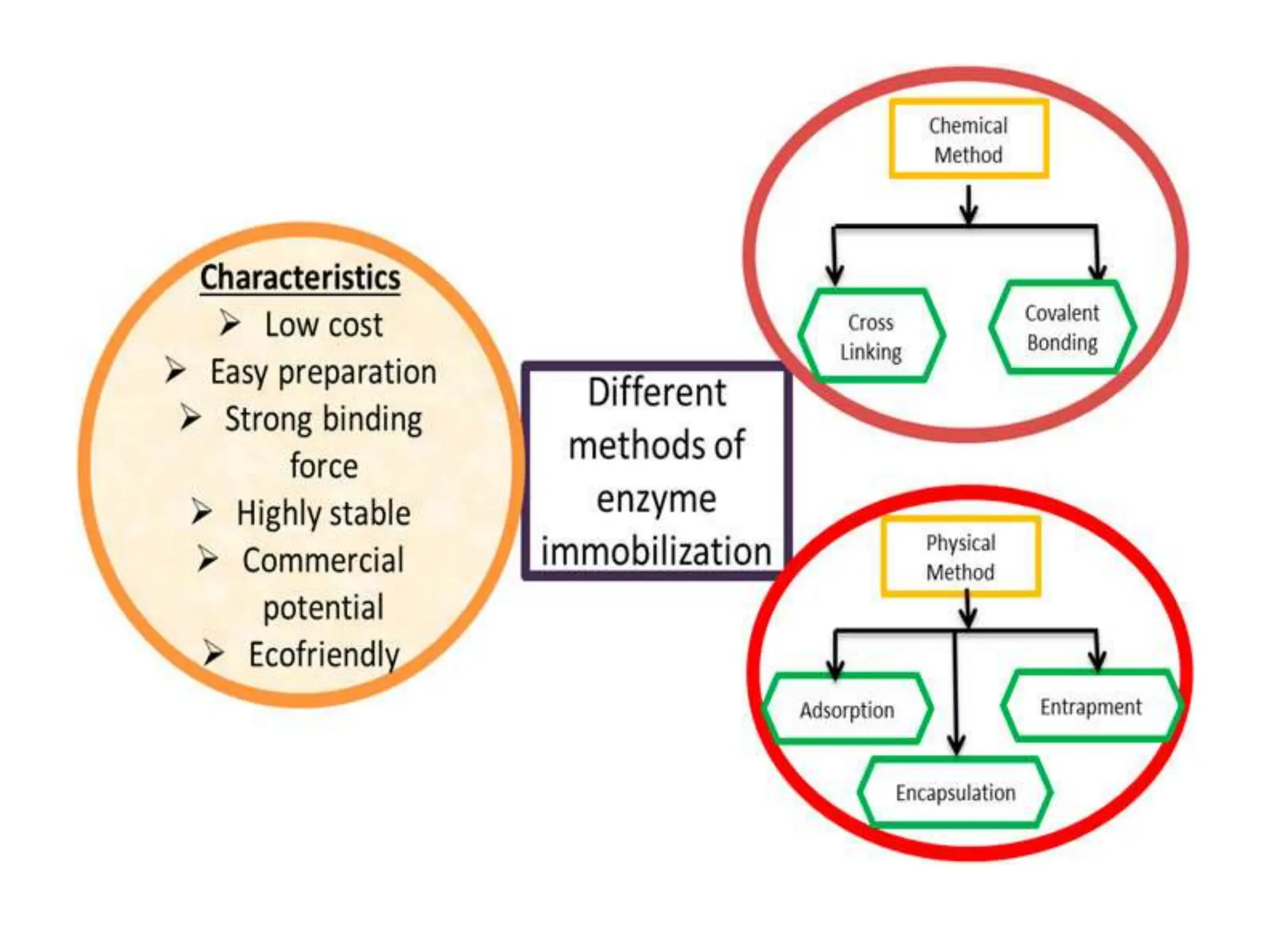
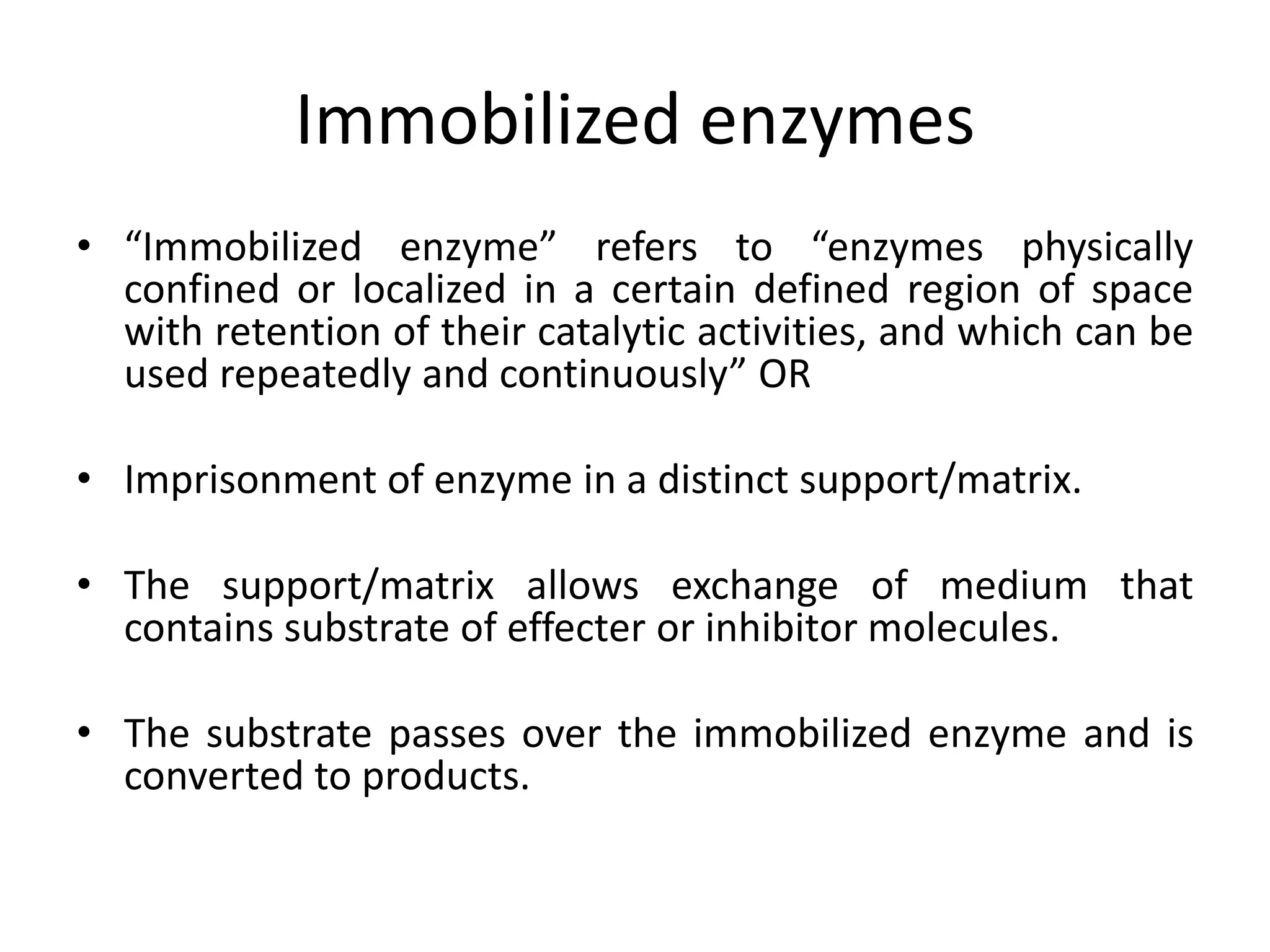
The document discusses enzyme immobilization, defining it as the confinement of enzymes in a specific area while retaining their catalytic activity, which allows for repeated use. It outlines the advantages such as increased efficiency and stability, alongside disadvantages like limited applications and potential activity loss. Various applications of immobilized enzymes in producing antibiotics, steroids, amino acids, and organic compounds are highlighted, along with the types of supports used for immobilization and methods of enzyme attachment.



![Supports/Matrix used in
immobilization
• The matrix that holds the enzyme should be:
• cheap and easily available.
• Should not react with medium and enzyme.
Three types of matrix are used:
1. Natural polymers: alginate, chitosan and chitin, collagen,
carrageenan, gelatin, cellulose, starch, pectin
2. Synthetic polymers: ion exchange resins/polymers [polyvinyl
chloride (PVC), UV activated Polyethylene glycol (PEG)]
3. Inorganic materials: ceramics, silica, glass, activated carbon,
charcoal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymeimmobilizations-24-240712180109-e68ec01e/75/Enzyme-Immobilization-S-24-adadaddaa-ppt-6-2048.jpg)