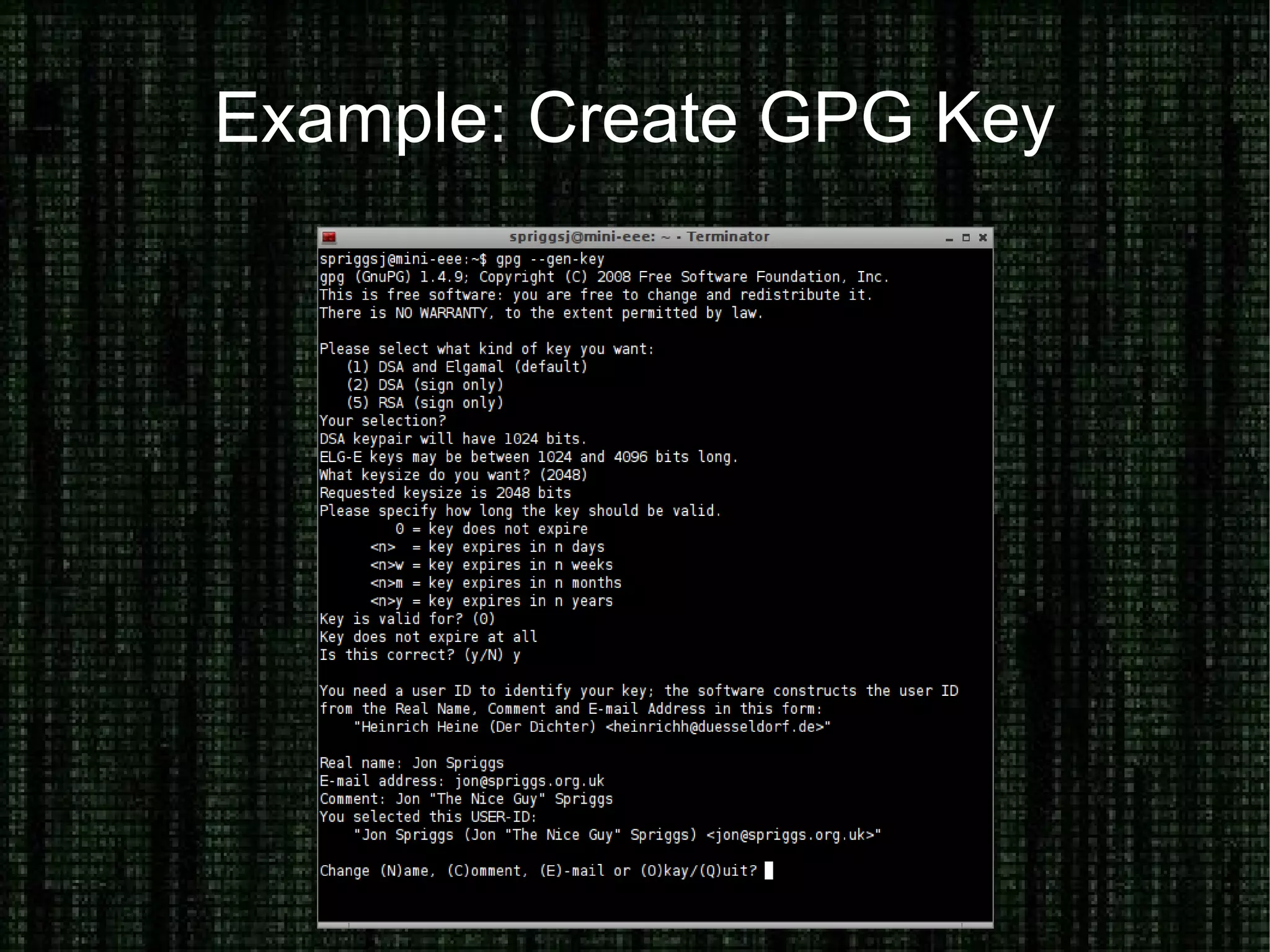
