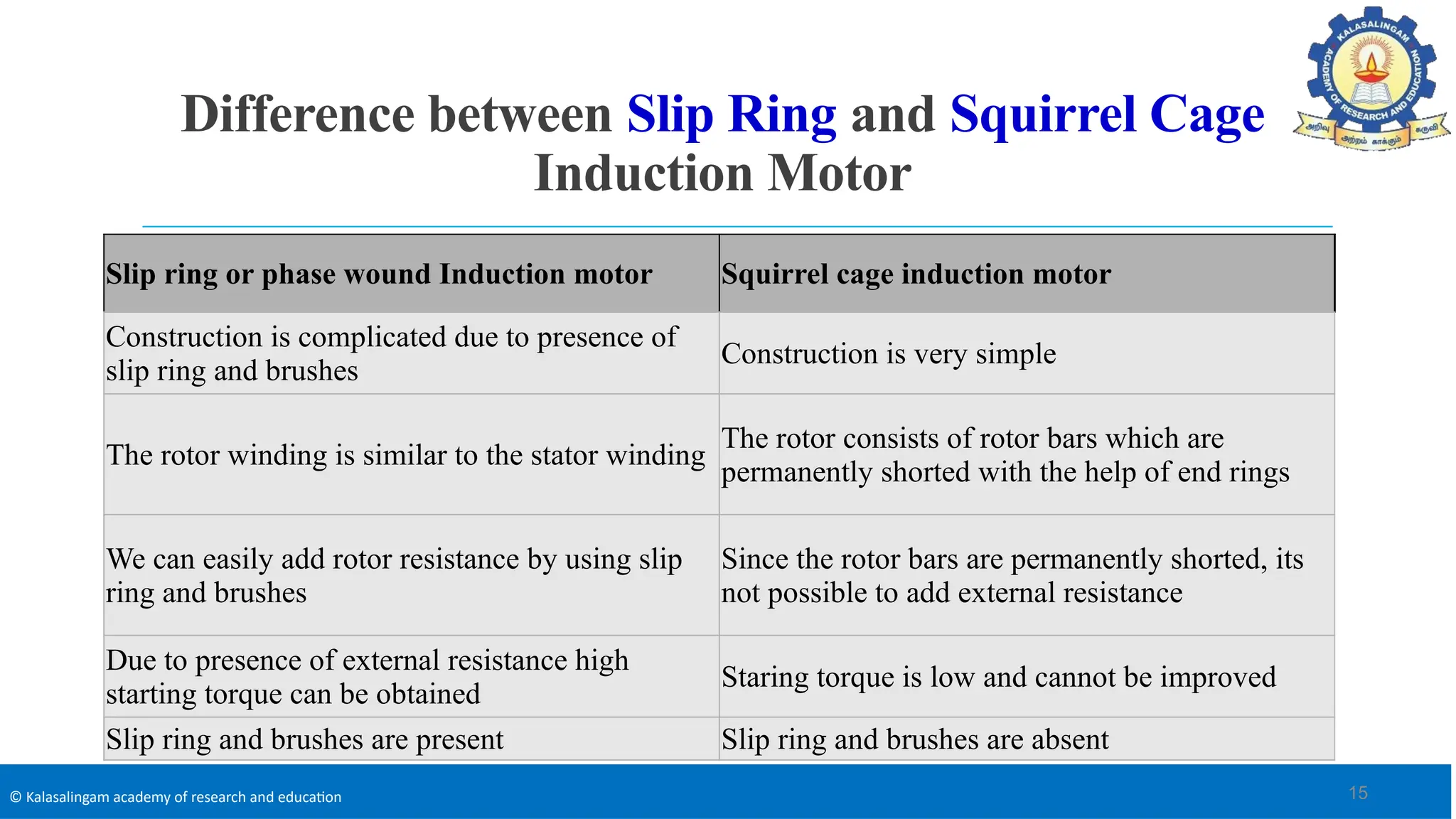
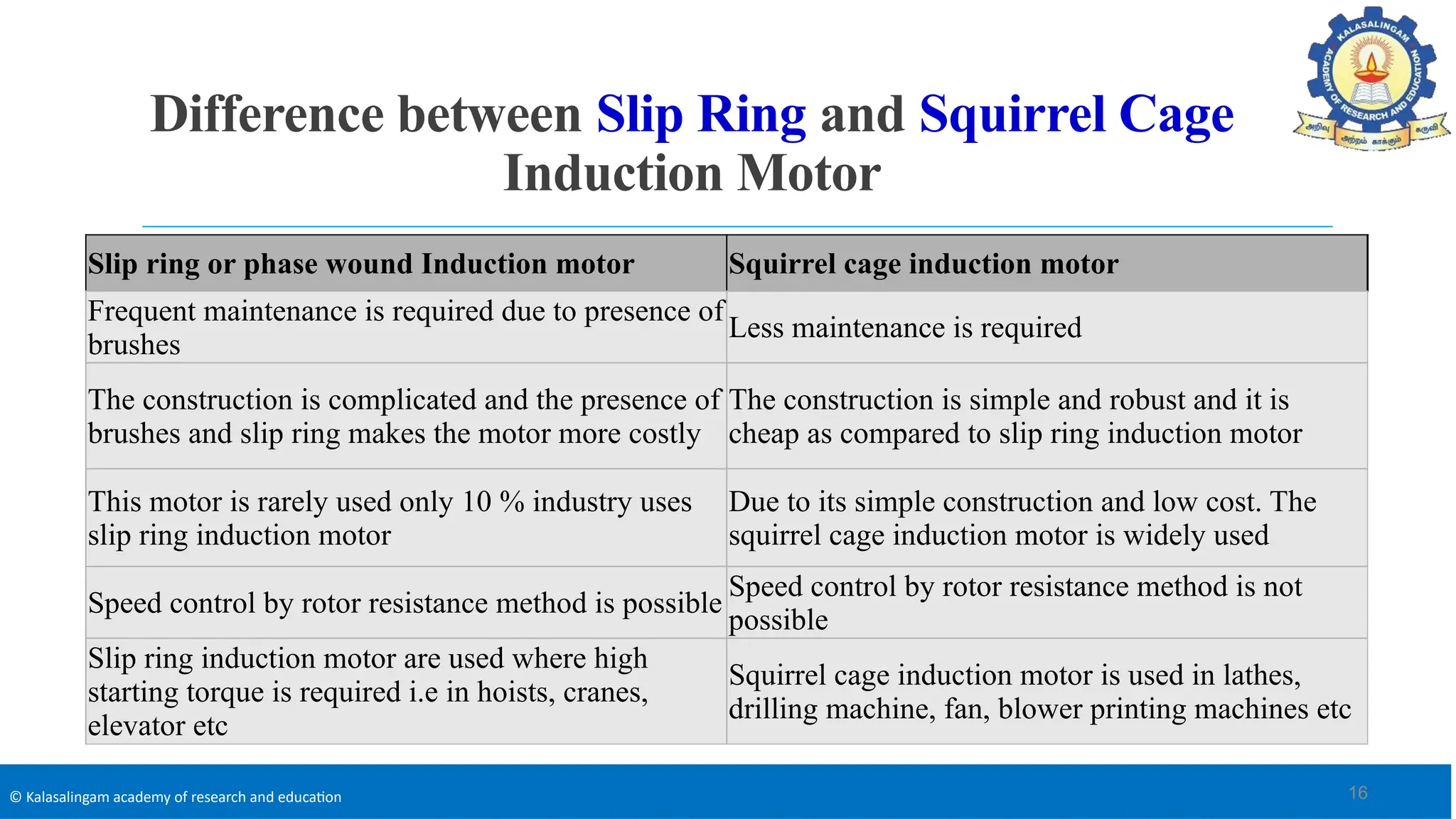
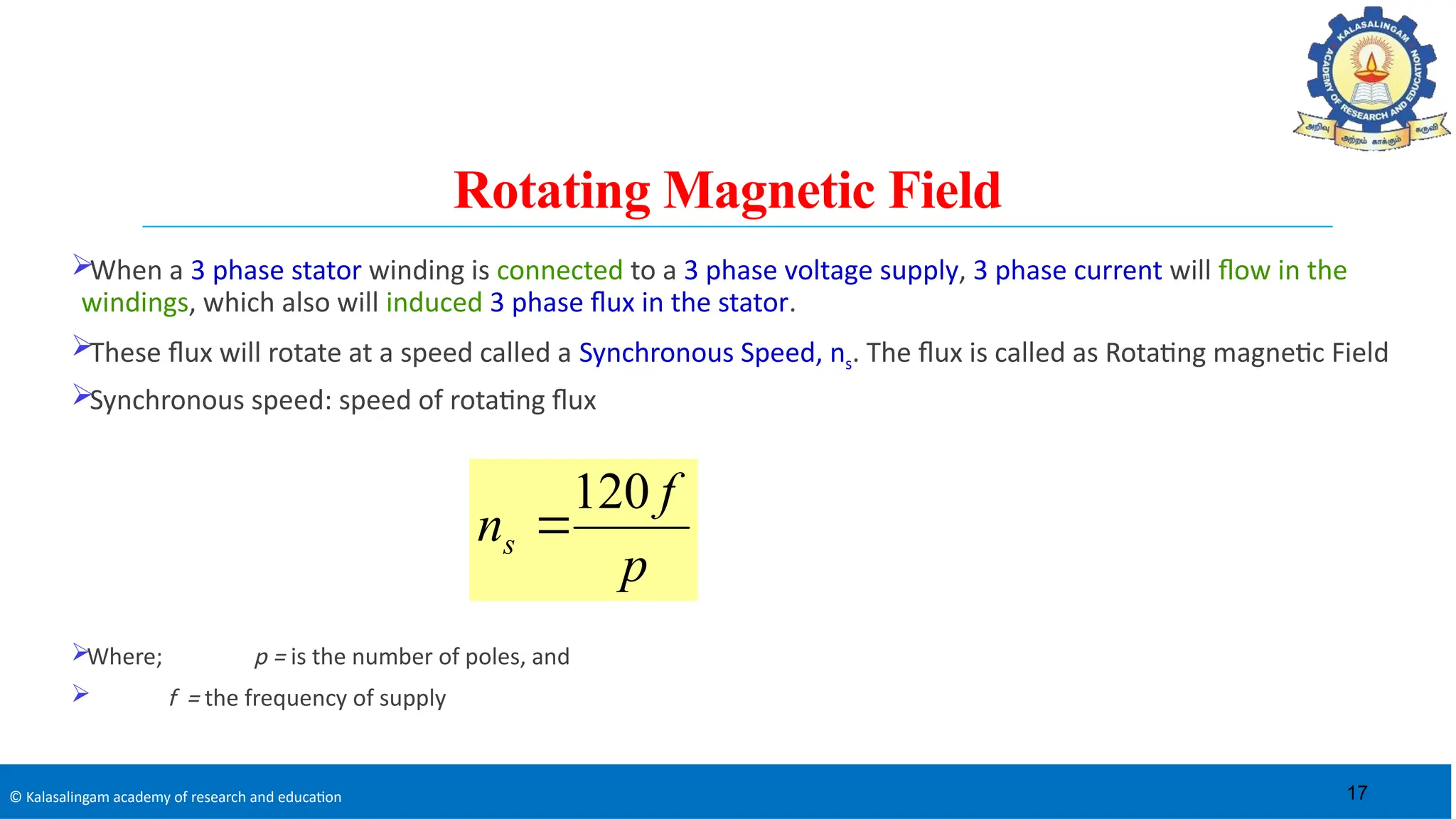
