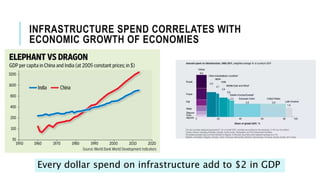
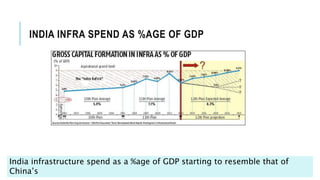
The document discusses India's infrastructure development and its implications for economic growth, highlighting the correlation between infrastructure spending and GDP. It emphasizes that while India is making progress, particularly in hard infrastructure, it must improve on soft infrastructure to enhance manufacturing competitiveness, especially in comparison to other countries in the MITI-V group. Government initiatives and increasing foreign direct investment in various sectors like roadways, railways, and ports are noted as key factors in the country's infrastructure push.