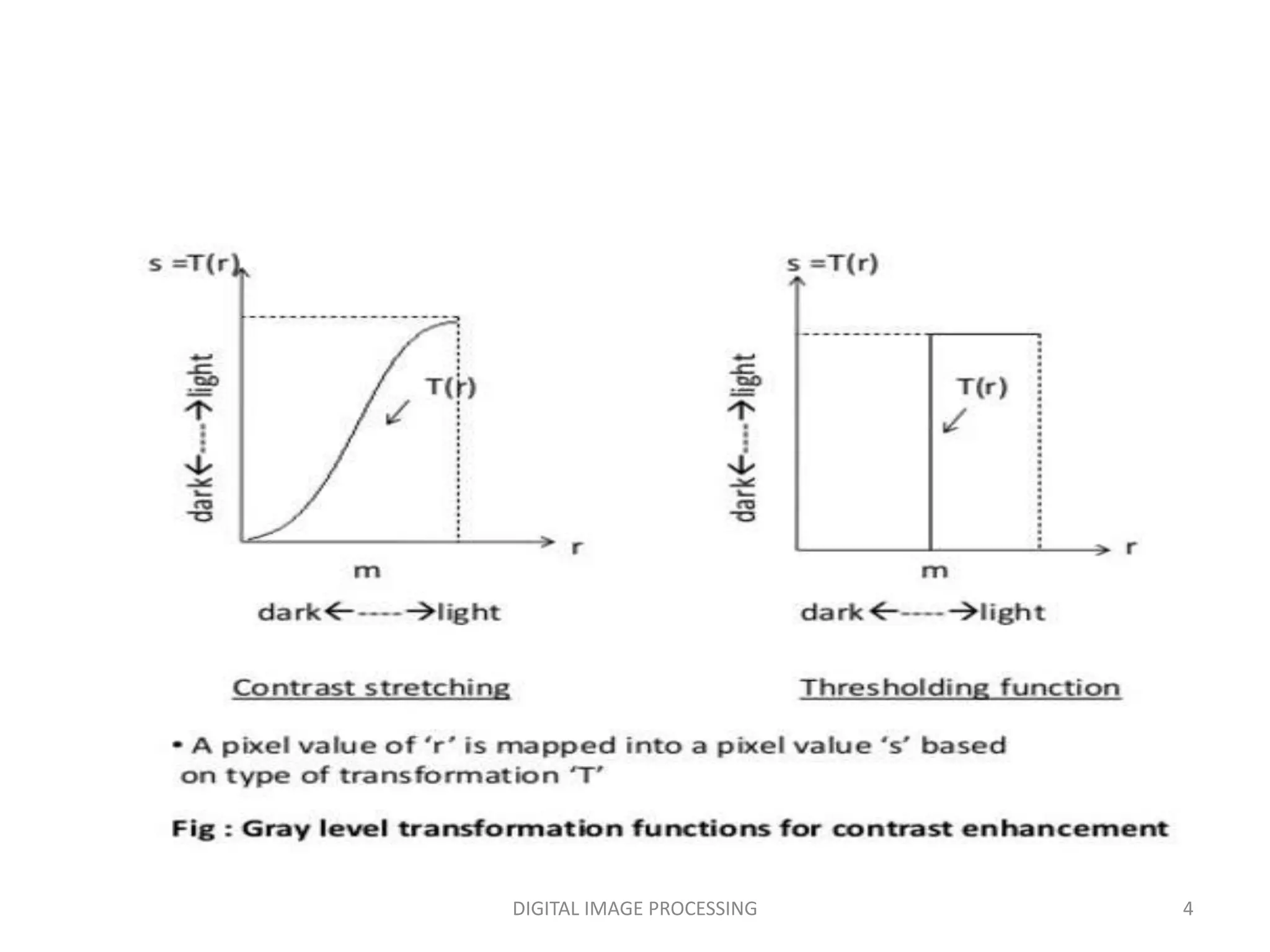
The document discusses various image enhancement techniques in digital image processing. It describes how image enhancement can be done using point operations, mask operations, and in the spatial and frequency domains. Some common point operations discussed include image negative, contrast stretching, thresholding, brightness enhancement, log transformation, and power law transformation. Contrast stretching can expand the range of intensity levels in an image. Thresholding converts an image to binary black and white. Log and power law transformations are used to expand values of dark pixels and compress values of bright pixels. Mask operations involve multiplying an image with a small matrix mask to perform operations like blurring and sharpening.







