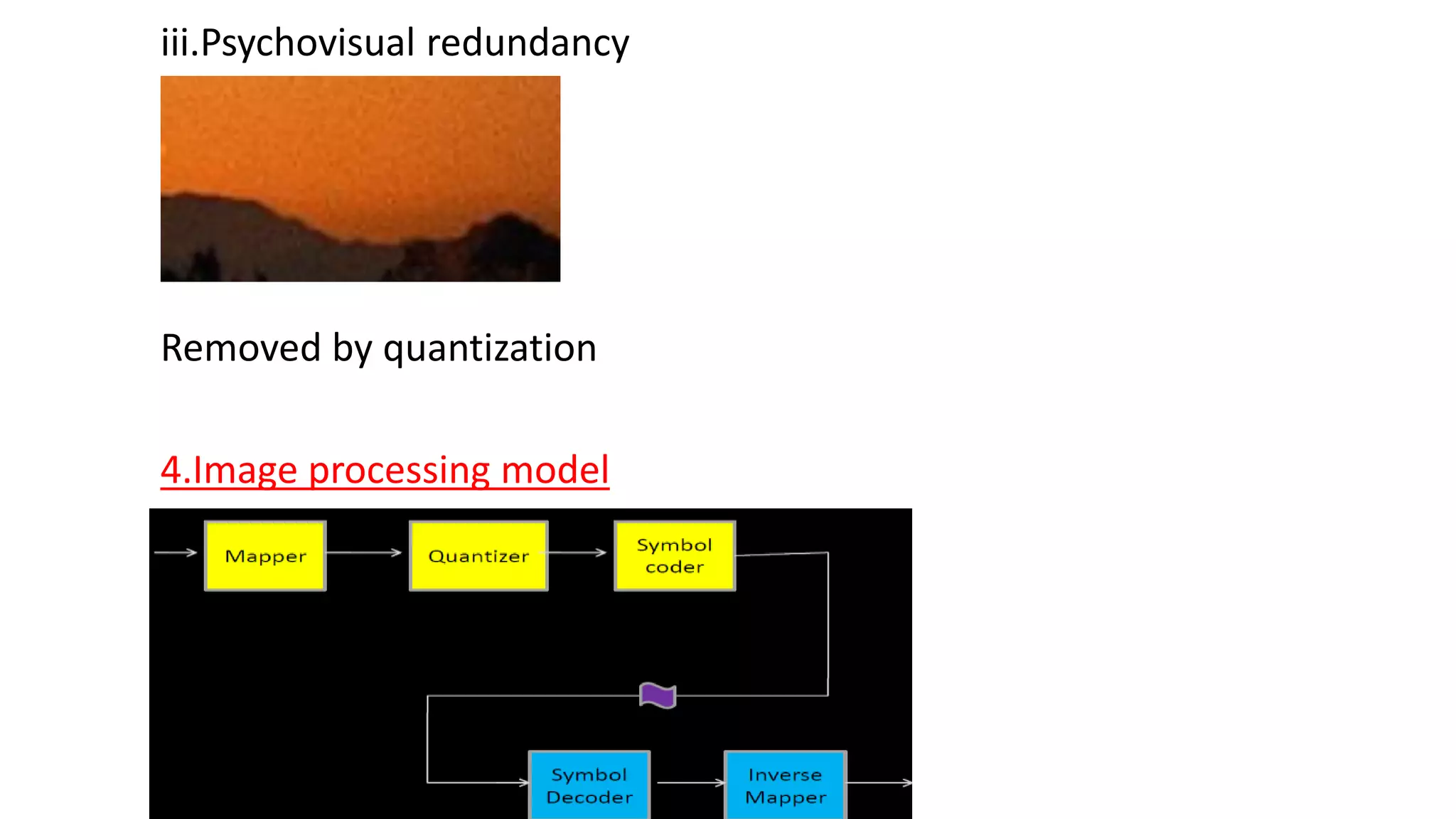
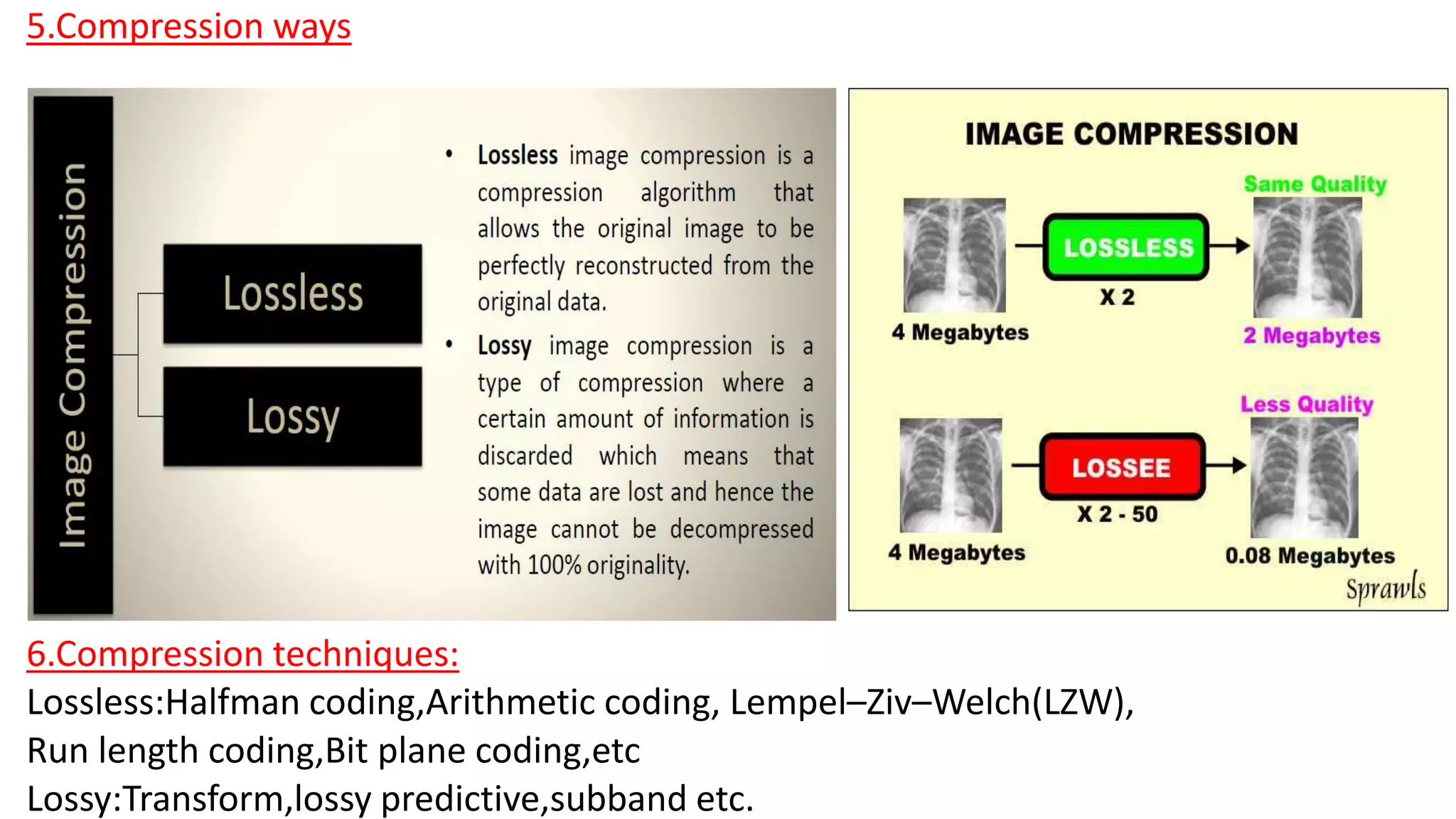
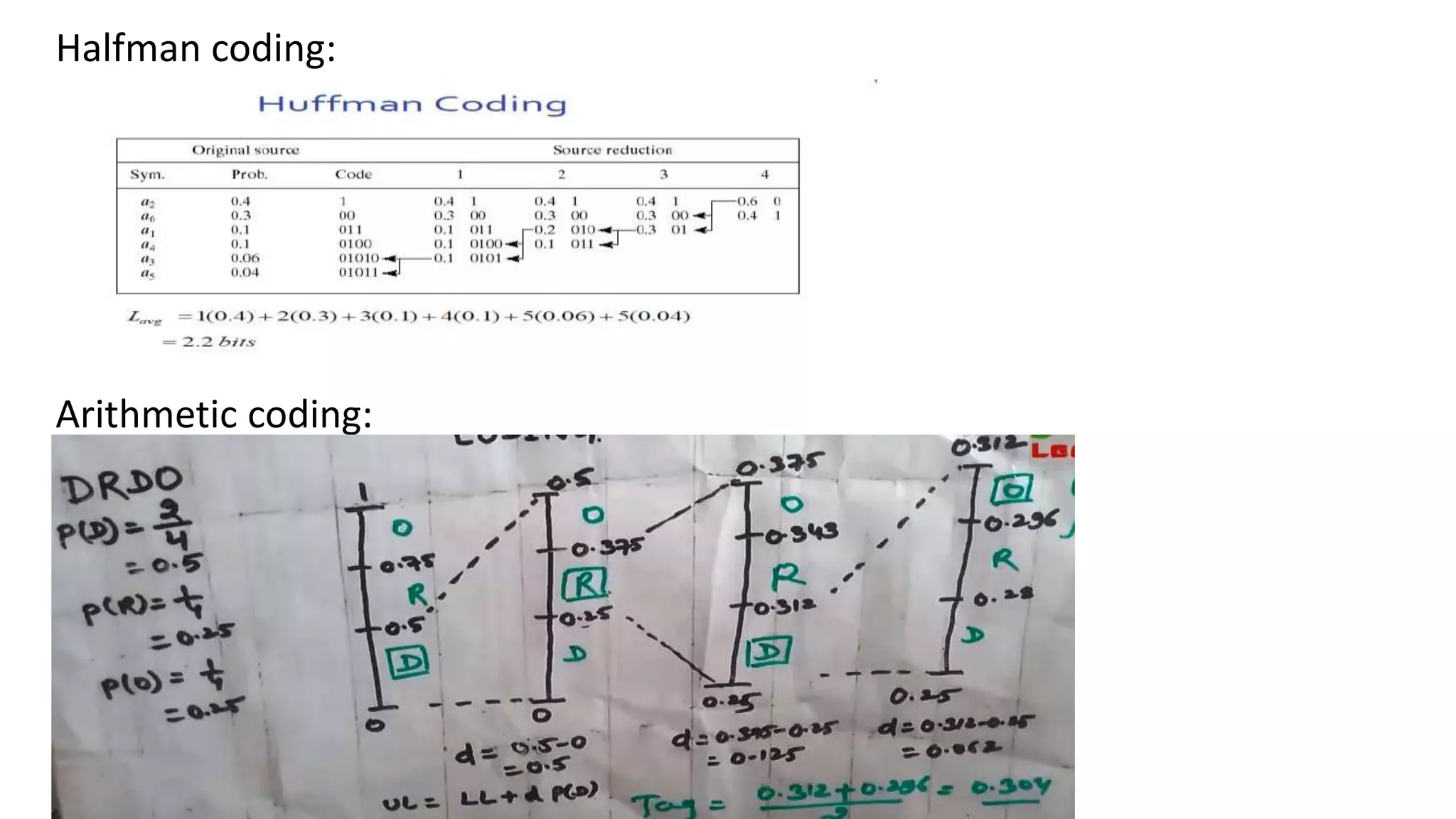
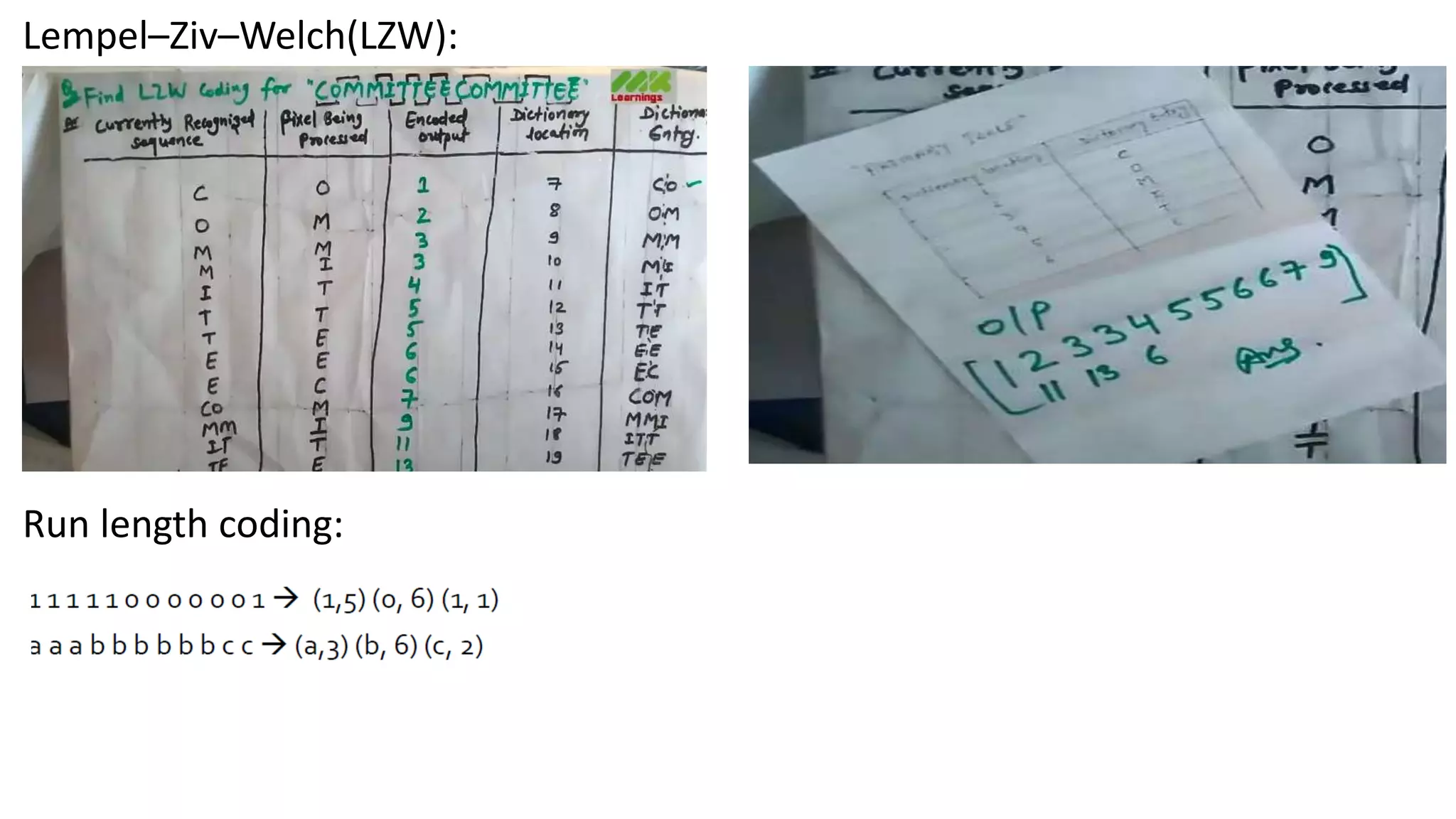
