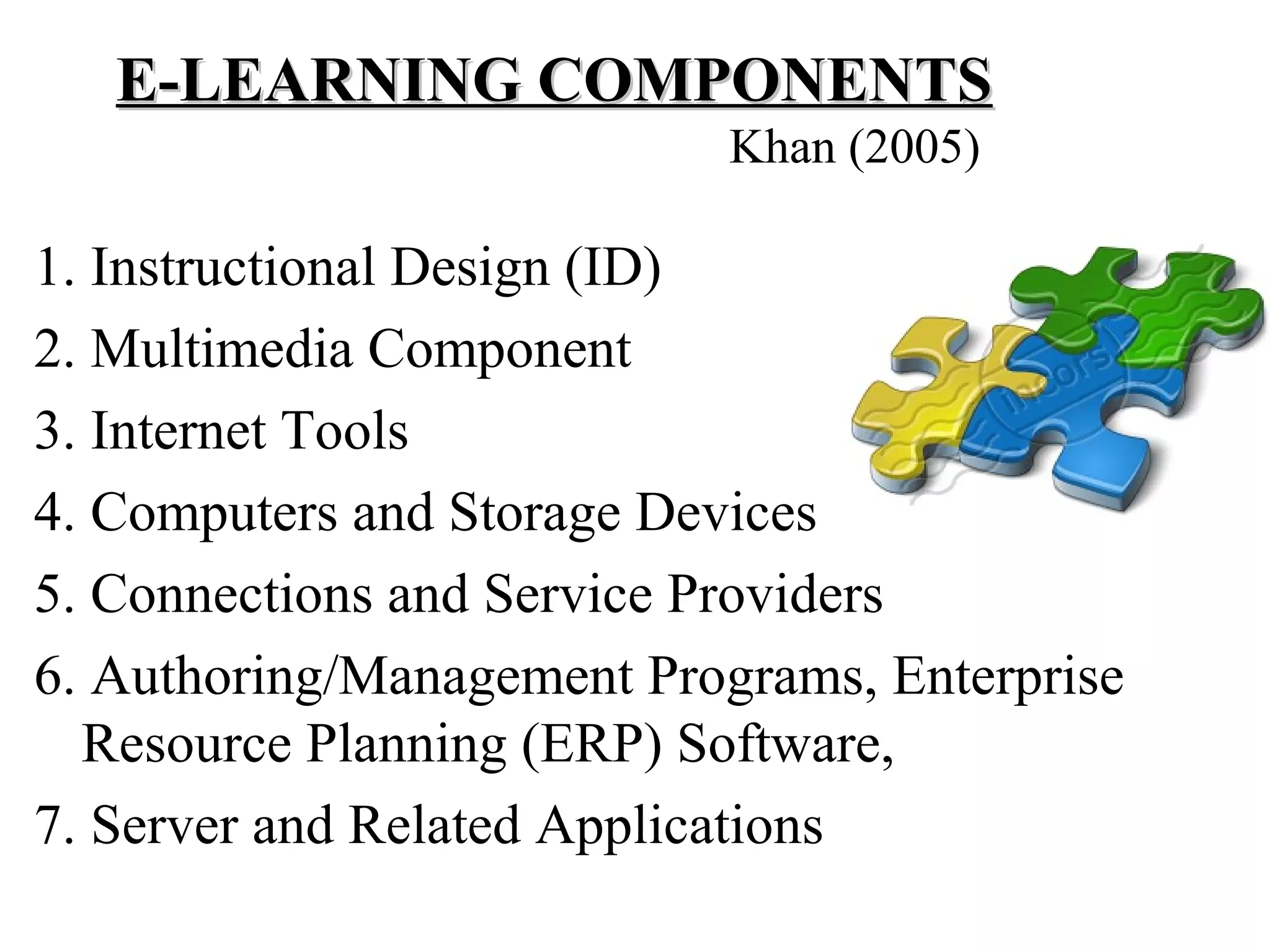
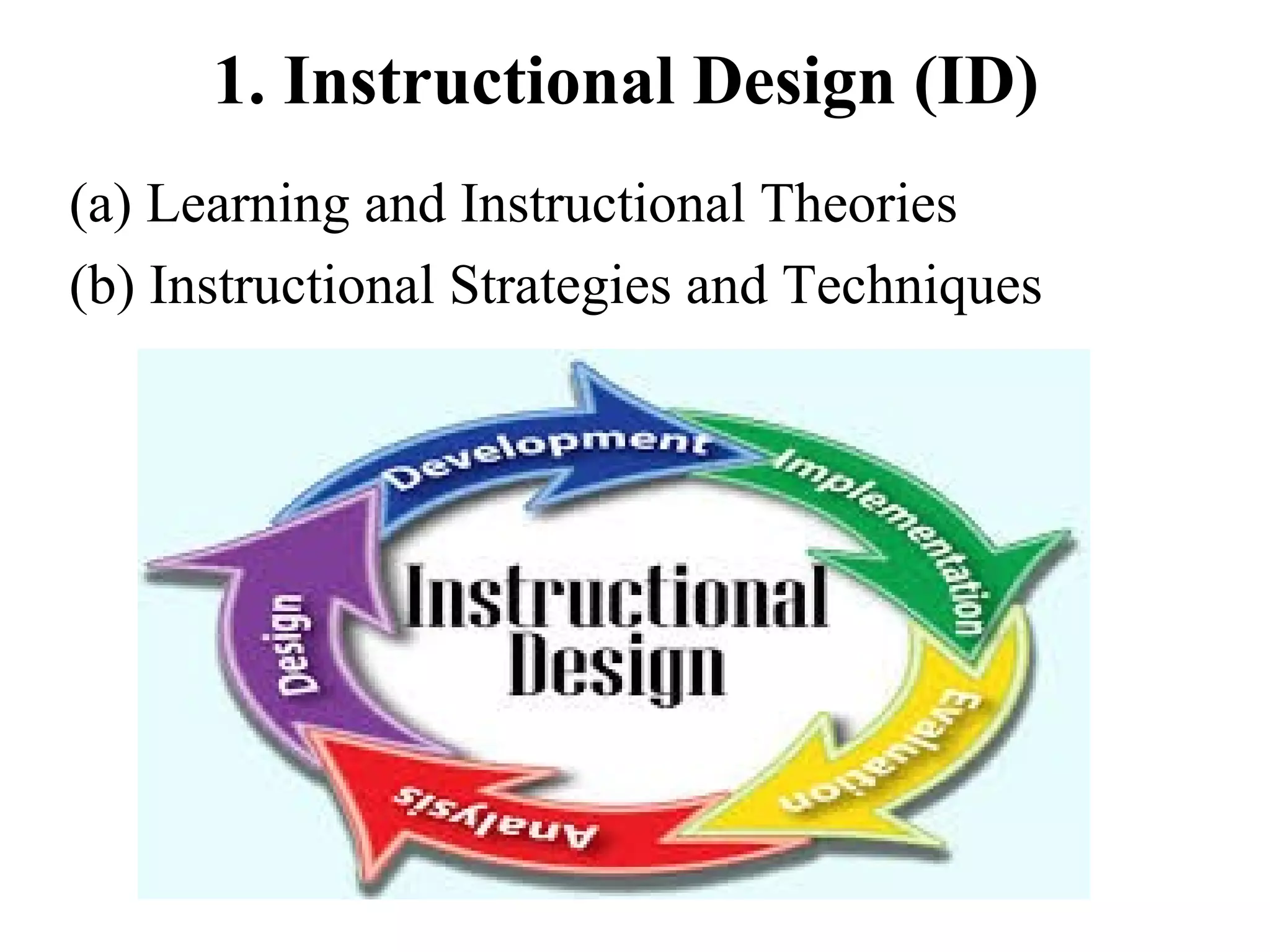
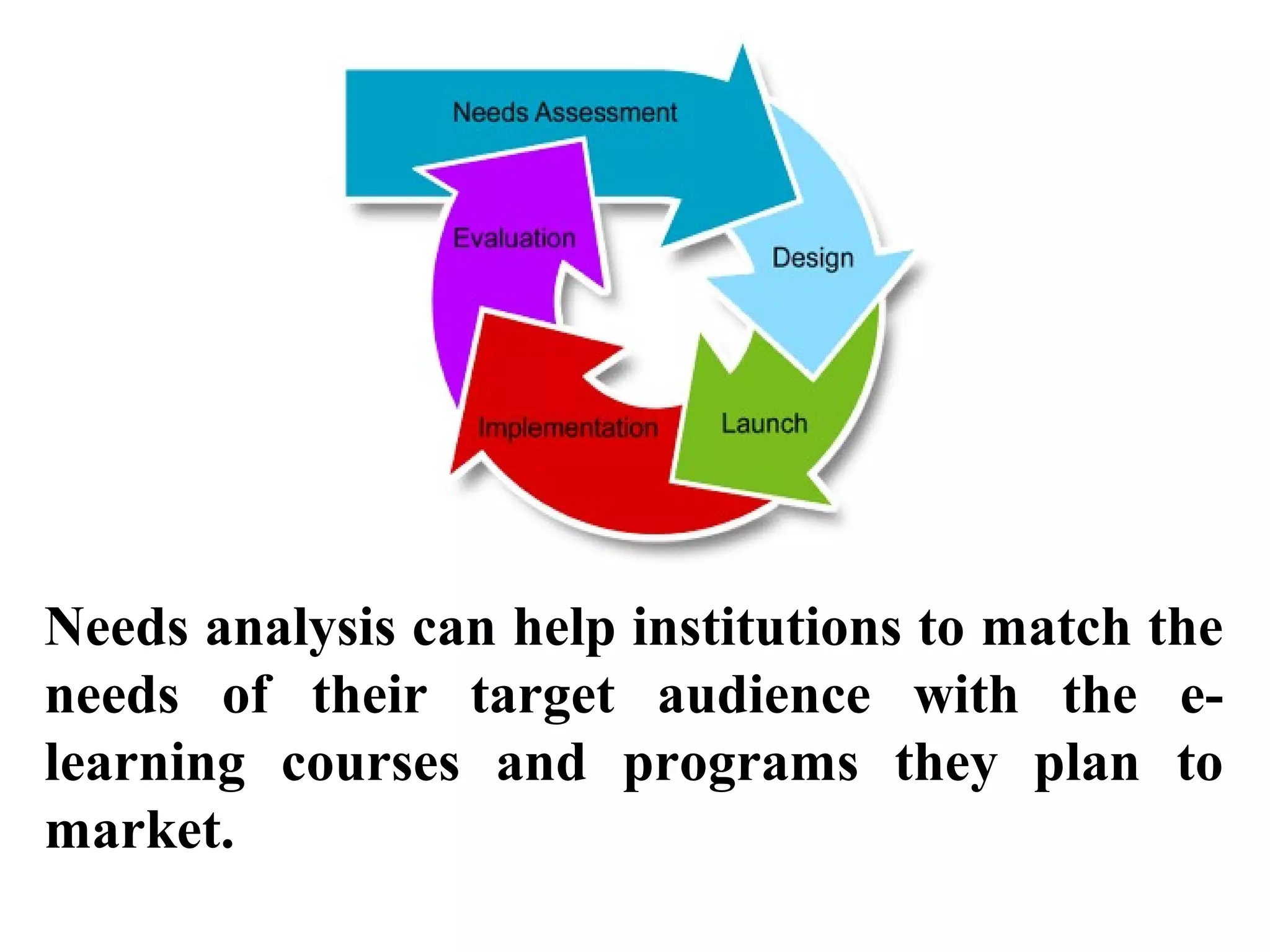
Needs assessment is important for implementing e-learning in colleges of education. It identifies performance areas where training should be applied. A needs assessment survey can help institutions match e-learning courses to learners' needs and analyze short and long-term e-learning strategy needs. It provides information on technological and support services required. Through needs assessment, an institution can establish e-learning goals. Conducting needs analysis on e-learning components and current computer skills of college faculties and students (future teachers) provides vital information about colleges' situations and facilitates decision making on e-learning usage and implementation.