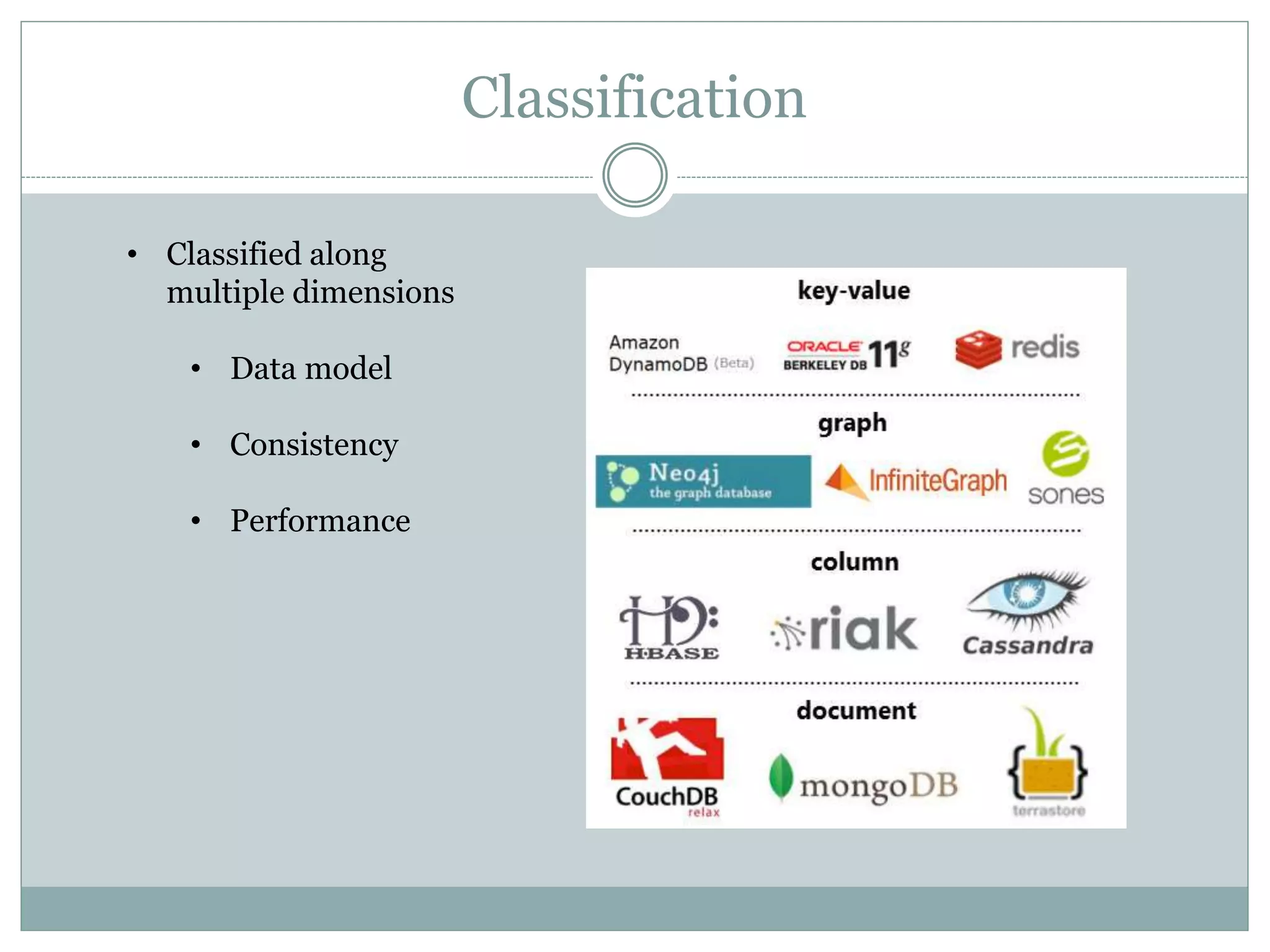
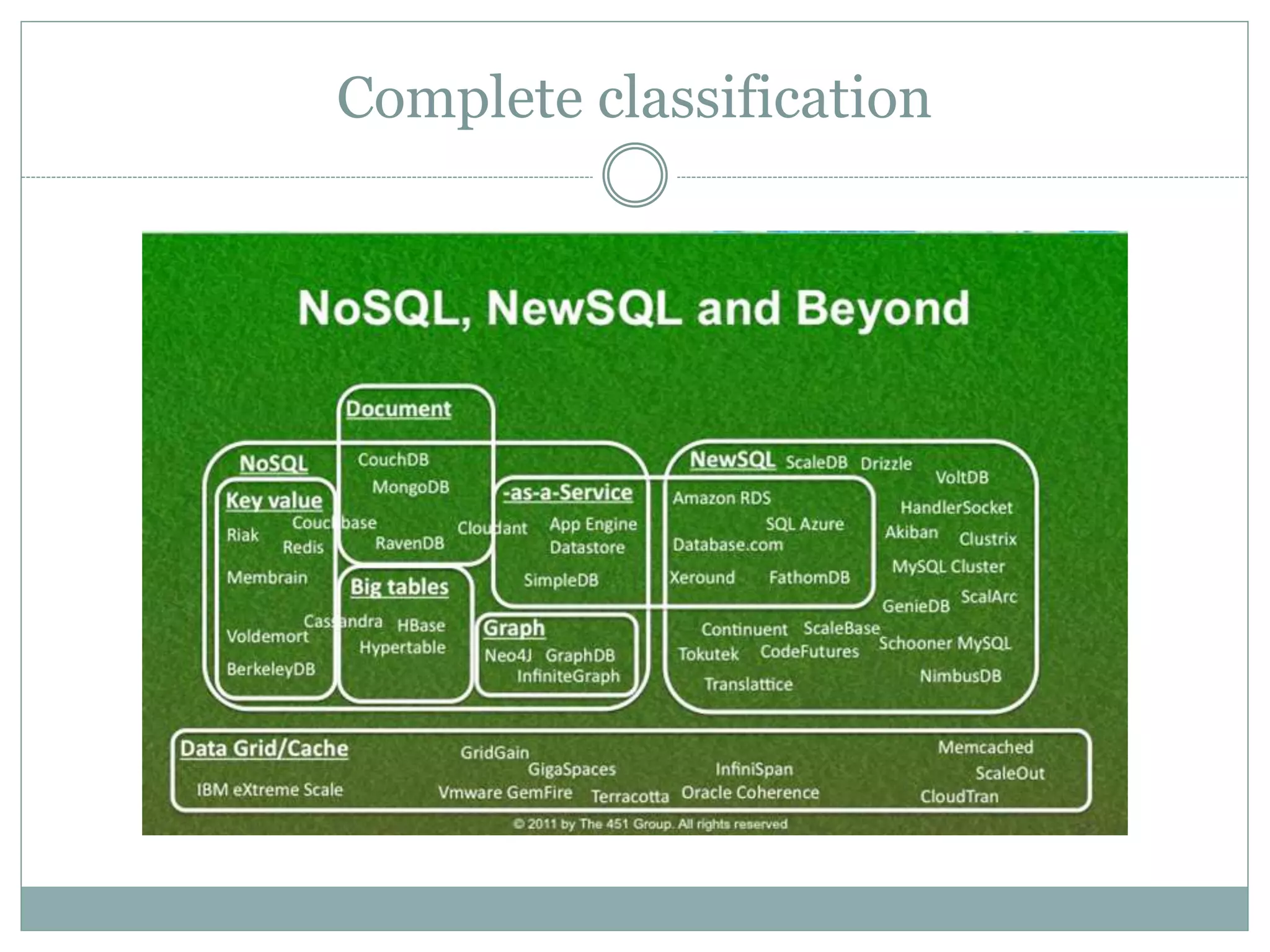
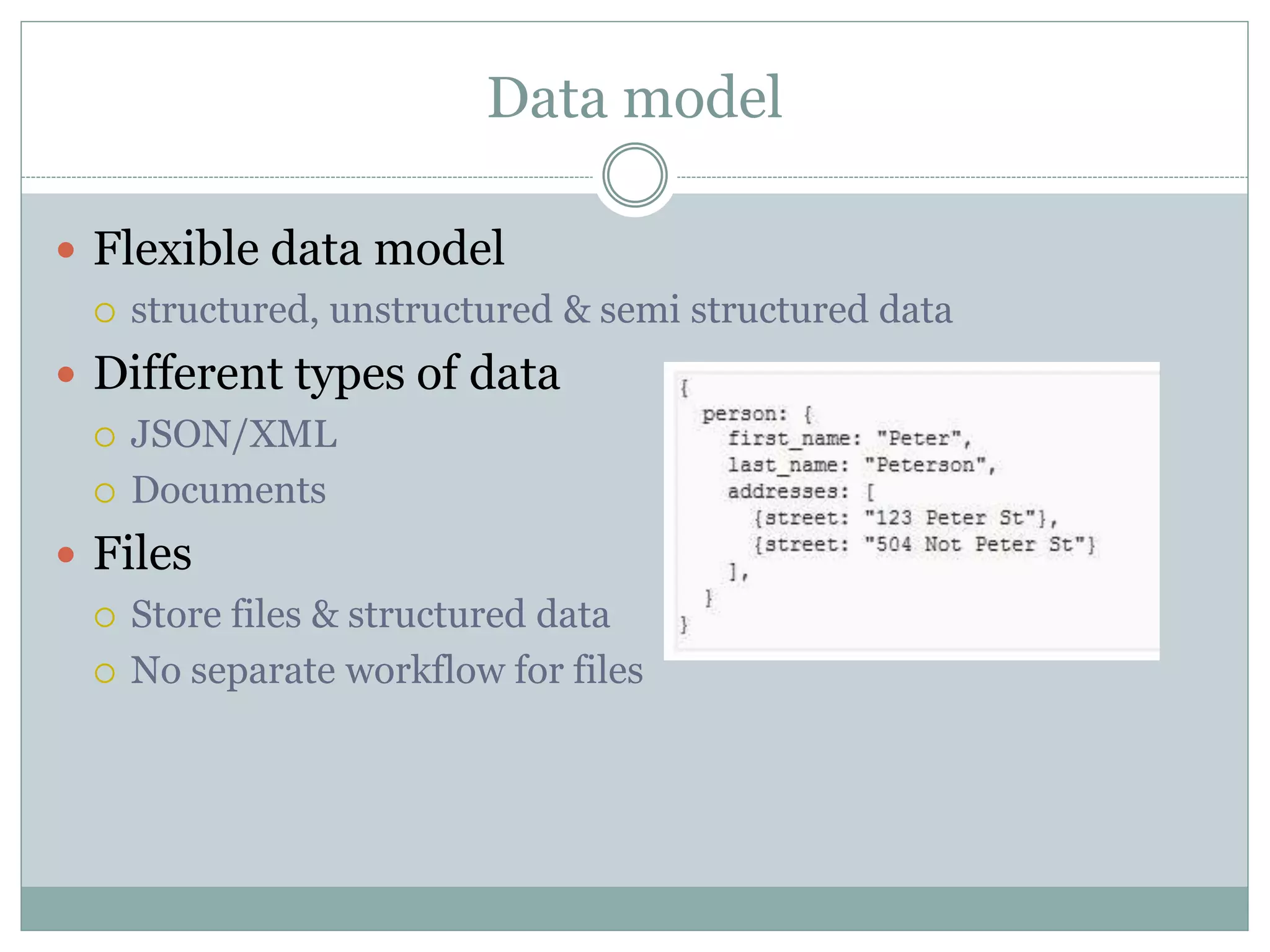
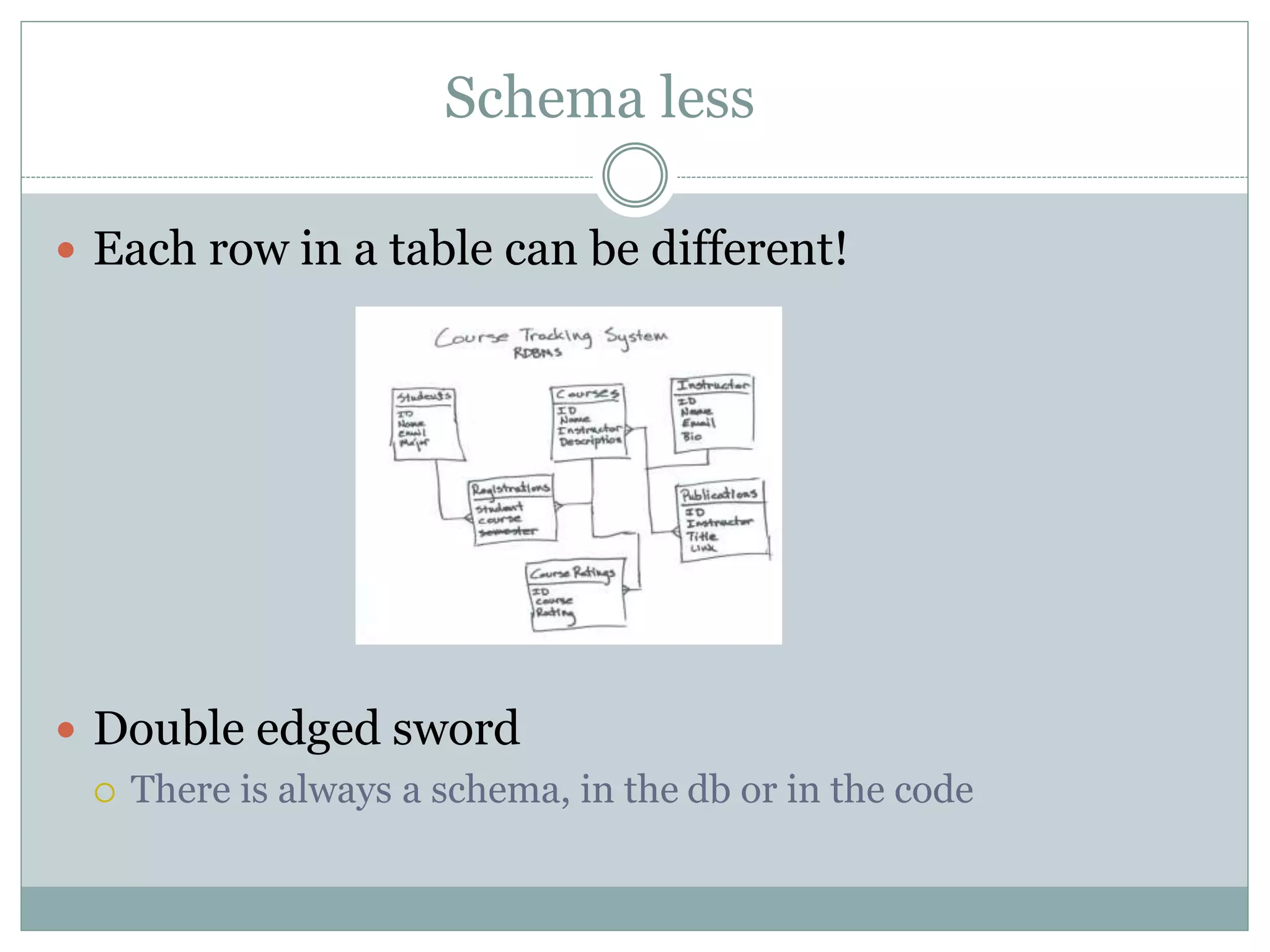