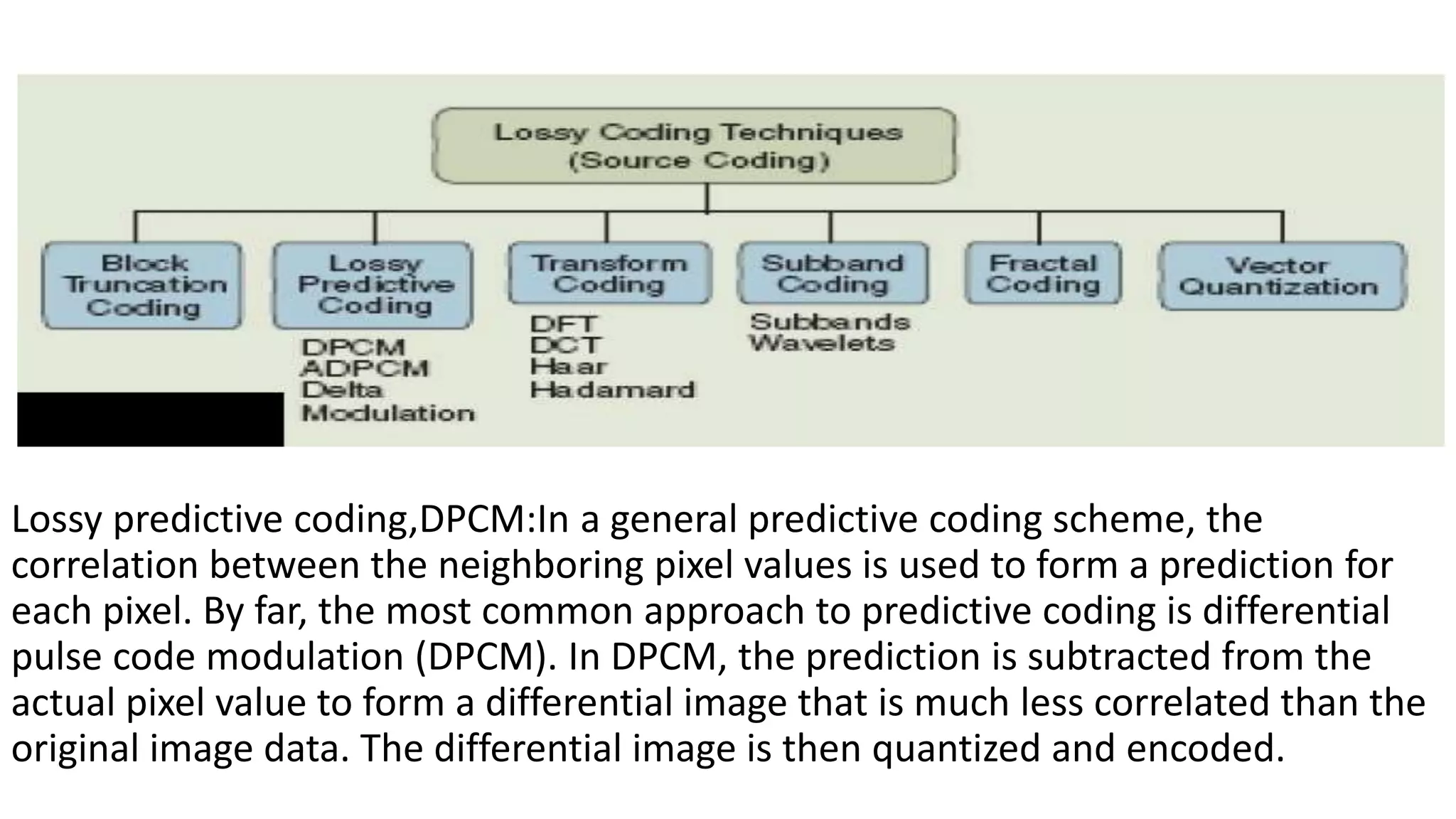
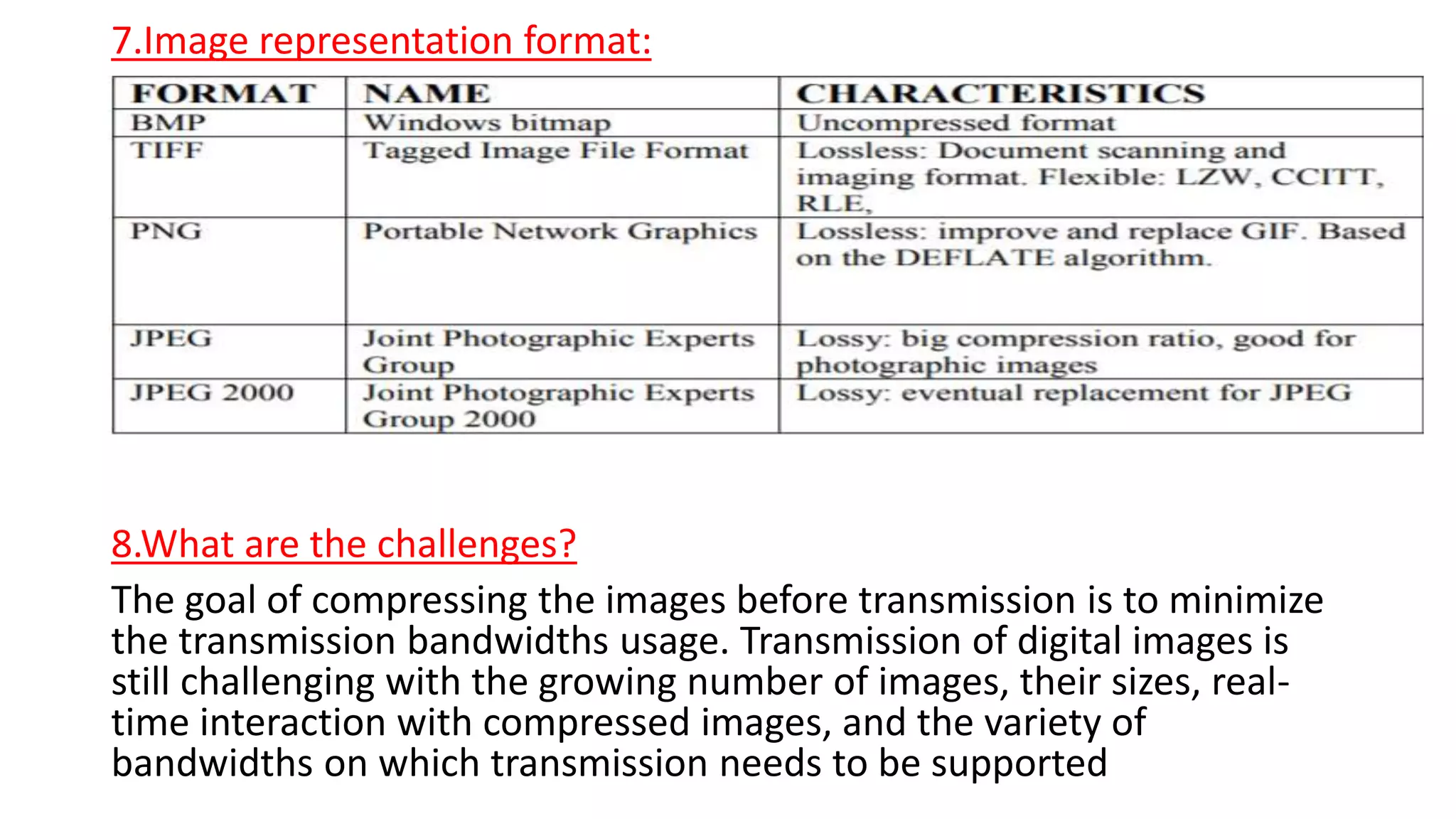
The document discusses image compression techniques. It begins by defining image compression as reducing irrelevant and redundant image data into an efficient form. It then describes the objectives of image compression and the basic problems it aims to address, such as removing different types of redundancy from images. The document outlines several common image compression models and techniques, including lossless techniques like run length encoding and lossy techniques like discrete cosine transform. It concludes by noting that image compression techniques help optimize limited resources like storage and bandwidth.