The document discusses blended learning and the integration of web technologies into language teaching. It defines blended learning as combining online and offline instruction. Blended learning provides benefits for both students and faculty by offering flexibility and active learning opportunities. However, a shift is needed from a teacher-centered approach to a more student-centered one that fosters autonomy and takes advantage of web tools. Constructivism, connectivism, and Web 2.0 can support this shift by emphasizing social and informal learning.




















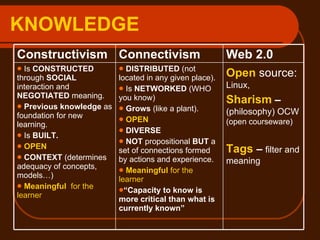


![Some conclusion: “ The nature of Web 2.0 tools make it more likely (…) [that] learners can also find ways of enhancing their learning, too. (…) The nature of the learning environments that most people inhabit – four physical walls (…) – and the enormous possibilities that Web 2.0 tools offer to both teachers and learners, make it inevitable that learning blends will be a feature of the language learning and more general educational landscape in the coming years. [this] will also inevitably have an impact on pedagogical processes (…) and potentially (…) on the ways that humans learn and learn languages in particular. From: http://www.swinburne.edu.au/hosting/ijets/journal/V7N2/pdf/Article2-Motteram&Sharma.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ilash-1-091011000006-phpapp02/85/Ilash-1-24-320.jpg)