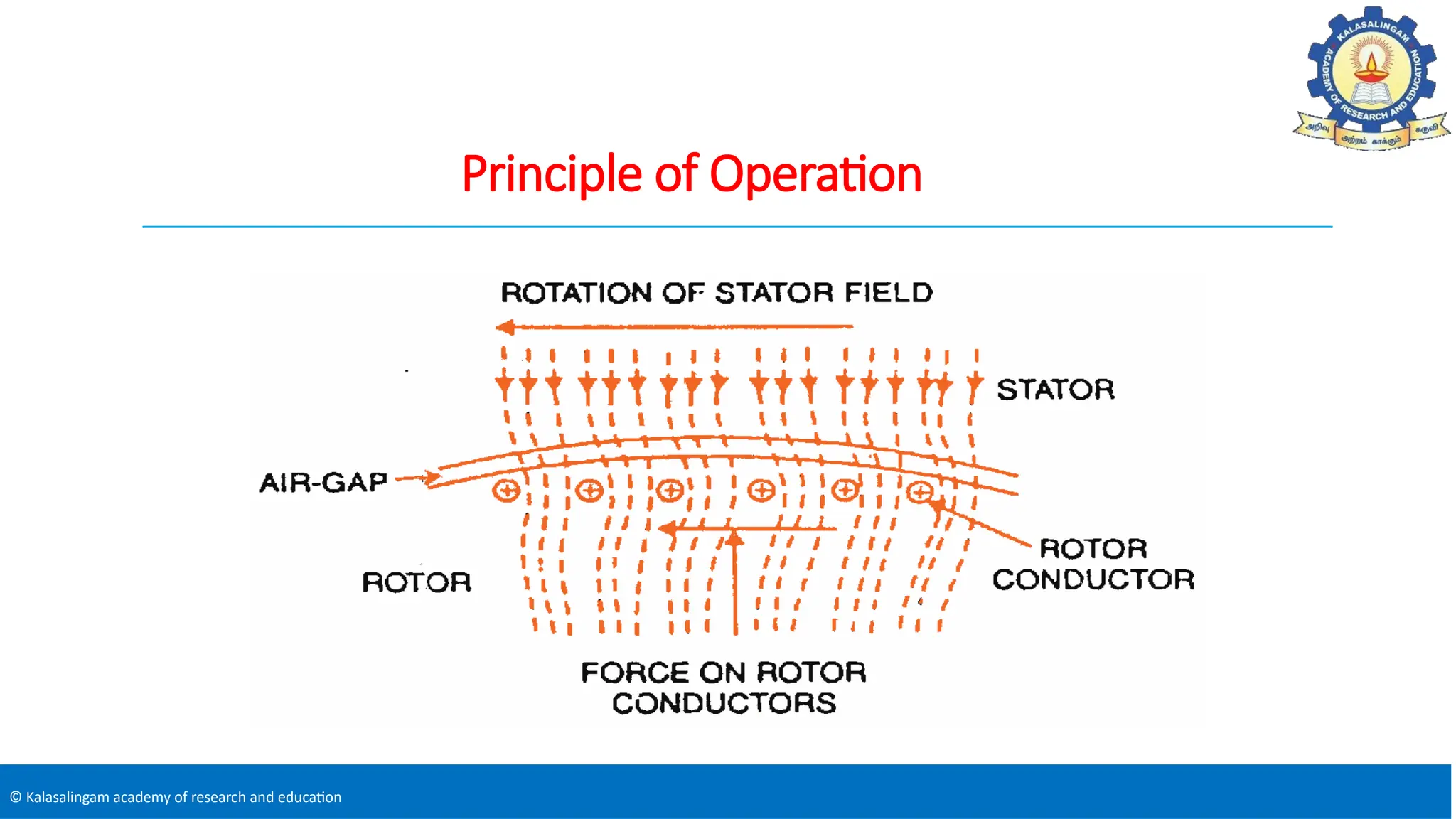
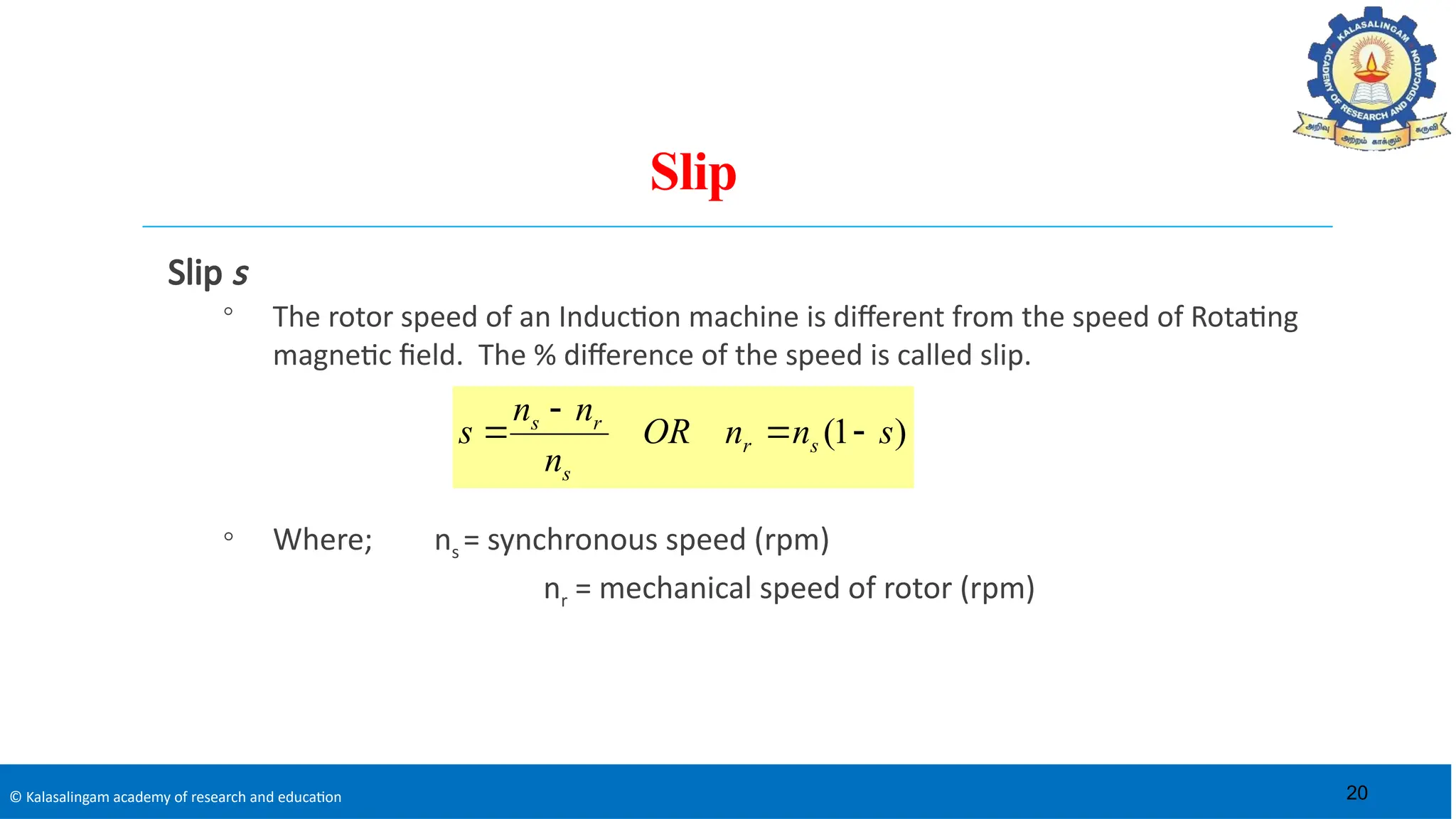
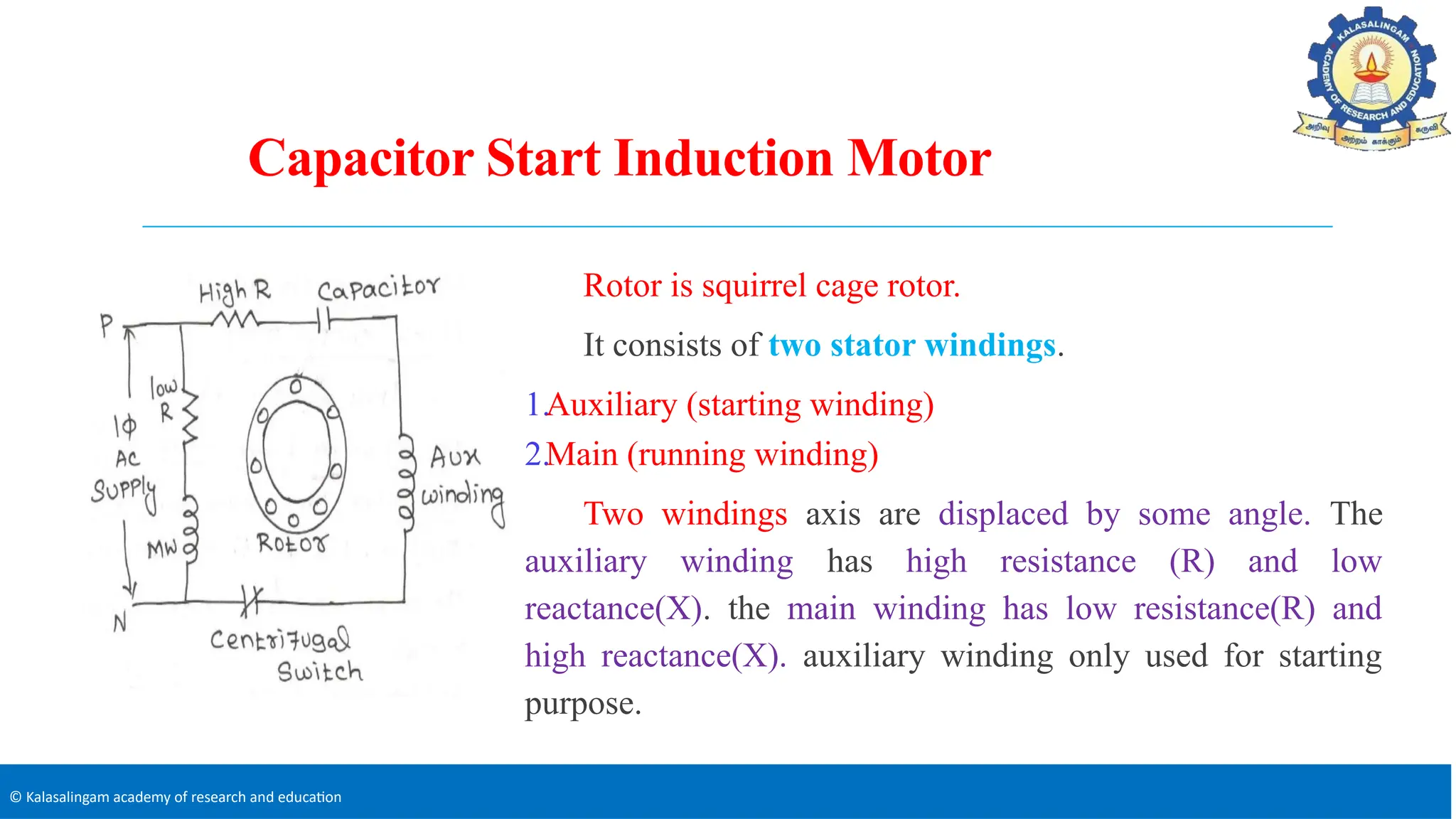
