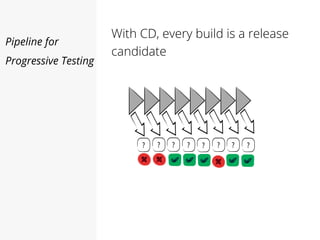
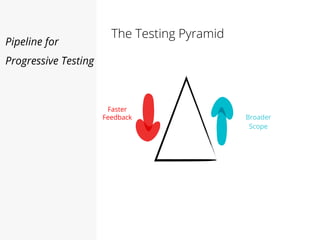
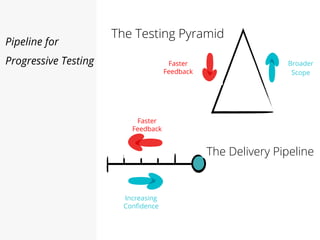
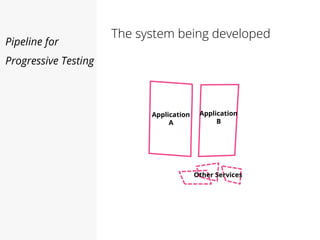
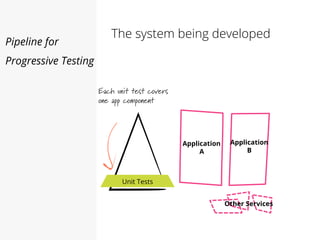
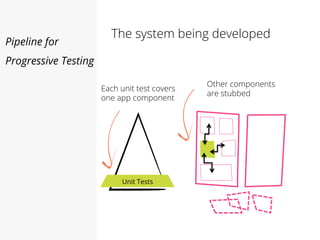
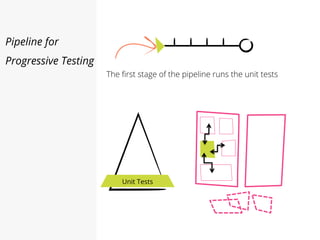
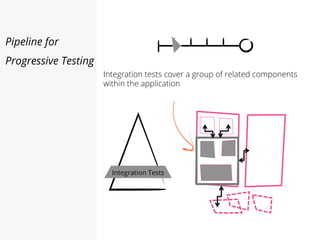
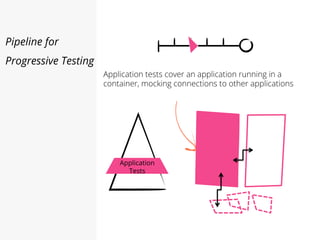
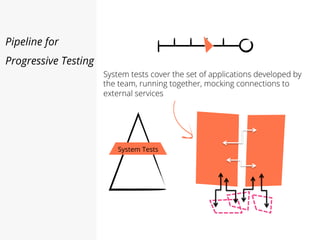
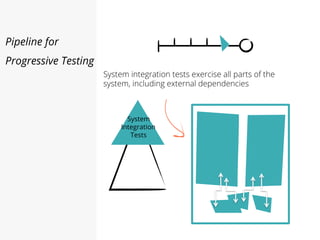
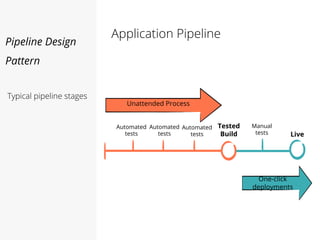
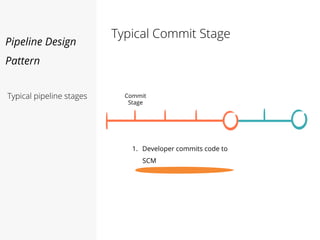
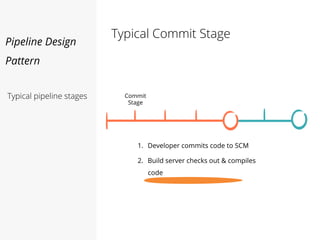
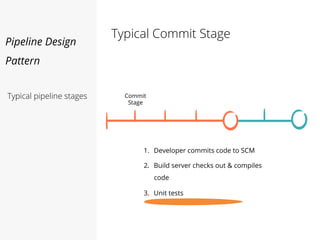
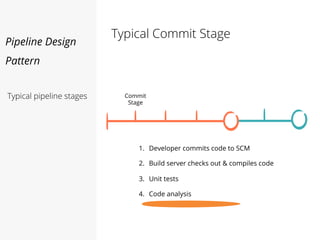
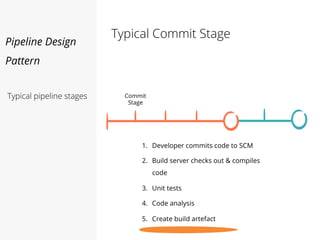
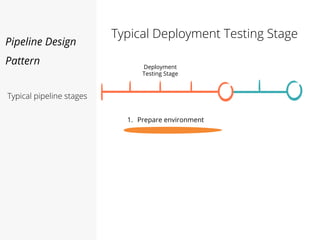
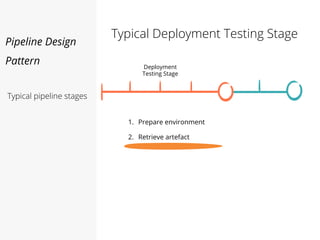
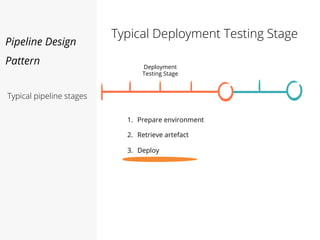
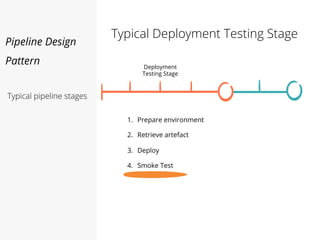
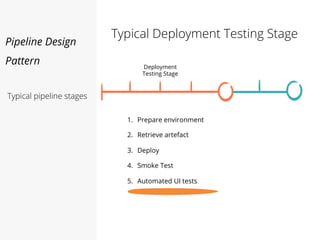
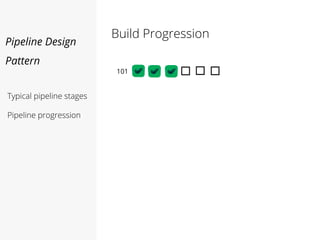