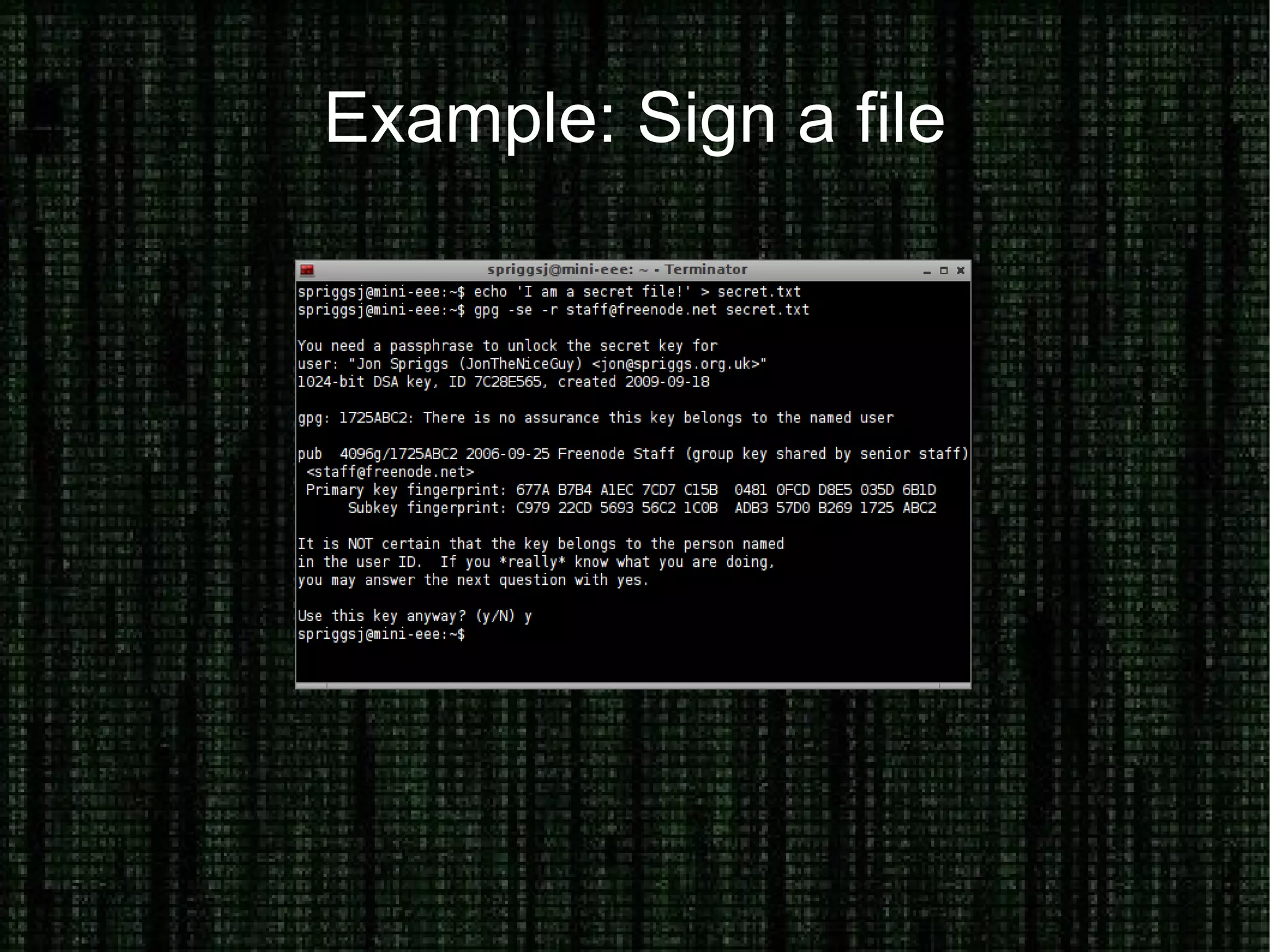
