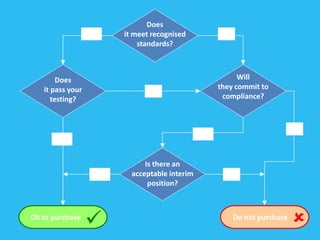
The document discusses ensuring procurement of IT solutions that comply with disability discrimination laws. It provides checklists of accessibility factors to consider for hardware, software, learning platforms and more. It emphasizes asking suppliers about the accessibility standards their solutions meet and testing the solutions directly with people with disabilities. Non-compliant suppliers may promise future improvements; it's important they commit to timelines and standards in contracts. Accessibility should be explicitly required in procurement documents and part of supplier selection and scoring.