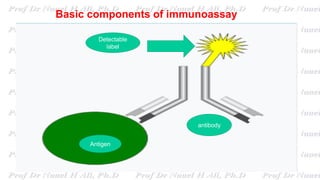
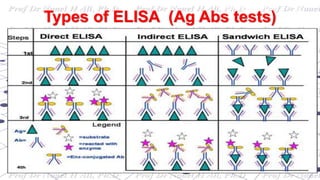
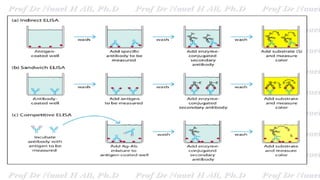
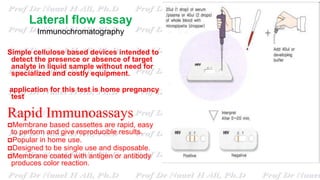
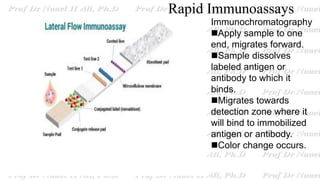
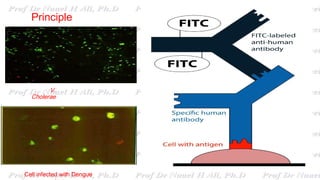
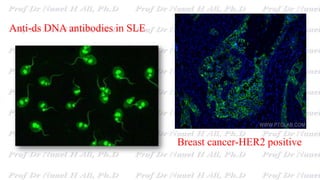
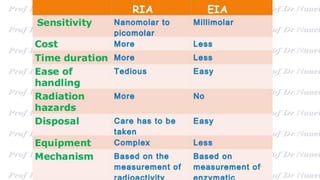
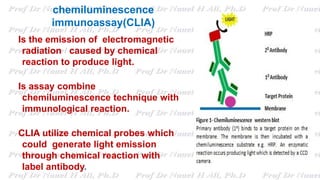
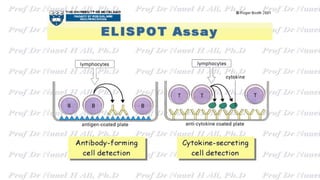
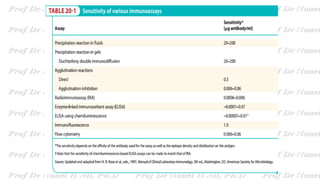
This document discusses various immunoassay techniques used to detect antigens and antibodies. It describes the basic principles of immunoassays which rely on the specific binding of antigens and antibodies. It then explains different types of immunoassays including ELISA, radioimmunoassay, fluorescence immunoassay, chemiluminescence immunoassay, lateral flow immunoassay, and their applications in detecting various targets like hormones, vitamins, and diagnostic markers.