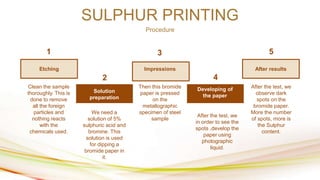
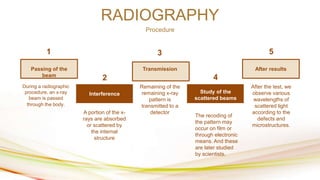
The document outlines non-destructive testing (NDT) methods used in engineering, particularly metallurgy, including sulphur printing, radiography, and magnetic particle testing. It details the procedures, applications, and advantages of each technique, highlighting their value in evaluating material properties, detecting defects, and ensuring product quality across various industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive. The content emphasizes how these innovative techniques can save time and costs while providing critical insights into material integrity.