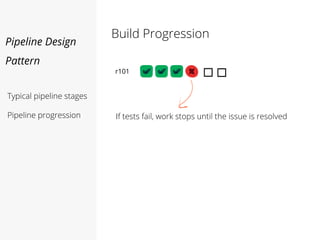
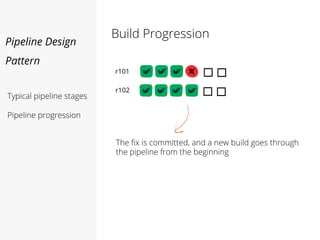
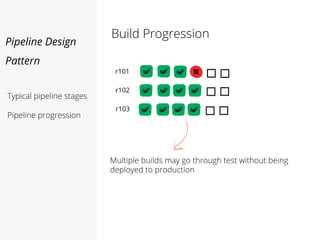
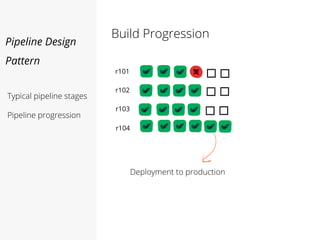
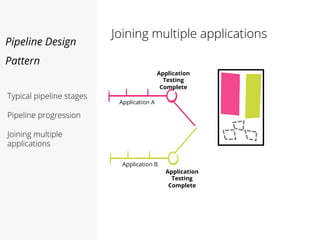
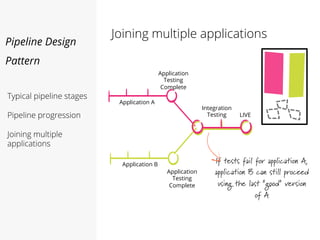
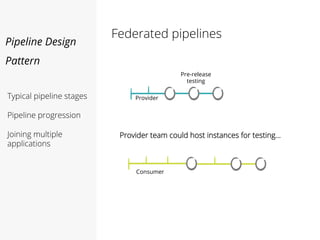
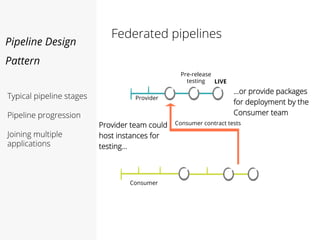
This document discusses pipelines for continuous delivery. It describes how pipelines can incorporate progressive testing from unit tests to system integration tests. A typical pipeline includes stages for committing code, building, running unit tests, code analysis, and creating build artifacts. Deployment testing stages prepare environments, deploy artifacts, and run smoke and UI tests. Best practices are to keep everything in source control and replicate production. The document also discusses how to structure pipelines for multiple applications and federated systems.