The future advanced testing technology workshop will be held in Tokyo, Japan, on November 1st-2nd, 2024, focusing on advancements in AI and testing technology, including discussions on AI general intelligence, trust, sustainability, and human-centered AI. Presenters from notable institutions will address topics such as responsible AI, machine learning testing challenges, and the integration of generative AI in software development. The document highlights the need for interdisciplinary collaboration and ethical considerations in AI development and the evolving landscape of software engineering due to AI advancements.





![HCAI, TAI and XAI
7
[Chamola+23] V. Chamola, et al., A Review of Trustworthy and Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI), IEEE Access, 11, 2023
• Responsible AI (RAI)
development, bringing to
the table issues including
but not limited to
fairness, explainability,
and privacy in AI, and
centering AI around
humans [Tahael+23]
Trustworthy AI (TAI) aspects [Chamola+23]
Explainable AI (XAI) approaches [EChamola+23]
[Tahael+23] M. Tahael, et al.., A Systematic Literature Review of Human-Centered, Ethical, and Responsible AI, arXiv:2302.05284v3, 2023
Human-centered AI
(HCAI) [Tahael+23]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-7-320.jpg)
![[Chamola+23] V. Chamola, et al., A Review of Trustworthy and Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI), IEEE Access, 11, 2023
[Noyori+23] Y. Noyori, H. Washizaki, et al., “Deep learning and gradient-based extraction of bug report features related to bug fixing time,” Frontiers in Computer Science, 5, 2023
XAI approaches and more
• XAI approaches in autonomous systems
[Chamola+23]
– Explanation and interpretations of DL models
– Observation-to-action guideline
– Causal inferences in/out of interpretations
– Goal-based forecasting
– Purpose/objective identification
• Technical and social reliability of
explanations
– E.g., fake explanation by surrogate models
and examples
• Counterfactual explanations
– What should be different in the input
instance to change the outcome [Guidotti24]
– Needs to consider constraint of ensuring the
existence of reasonable actions for as many
instances as possible [Kanamori+24]
8
[Guidotti24] Riccardo Guidotti, Counterfactual explanations and how to find them: literature review and benchmarking, Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 38, 2024
[Kanamori+24] K. Kanamori, et al., Learning Decision Trees and Forests with Algorithmic Recourse, ICML 2024
using 19990914 build on
win98 … with the same server
the problem was with … to figure
out what the actual bug …
Short bug-fixing-time Long bug-fixing-time
[Noyori+23]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-8-320.jpg)
![Knowledge Area
Topic Topic
Reference
Material
Body of Knowledge Skills Competencies Jobs / Roles
SWEBOK
Software Engineering Professional Certifications
SWECOM
EITBOK
Learning courses
9
Guide to the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge (SWEBOK) [Washizaki24]
https://www.computer.org/education/bodies-of-knowledge/software-engineering
• Guiding researchers and practitioners to identify and have
common understanding on “generally-accepted-knowledge”
in software engineering
• Foundations for certifications and educational curriculum
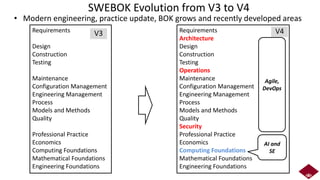
• ‘01 v1, ‘04 v2, ‘05 ISO adoption, ‘14 v3, ’24 v4 just published!
[Washizaki24] H. Washizaki, eds., Guide to the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge (SWEBOK Guide), Version 4.0, IEEE Computer Society, 2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-9-320.jpg)