![Image Negative
Negative images are useful for enhancing white or grey
detail embedded in dark regions of an image.
The negative of an image with gray levels in the range
[0,L-1] is obtained by using the expression
s = L -1 - r
L-1 = Maximum pixel value .
r = Pixel value of an image.
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement1-220905201325-0d205779/75/image-enhancement-pptx-9-2048.jpg)

![Image Negative
Matlab code : % program for image enhancement using image negative
clear all
clc
close all
a=imread('clown.png');
[m,n]=size(a);
for i=1:1:m
for j=1:1:n
b(i,j)=255-a(i,j);
end
end
subplot(1,2,1),subimage((a)),title('Original Image');
subplot(1,2,2),subimage((b)),title('Image after image
negative transformation')
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement1-220905201325-0d205779/75/image-enhancement-pptx-11-2048.jpg)




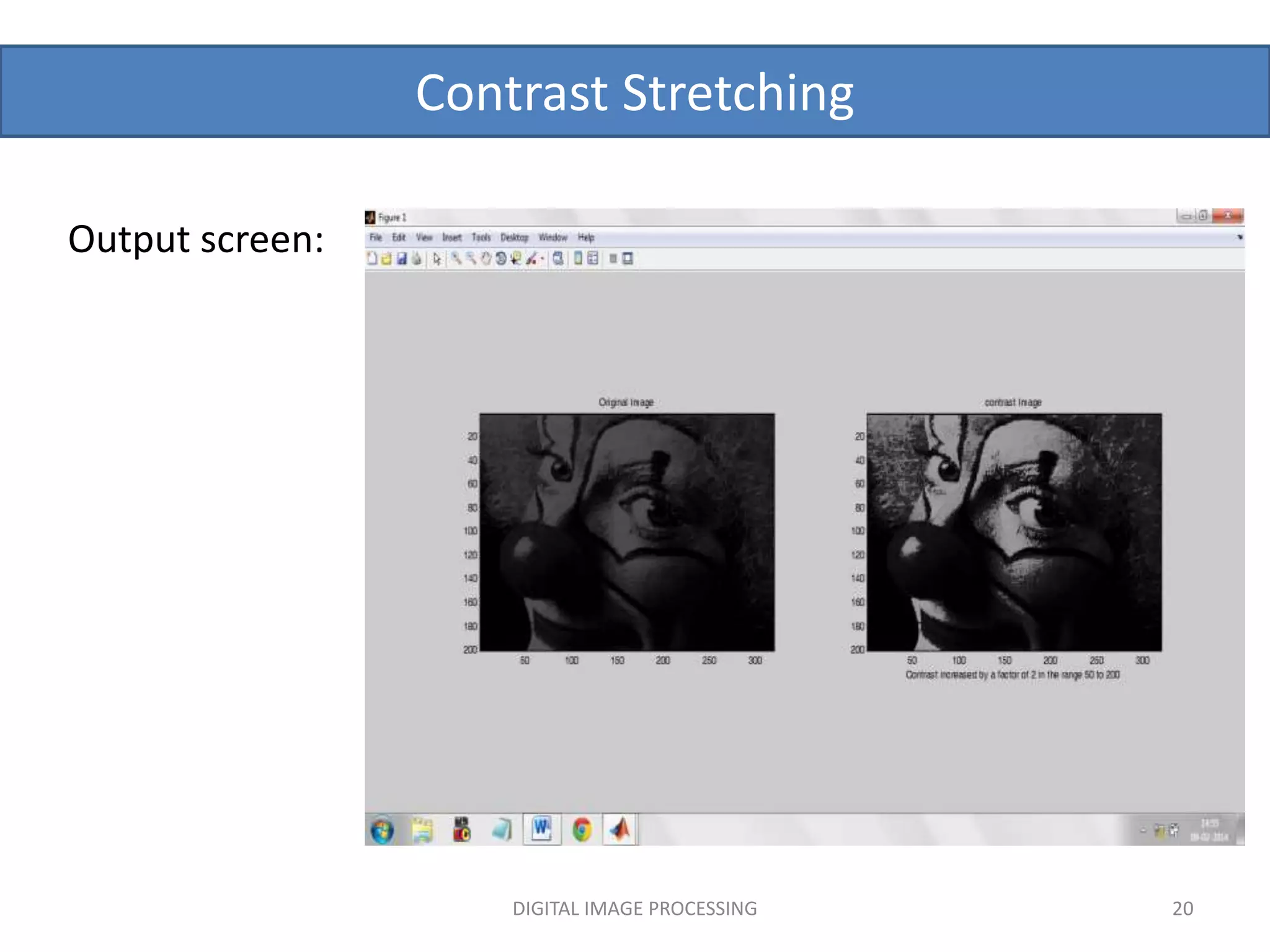