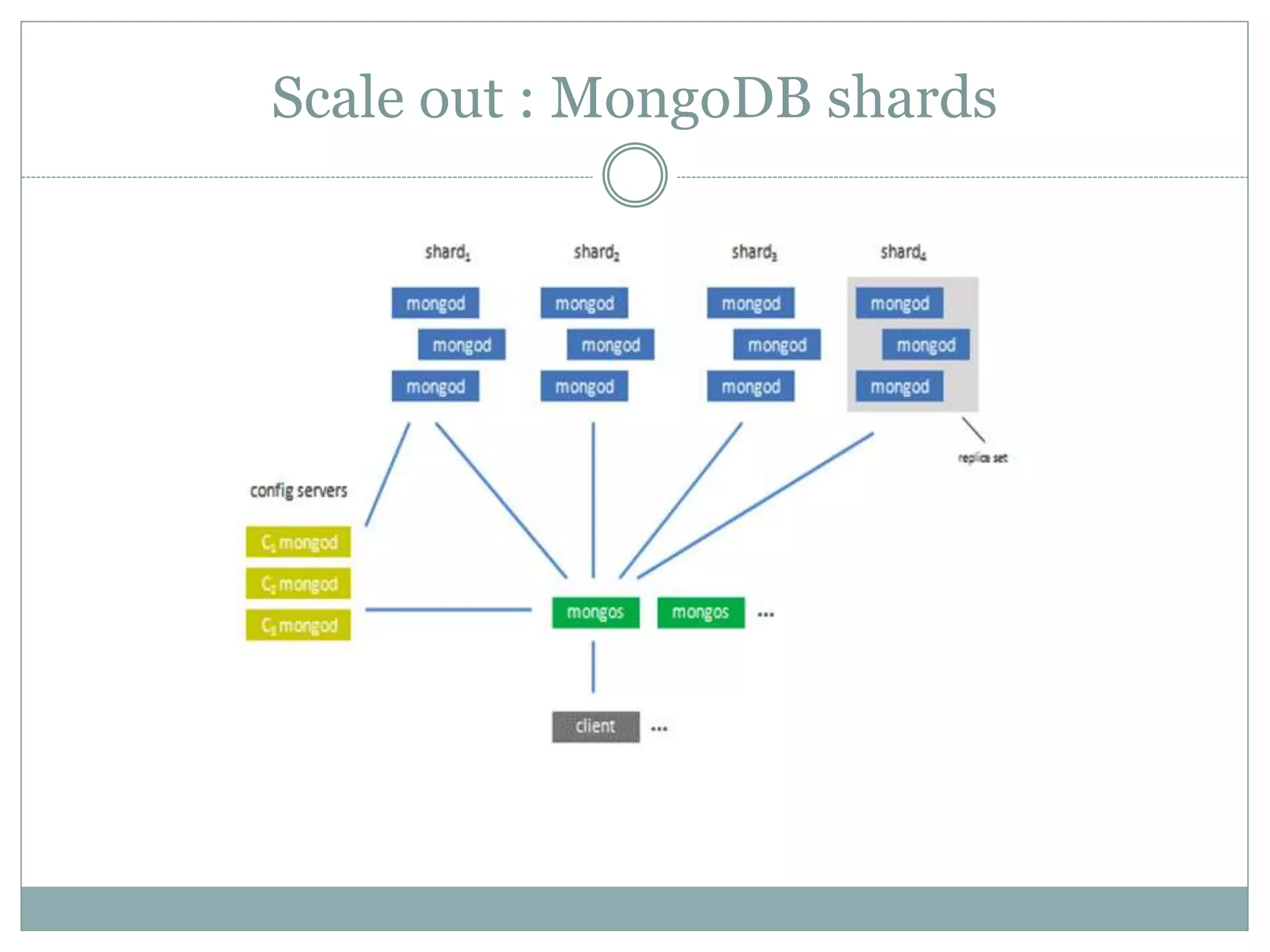
This document discusses NoSQL databases and why they are used. It begins by defining NoSQL as "not only SQL" or "not SQL" databases that do not use a relational schema. The need for NoSQL databases arose in the early 2000s due to difficulties scaling MySQL databases for large amounts of data. NoSQL databases are classified based on their data model, consistency, and performance. They offer flexible data models including structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. NoSQL databases focus on developer agility by being easy to use and integrate with modern frameworks. While they scale well horizontally, they generally lack ACID compliance and transaction support of relational databases.