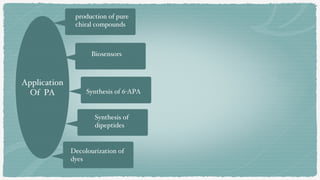
This document discusses immobilization of penicillin G acylase (PGA), an enzyme used in the production of semi-synthetic penicillins. PGA hydrolyzes penicillin G into phenylacetic acid and 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA). Immobilizing PGA enhances its stability and reusability, making it suitable for industrial production of 6-APA. Various studies have immobilized PGA using methods like covalent binding to vinyl copolymers, double entrapment in agar-polyacrylamide resins, and attachment to silica gel carriers. Immobilized PGA shows improved reaction rates and stability over free enzyme.