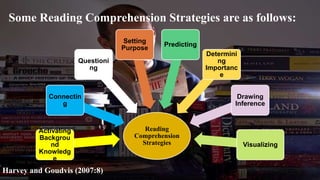
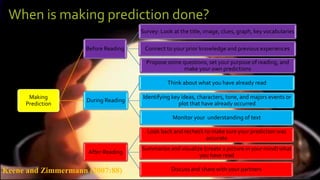
This document discusses reading strategies for making predictions to improve reading comprehension. It explains that making predictions allows readers to think ahead and engage more with a text by guessing what may happen based on clues. The document provides examples of predicting different objects and characters. It also presents a "fix-up chart" strategy where readers preview a text, set a purpose, connect to prior knowledge, make predictions, monitor comprehension, and make inferences while reading. The strategy is demonstrated by predicting the content of an article about Malaysia saying Cadbury products are free from pork.