![Metamodel
ML
evaluation
Visualizing issues
ML
evaluation
Visualizing resolution
OK
OK OK
Failed Failed
OK OK
OK
O
K
OK OK OK
[ML.VP1🡨
AI.VP1]
Providereliable
real-timeobject
detectionsystem
fordriving
decisionmakingin
highway(incl.
trafficsign
detectionand
lane/vehicle
detection)
• [ML.DS1]Procured
datasets
• [ML.DS2]Internal
databasefrom
collectionduring
operation
• [ML.DC1]Openand
commercialdatasets
• [ML.DC2]Data
collectedduring
operation(imageand
identificationresult)
•[ML.F1🡨
AI.D1/AI.D3]
Boundingbox
forobject(incl.
othervehicles
orsigns)
•[ML.F2🡨
AI.D2]Ridge
detectionfor
lanedetection
[ML.BM1]
Modelswillbe
developed,
tested,and
deployedtocars
monthly
• [ML.PT1]Input:
imagefromsensors
• [ML.PT2←AI.D]
Output:trafficsigns,
lanemarking,
vehicles,and
pedestrians.
[ML.De1]Use
predictionresults
fordecision-
makinginself-
drivingsystem
[ML.IS1]
Usingtestdata,
achieveveryhigh
recallandhigh
precisionin
followingcondition:
night,rainy,and
generalcondition
Datasetsissplitinto
80:20ratio
[ML.MP1]
Predictionshould
bemadein
batchesreal
time.
[ML.M1]Inputdatamonitoring
[ML.VP1🡨
AI.VP1]
Providereliable
real-timeobject
detectionsystem
fordriving
decisionmakingin
highway(incl.
trafficsign
detectionand
lane/vehicle
detection)
• [ML.DS1]Procured
datasets
• [ML.DS2]Internal
databasefrom
collectionduring
operation
• [ML.DC1]Openand
commercialdatasets
• [ML.DC2]Data
collectedduring
operation(imageand
identificationresult)
•[ML.F1🡨
AI.D1/AI.D3]
Boundingbox
forobject(incl.
othervehicles
orsigns)
•[ML.F2🡨
AI.D2]Ridge
detectionfor
lanedetection
[ML.BM1]
Modelswillbe
developed,
tested,and
deployedtocars
monthly
• [ML.PT1]Input:
imagefromsensors
• [ML.PT2←AI.D]
Output:trafficsigns,
lanemarking,
vehicles,and
pedestrians.
[ML.De1]Use
predictionresults
fordecision-
makinginself-
drivingsystem
[ML.IS1]
Usingtestdata,
achieveveryhigh
recallandhigh
precisionin
followingcondition:
night,rainy,and
generalcondition
Datasetsissplitinto
80:20ratio
[ML.MP1]
Predictionshould
bemadein
batchesreal
time.
[ML.M1]Inputdatamonitoring
[ML.VP1🡨
AI.VP1]
Providereliable
real-timeobject
detectionsystem
fordriving
decisionmakingin
highway(incl.
trafficsign
detectionand
lane/vehicle
detection)
•[ML.DS1]Procured
datasets
•[ML.DS2]Internal
databasefrom
collectionduring
operation
•[ML.DC1]Openand
commercialdatasets
•[ML.DC2]Data
collectedduring
operation(imageand
identificationresult)
•[ML.F1🡨
AI.D1/AI.D3]
Boundingbox
forobject(incl.
othervehicles
orsigns)
•[ML.F2🡨
AI.D2]Ridge
detectionfor
lanedetection
[ML.BM1]
Modelswillbe
developed,
tested,and
deployedtocars
monthly
•[ML.PT1]Input:
imagefromsensors
•[ML.PT2←AI.D]
Output:trafficsigns,
lanemarking,
vehicles,and
pedestrians.
[ML.De1]Use
predictionresults
fordecision-
makinginself-
drivingsystem
[ML.IS1]
Usingtestdata,
achieveveryhigh
recallandhigh
precisionin
followingcondition:
night,rainy,and
generalcondition
Datasetsissplitinto
80:20ratio
[ML.MP1]
Predictionshould
bemadein
batchesreal
time.
[ML.M1]Inputdatamonitoring
Adding repair-strategy
ML training
ML repair
SE4AI: System modeling and MLOps integration [Takeuchi+24][Husen+24]
12
[Husen+24] J. H. Husen, H. Washizaki, et al., Integrated Multi-view Modeling for Reliable Machine Learning-Intensive Software Engineering, Software Quality Journal, 32, 2024
[Takeuchi+24] H. Takeuchi, et al., Enterprise Architecture-based Metamodel for Machine Learning Projects and its Management, Future Generation Computer Systems, 2024
Requirements
Construction
Design
Test
Architecture
Operations
Economics
Models and Methods
Quality
Requirements
analysis and design](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-12-320.jpg)

![ML Testing: Approaches and challenges in industry [Rahman+23]
• ML model implementation testing
– Performance-based testing: Sanity
checks, performance against
benchmark/baseline, cross-
model/algorithm/language/platform
testing
– Visualization
– Traditional unit testing and debugging
– Domain knowledge-based validation
• ML code defect detection
– Performance based symptoms
– Training behaviors
– Model output
• Challenges of testing ML applications
– Black-box nature of ML models
– Model’s robustness to errors
– Data quality
– Volatile performance
– Domain expertise
– Cost
– Lack of concrete methodology
– Interpretability, explainability
• Challenges of post-deployment testing
– Test data
– Performance
– Resource requirements
– System complexity
– Platform diversity
– Adaptability
– User satisfaction
14
[Rahman+23] M.S. Rahman, F. Khomh, A. Hamidi, J. Cheng, G. Antoniol, H. Washizaki, “Machine Learning Application Development: Practitioners’ Insights,”
Software Quality Journal, 31, 2023.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-14-320.jpg)
![ML Testing: Topics and approaches
• Bugs & debugging
• Explanations
• Quality testing
• Test architecture & languages
• Test case: Generation &
selection
• Testing metrics
• Testing methods [Sherin+19][Wan+24]
– Metamorphic testing
– Coverage based testing
– Adversarial testing
– Mutation testing
– Symbolic & concolic testing
– Multi-implementation testing
– Evolutionary computing
– Search-based testing
– Fuzzing
– Combinatorial testing
15
[Fernandez+22] S.M. Fernández, et al., Software Engineering for AI-Based Systems: A Survey. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 31(2), 2022
[Wan+24] X. Wan, et al., Coverage-guided fuzzing for deep reinforcement learning systems, JSS, 210, 2024
[Sherin+19] S. Sherin, et al., A Systematic Mapping Study on Testing of Machine Learning Programs, arXiv:1907.09427, 2019
[Fernandez+22]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-15-320.jpg)
![ML Testing: Taxonomy
16
[Song+22] Q. Song, et al., Exploring ML testing in
practice – Lessons learned from an interactive rapid
review with Axis Communications, CAIN 2022
[Zhang+22] J.M. Zhang, et al., Machine
Learning Testing: Survey, Landscapes and
Horizons, TSE, 48(1), 2022](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-16-320.jpg)
![AI/ML for Testing: Topics [Yang+22]
• Bug-related detection
• Bug localization
• Vulnerability detection
• Testing techniques
• Test case generation
• Program analysis
17
[Yang+22] Y. Yang, et al., A Survey on Deep Learning for Software Engineering, ACM Computing Surveys, 54(10), 2022](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-17-320.jpg)

![19
[Wang+24] J. Wang, et al., Software Testing with Large Language Models: Survey,
Landscape, and Vision, TSE, 2024
AI/ML for Testing: LLM for testing [Wang+24]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fattw2024-ai-testing-241104023659-73673d62/85/IEEE-Software-Testing-Technology-Development-Trend-19-320.jpg)
