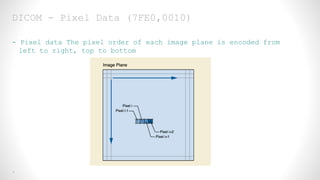
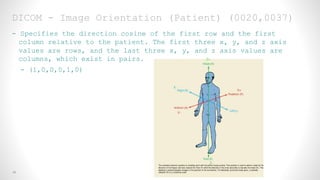
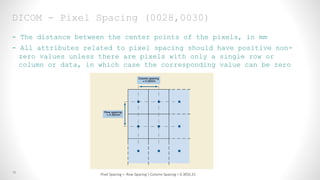
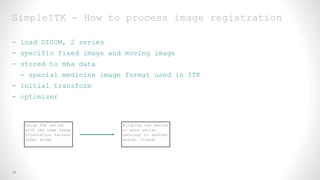
This document provides an overview of medical image registration using SimpleITK. It first discusses relevant DICOM image metadata fields like pixel data, bits allocated, and image orientation. It then defines image registration as aligning a target image to a source image using a transform and optimization process. Finally, it outlines the SimpleITK registration framework which loads images, applies an initial transform, uses a metric and optimizer to improve alignment between fixed and moving images.