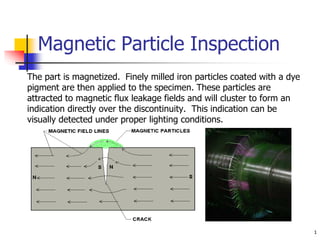
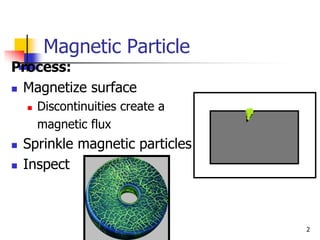
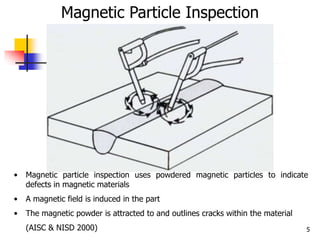
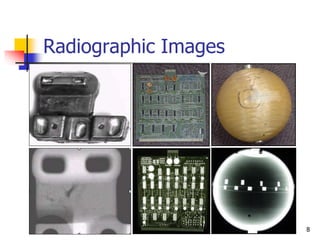
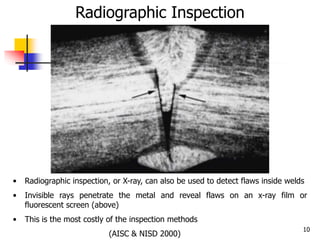
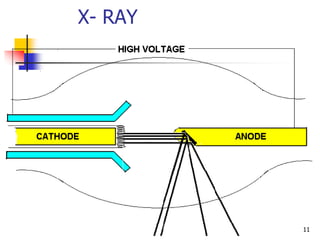
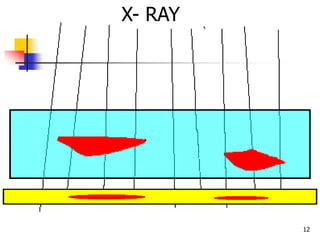
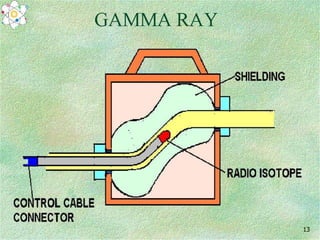
The document describes two non-destructive testing methods: magnetic particle inspection and radiographic inspection. Magnetic particle inspection involves magnetizing a specimen and applying iron particles to detect surface and some subsurface defects, while radiographic inspection uses x-rays to reveal internal flaws by capturing varying exposures on film. Both methods have health risks and differ in cost and application, with radiography being the more expensive option.