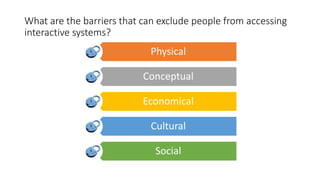
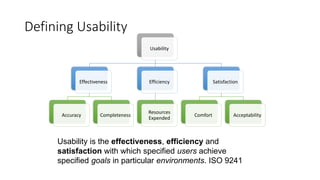
This document provides an overview of accessibility for digital interactions. It discusses why accessibility is important by allowing environments and objects to be used by as many people as possible. The document outlines potential barriers that can exclude people from accessing interactive systems, including physical, conceptual, economic, cultural and social barriers. It then discusses how people with disabilities use the web, including screen readers and the importance of page layout. The document also covers guidelines like Section 508, ADA, WCAG 2.0 and 2.1, and different conformance levels. It provides tools and considerations for quality engineering, UX design, and front-end development to achieve accessibility.