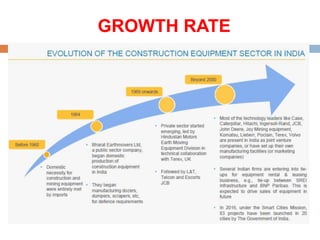
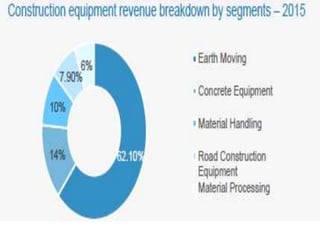
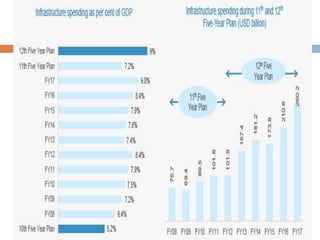
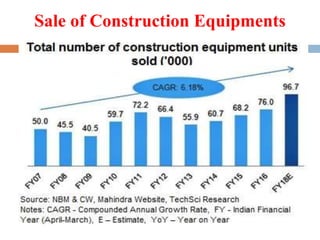
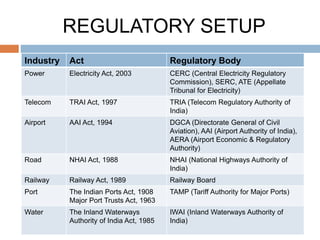
The infrastructure sector is a key driver of the Indian economy, contributing 5% of India's GDP. It includes electricity, roads, ports, airports, railways, and telecommunications. The government has allocated nearly $400 billion for infrastructure in the upcoming fiscal year. India needs $450 billion in infrastructure investment over the next 5 years, with 70% needed for power, roads, and urban development. Growth in the construction equipment industry is expected to reach $5 billion by 2020 due to increased investment in infrastructure projects.