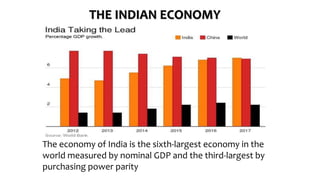
The document provides an overview of Indian culture, traditions, and society. It discusses the national flag and its symbols, demographics, languages spoken, family values, greetings, religions practiced, festivals celebrated, arts, architecture, agriculture, clothing, music and dance traditions. Business is mainly conducted in English but understanding cultural etiqutes is important. India has a long and diverse cultural history and is a country with unity in diversity.