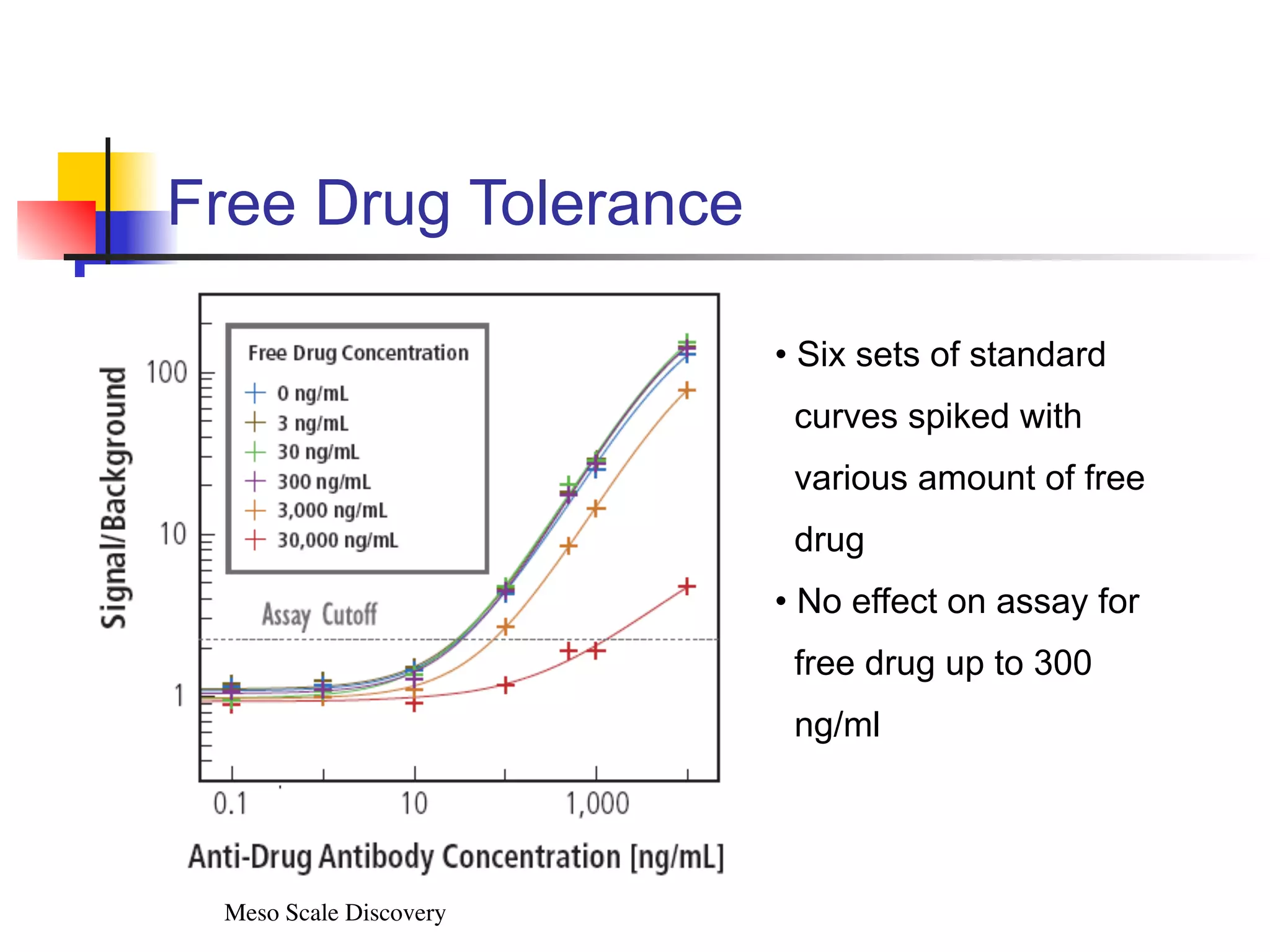
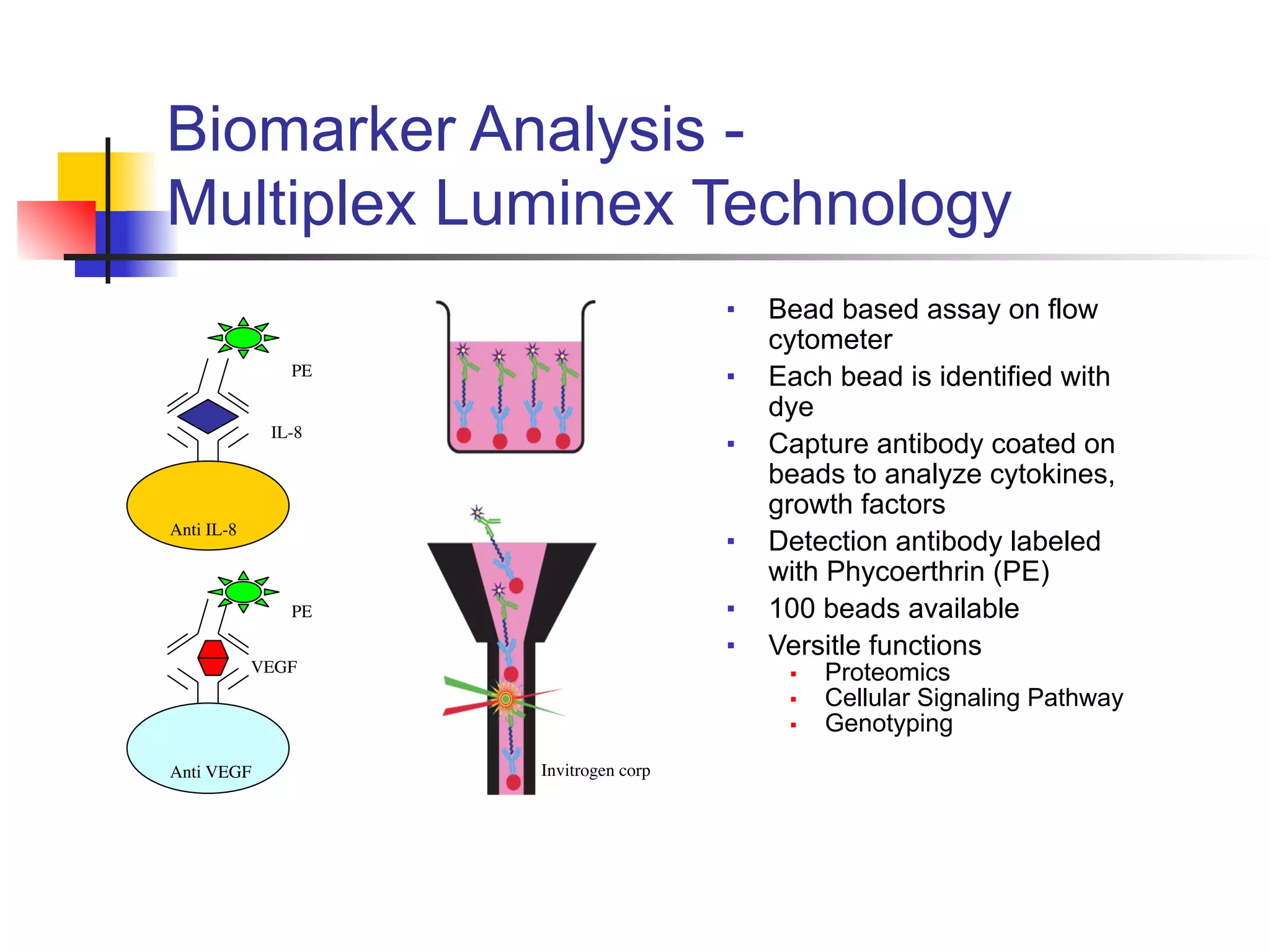
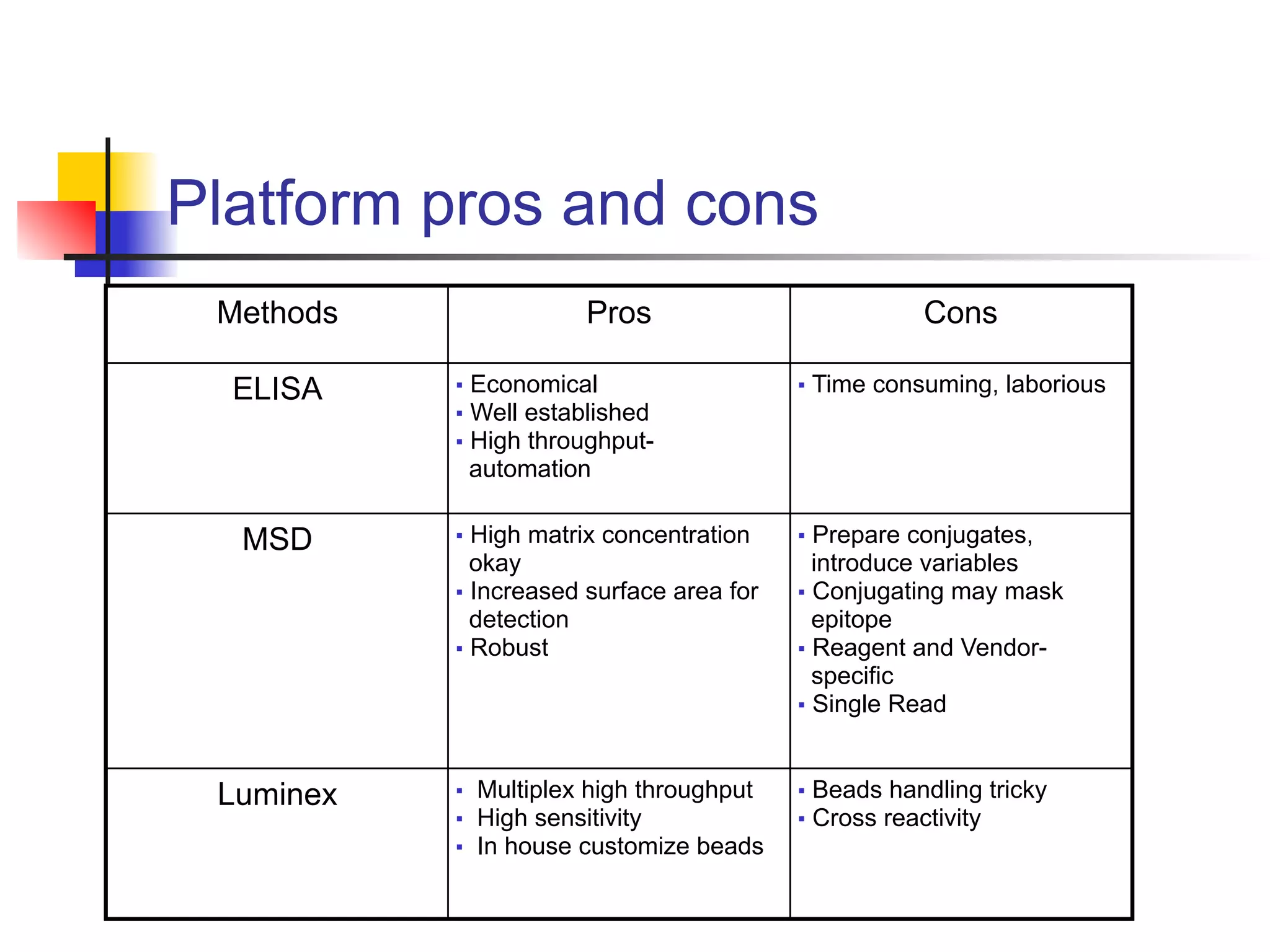
This document provides an overview of various immunoassay types and platforms used in preclinical drug development, including ELISA, Meso Scale Discovery (MSD), and Luminex multiplex technologies. It discusses using ELISA to measure drug exposure through pharmacokinetic assays and evaluate immunogenicity. MSD platforms like electrochemiluminescence allow detection of analytes in higher matrix concentrations with increased sensitivity. Luminex multiplex technology enables high-throughput analysis of multiple biomarkers simultaneously through bead-based assays. The document emphasizes the importance of robust analytical assays for drug development and monitoring biomarkers to contribute to successful drug discovery.