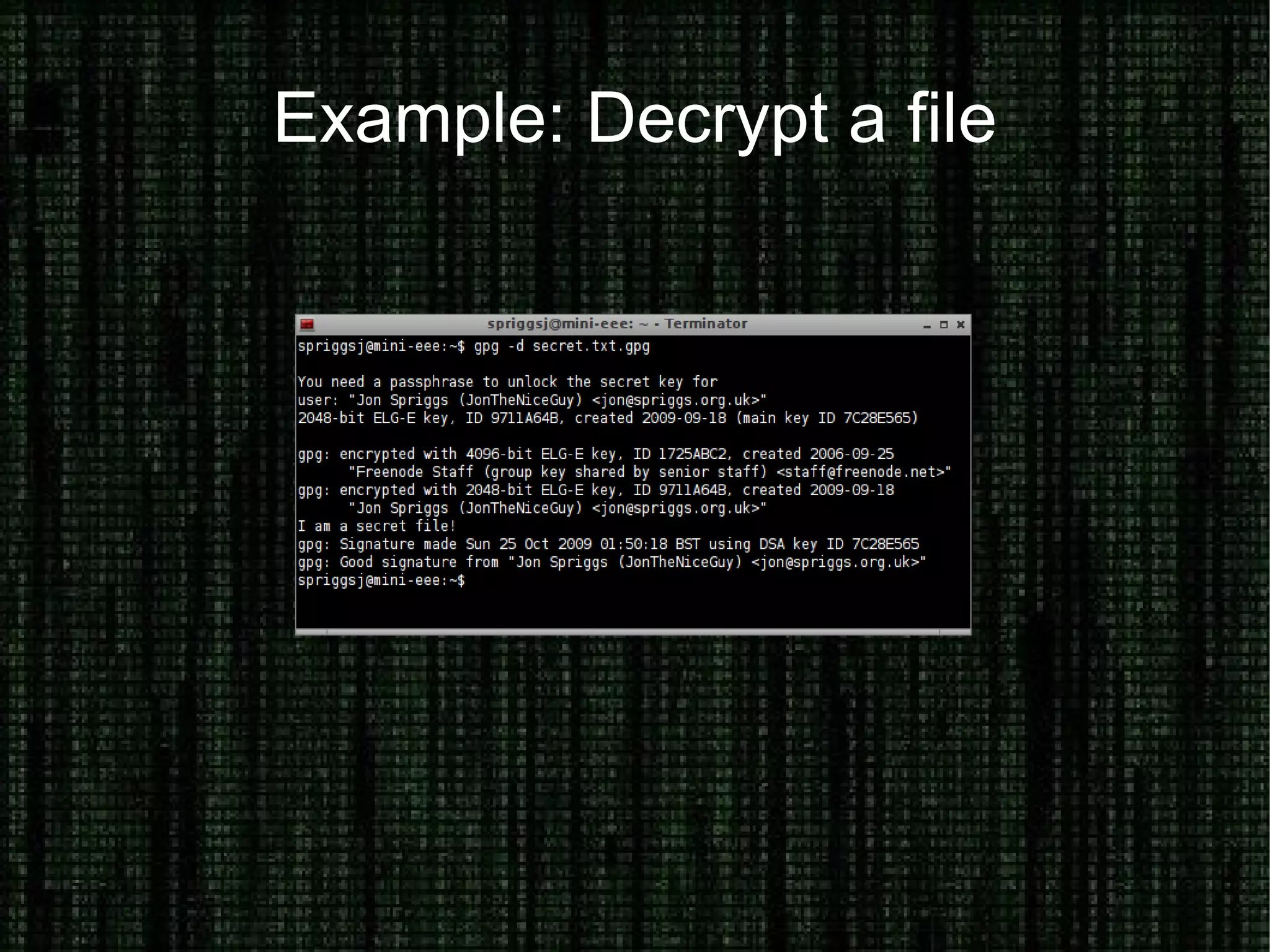