![Contrast Stretching
Matlab code: % program to increase the contrast of an image
x=input('Enter the factor which contrast should be
increased');
a=imread('clown.png');
[m,n]=size(a);
for i=1:1:m
for j=1:1:n
b(i,j)=a(i,j)*x;
end
end
subplot(1,2,1),subimage(a),title('Original Image');
subplot(1,2,2),subimage(b),title('contrast
Image'),xlabel(sprintf('Contrast increased by a factor of
%g',x));
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING 16
Contrast Stretching By Multiplication of each pixel with a scalar.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement1-220905201325-0d205779/75/image-enhancement-pptx-16-2048.jpg)

![Contrast Stretching
Matlab code: % program to increase the contrast of an image
x=input('Enter the factor which contrast should be
increased');
a=imread('clown.png');
[m,n]=size(a);
for i=1:1:m
for j=1:1:n
if(a(i,j)<50)
b(i,j)=a(i,j);%slope of transfer function between i/p
and o/p is 1
elseif (a(i,j)>200)
b(i,j)=a(i,j);
else
b(i,j)=a(i,j)*x;%slope of transfer function between i/p
and o/p is x.Hence contrast of some particular pixel value
range increased
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING 18
Contrast Stretching by using threshold function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement1-220905201325-0d205779/75/image-enhancement-pptx-18-2048.jpg)






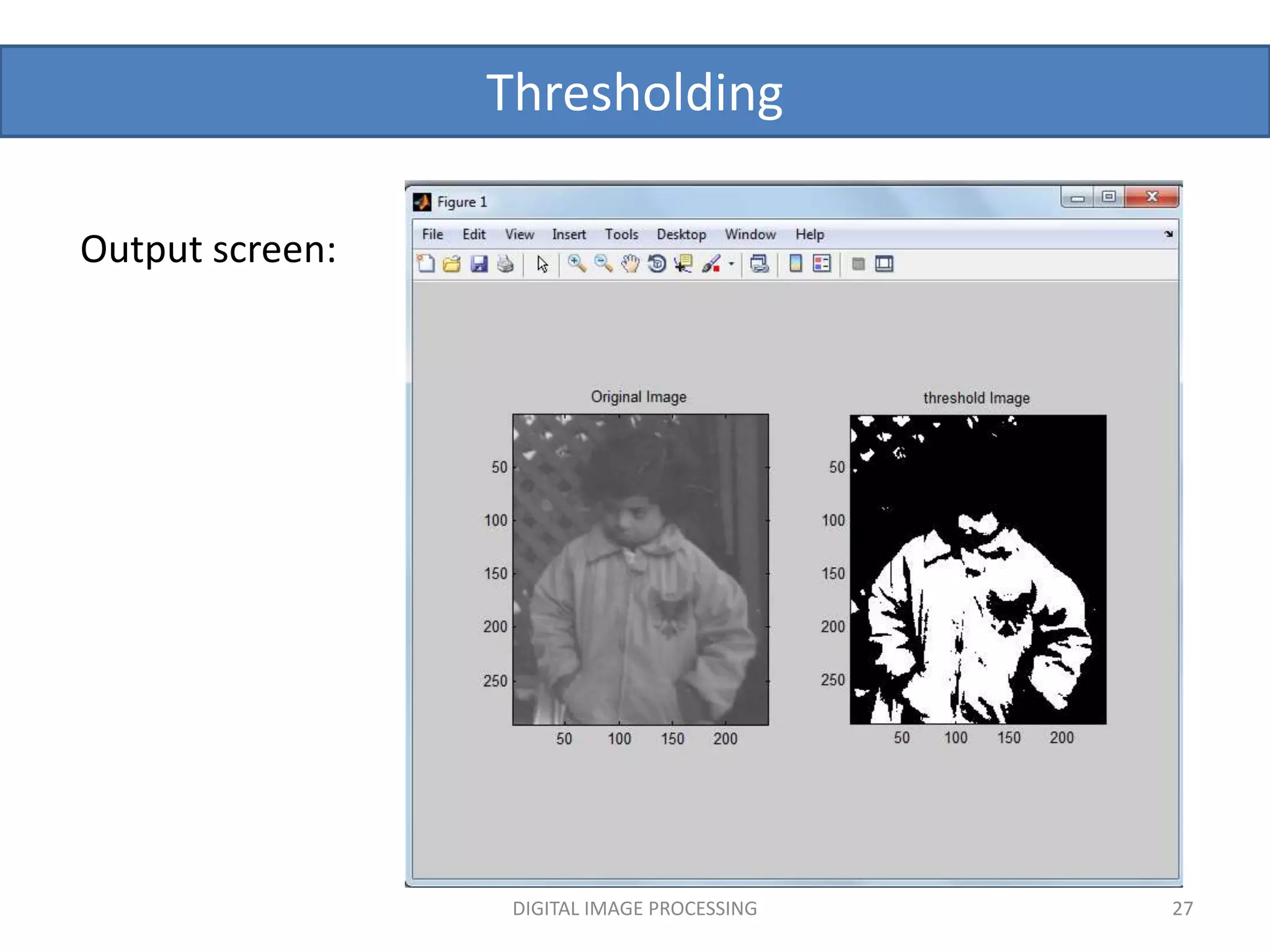
![Thresholding
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING 26
Matlab code: % program for image thresholding
a=imread('pout.tif');
[m,n]=size(a);
for i=1:1:m
for j=1:1:n
if(a(i,j)<125)
b(i,j)=0;%pixel values below 125 are mapped to zero
else
b(i,j)=255;%pixel values equal or above 125 are mapped to 255
end
end
end
subplot(1,2,1),subimage(a),title('Original Image');
