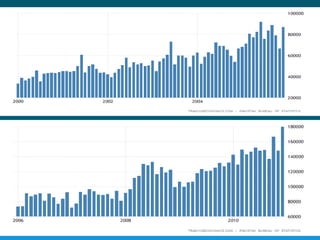
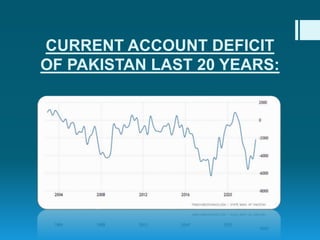
Pakistan relies heavily on imports to support its population, with major imports including mineral fuels, electrical equipment, machinery, and pharmaceuticals. In 2021, total imports reached approximately $69.04 billion, showcasing a significant increase from the previous year, while exports were valued at $34.57 billion. The current account deficit indicates an imbalance where imports exceed exports, prompting the need for strategies to increase domestic productivity and exports.