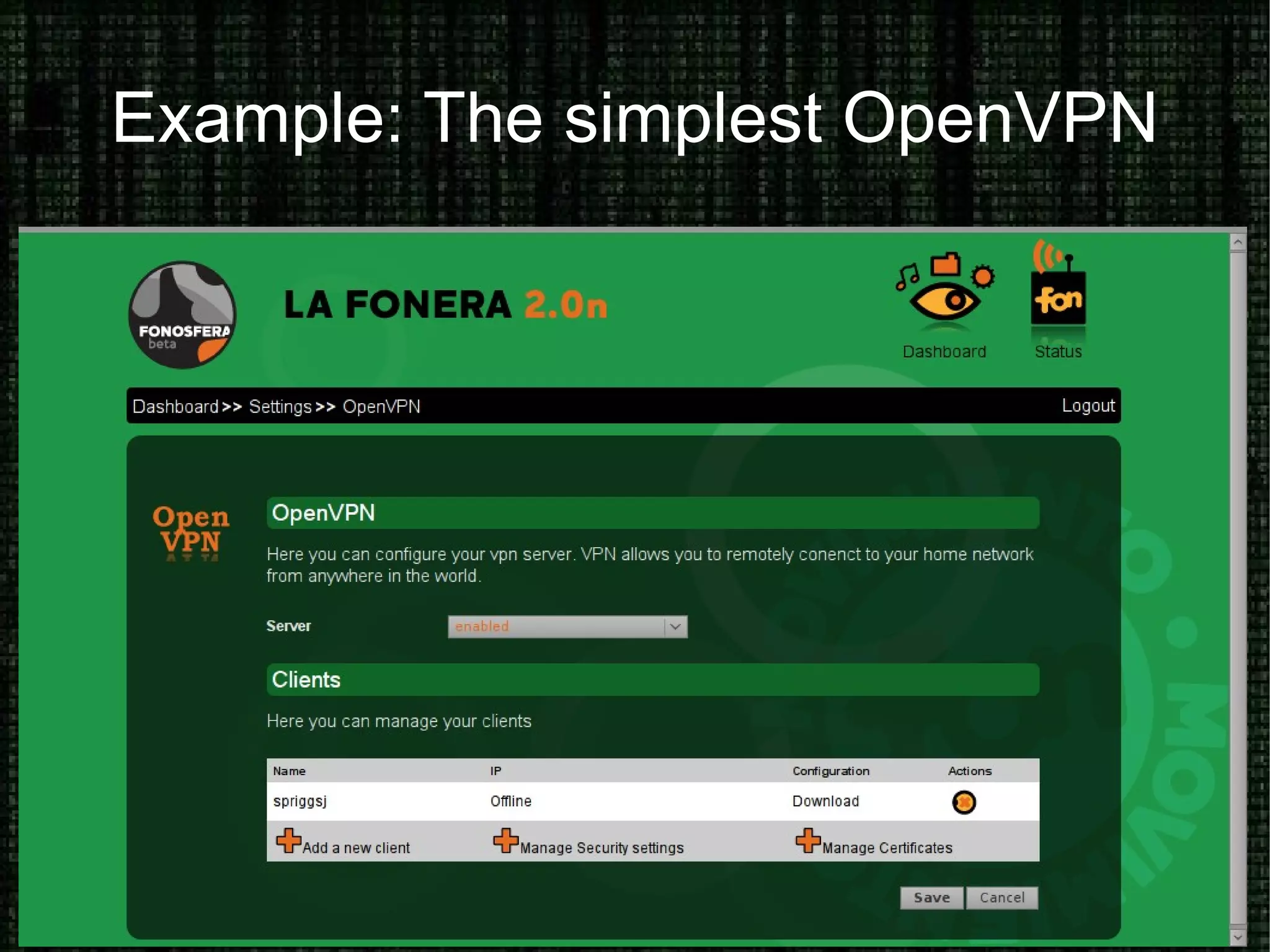