subplot(1,2,2),subimage(b),title('threshold Image');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement1-220905201325-0d205779/75/image-enhancement-pptx-26-2048.jpg)

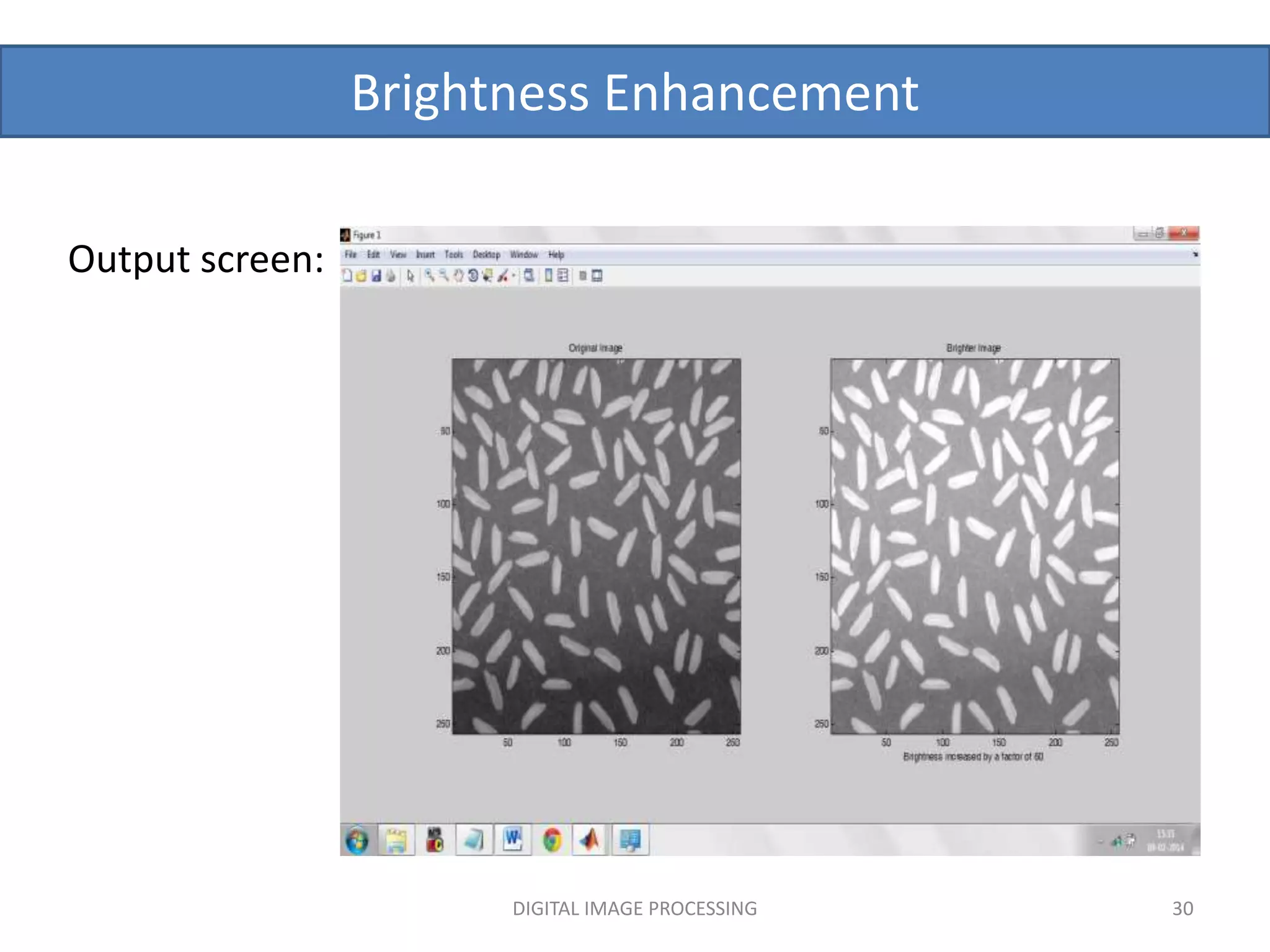
![Brightness Enhancement
Matlab code : % program to increase the brightness of an image
x=input('Enter the factor which brightness should be increased');
a=imread('clown.png');
[m,n]=size(a);
for i=1:1:m
for j=1:1:n
b(i,j)=a(i,j)+x;
end
end
subplot(1,2,1),subimage(a),title('Original Image');
subplot(1,2,2),subimage(b),title('Brighter
Image'),xlabel(sprintf('Brightness increased by a factor of %g',x));
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement1-220905201325-0d205779/75/image-enhancement-pptx-29-2048.jpg)

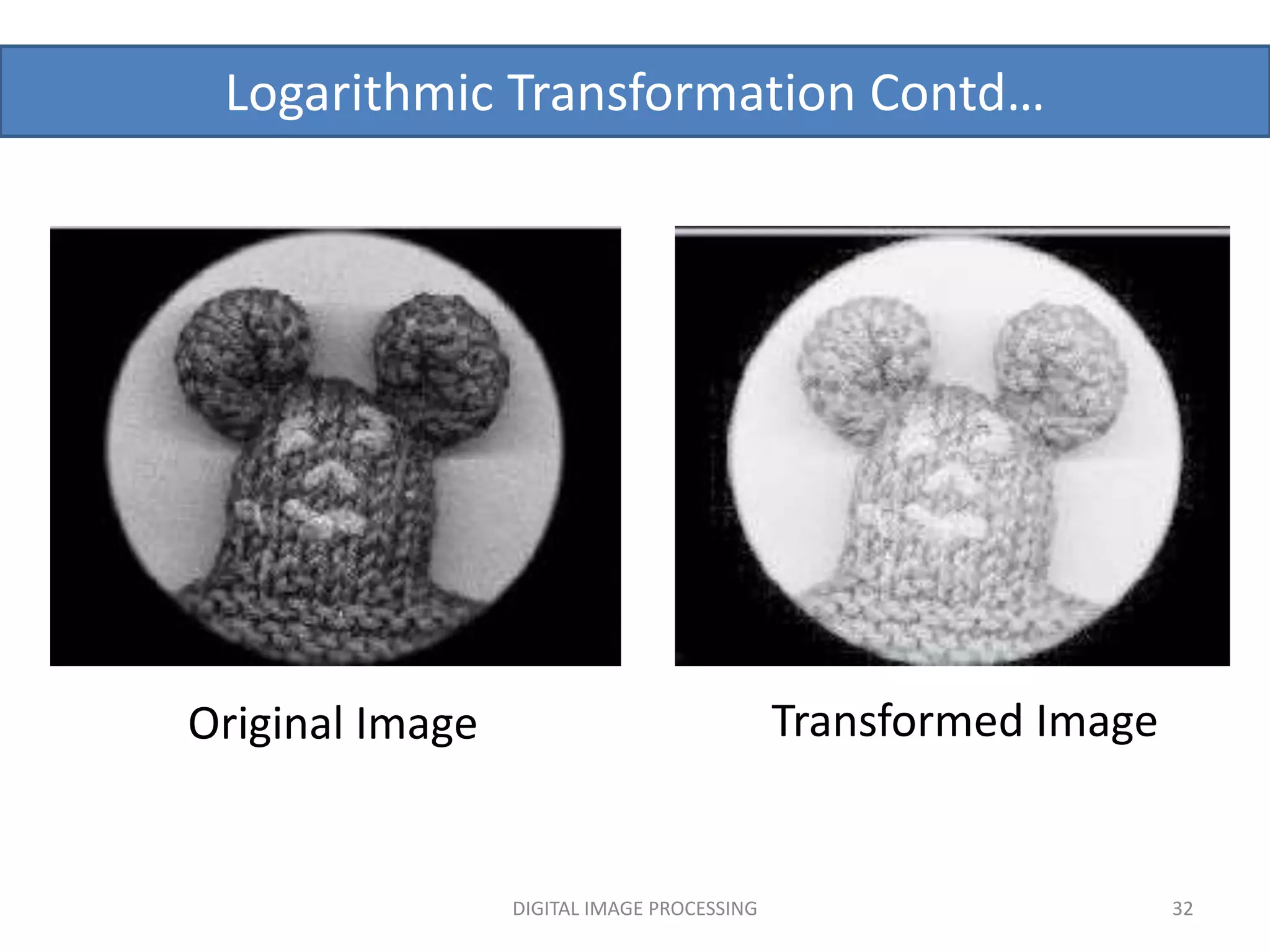
![Log Transformation
Matlab code: % program for image enhancement using logarithmic
transformation
A=input('Enter the value of constant A');
a=imread('clown.jpg');
a=rgb2gray(a);
[m,n]=size(a);
a=double(a);
for i=1:1:m
for j=1:1:n
b(i,j)=A*log(1+a(i,j));
end
end
figure,subplot(1,2,1),subimage(uint8(a)),title('Original Image');
subplot(1,2,2),subimage(uint8(b)),title('Image after logarithmic
transformation'),xlabel(sprintf('Constant is %g',A));
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement1-220905201325-0d205779/75/image-enhancement-pptx-33-2048.jpg)




![Power Law Transformation
Matlab code:
% program for image enhancement using power law
A=input('Enter the value of constant A');
x=input('Enter the value of power x');
a=imread('clown.png');
[m,n]=size(a);
for i=1:1:m
for j=1:1:n
b(i,j)=A*(a(i,j)^x);
end
end
subplot(1,2,1),subimage(a),title('Original Image');
subplot(1,2,2),subimage(b),title('Image after power law
transformation'),xlabel(sprintf('Constant is %gnPower is
%g',A,x));
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancement1-220905201325-0d205779/75/image-enhancement-pptx-38-2048.jpg)


