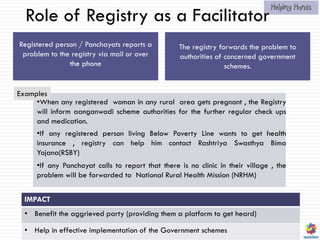
The document proposes a centralized registry to universalize access to quality primary healthcare in India. It outlines the current problems with healthcare access and affordability in India. The proposed solution is a centralized registry that maintains a database of patients, medical facilities, community workers and more. It would act as a facilitator to connect people to existing government health schemes and improve access to affordable generic medicines. The registry would be supported by initiatives like an online doctors' forum, mobile health apps, and organizational structure.