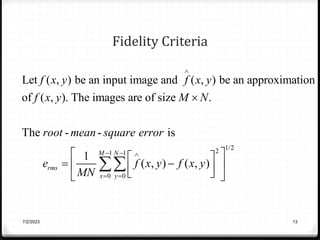
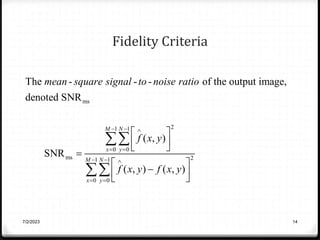
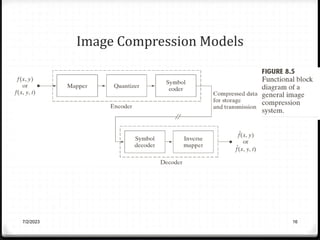
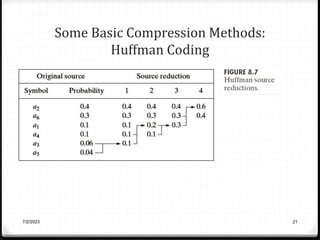
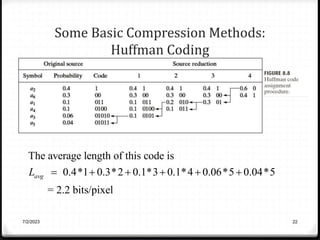
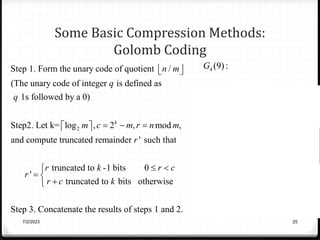
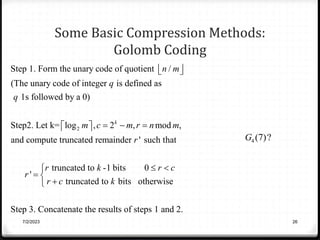
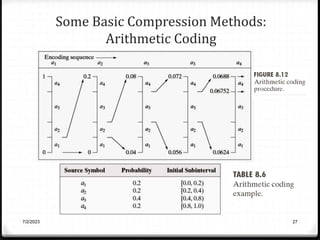
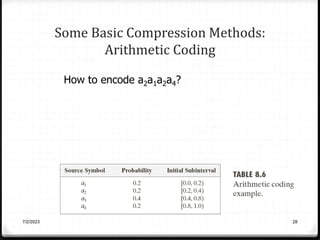
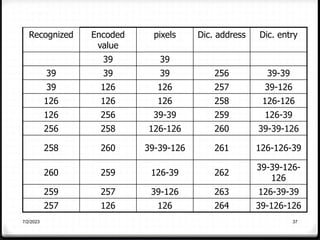
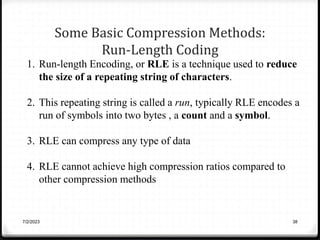
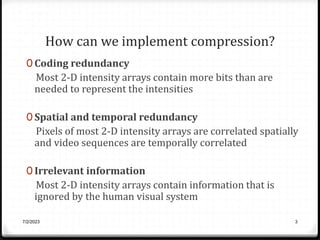
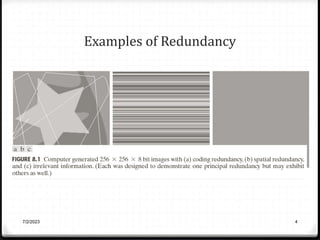
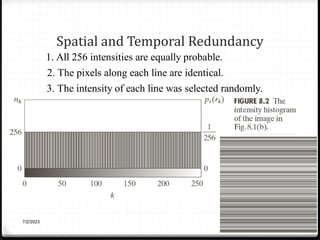
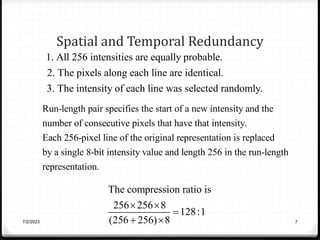
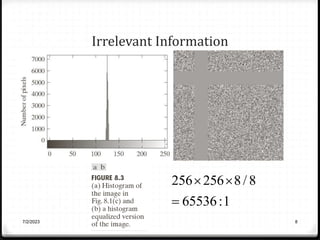
Relative data redundancy (R) is defined as 1 - 1/C, where C is the compression ratio defined as the original number of bits (b) divided by the compressed number of bits (b'). R indicates the percentage of redundant data in the original representation. Common sources of redundancy in images include coding redundancy from correlated pixel intensities, spatial redundancy between neighboring pixels, temporal redundancy between video frames, and irrelevant visual information ignored by the human eye. Popular lossless compression methods like Huffman coding, Golomb coding, LZW, run-length coding, and arithmetic coding aim to remove these redundancies to compress data in a lossless manner.



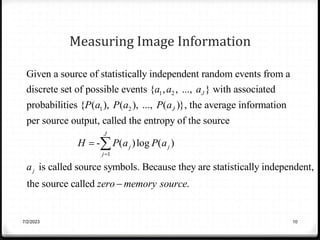
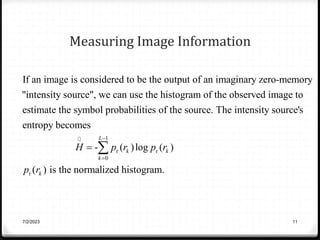
![Measuring Image Information
2 2 2 2
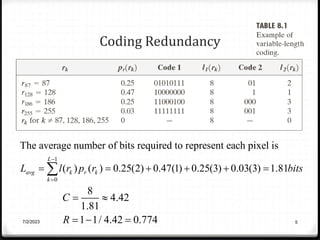
For the fig.8.1(a),
[0.25log 0.25 0.47log 0.47 0.25log 0.25 0.03log 0.03]
1.6614 bits/pixel
H
7/2/2023 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect18compression1-230702161628-6fb98c1a/85/Image-compression1-ppt-12-320.jpg)