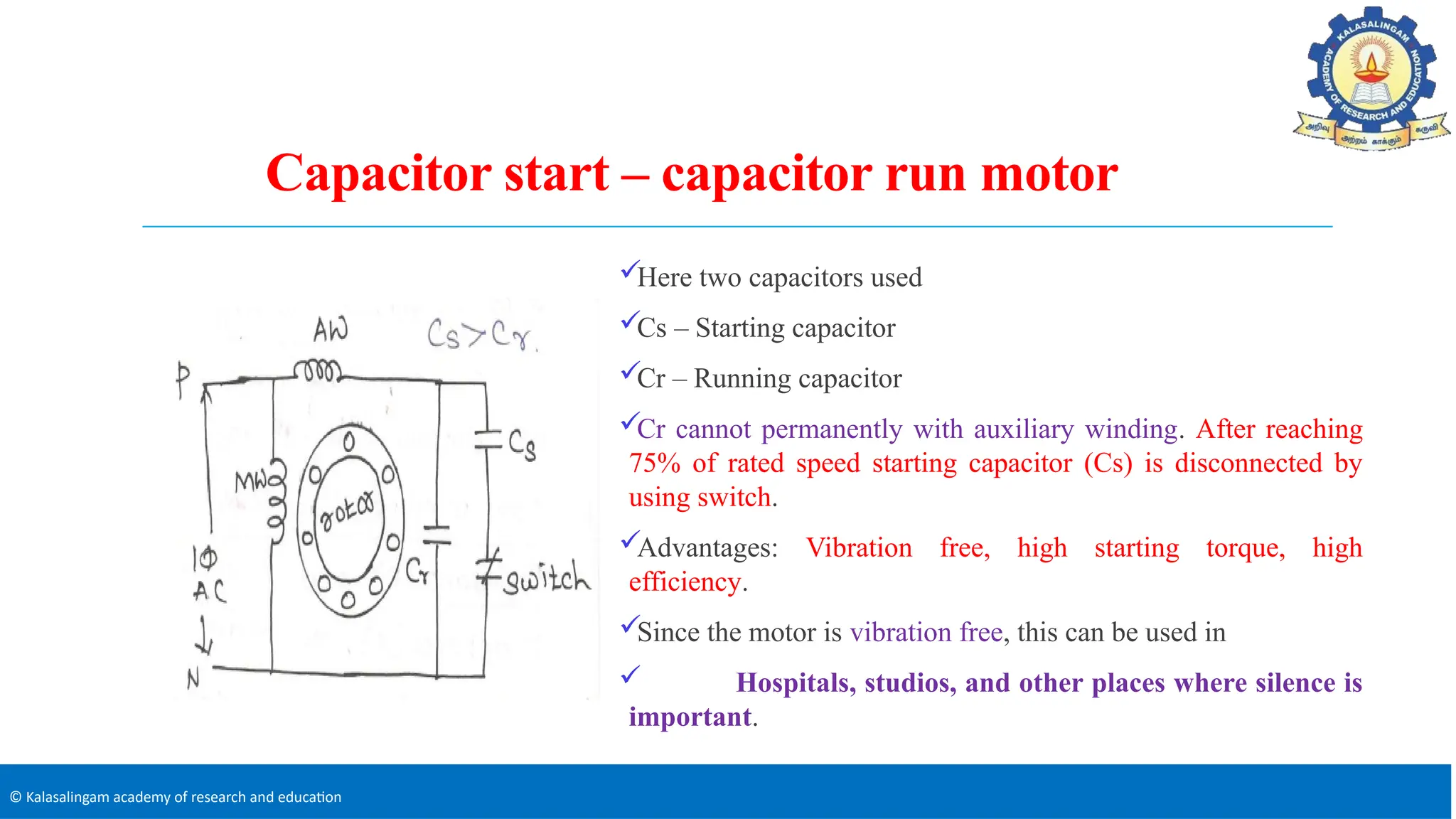
The document covers the basics of electrical machines, focusing on induction motors which convert electrical energy into mechanical energy and are widely used in various applications. It details the construction and operation of both three-phase and single-phase induction motors, highlighting types such as squirrel cage and slip ring motors, as well as their respective advantages and applications. Additionally, it explains the principles of rotating magnetic fields, motor starting mechanisms, and differences in motor characteristics.