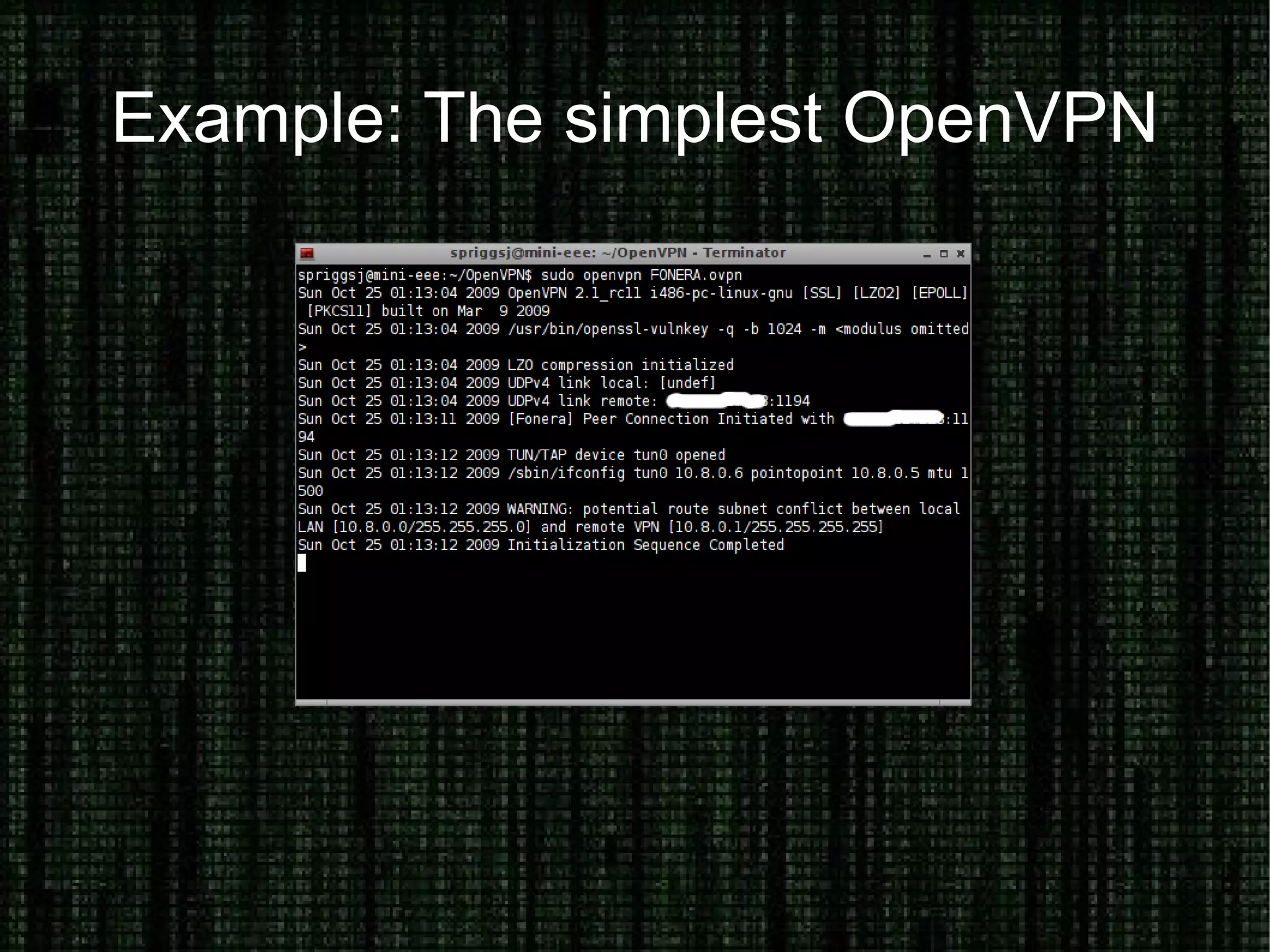
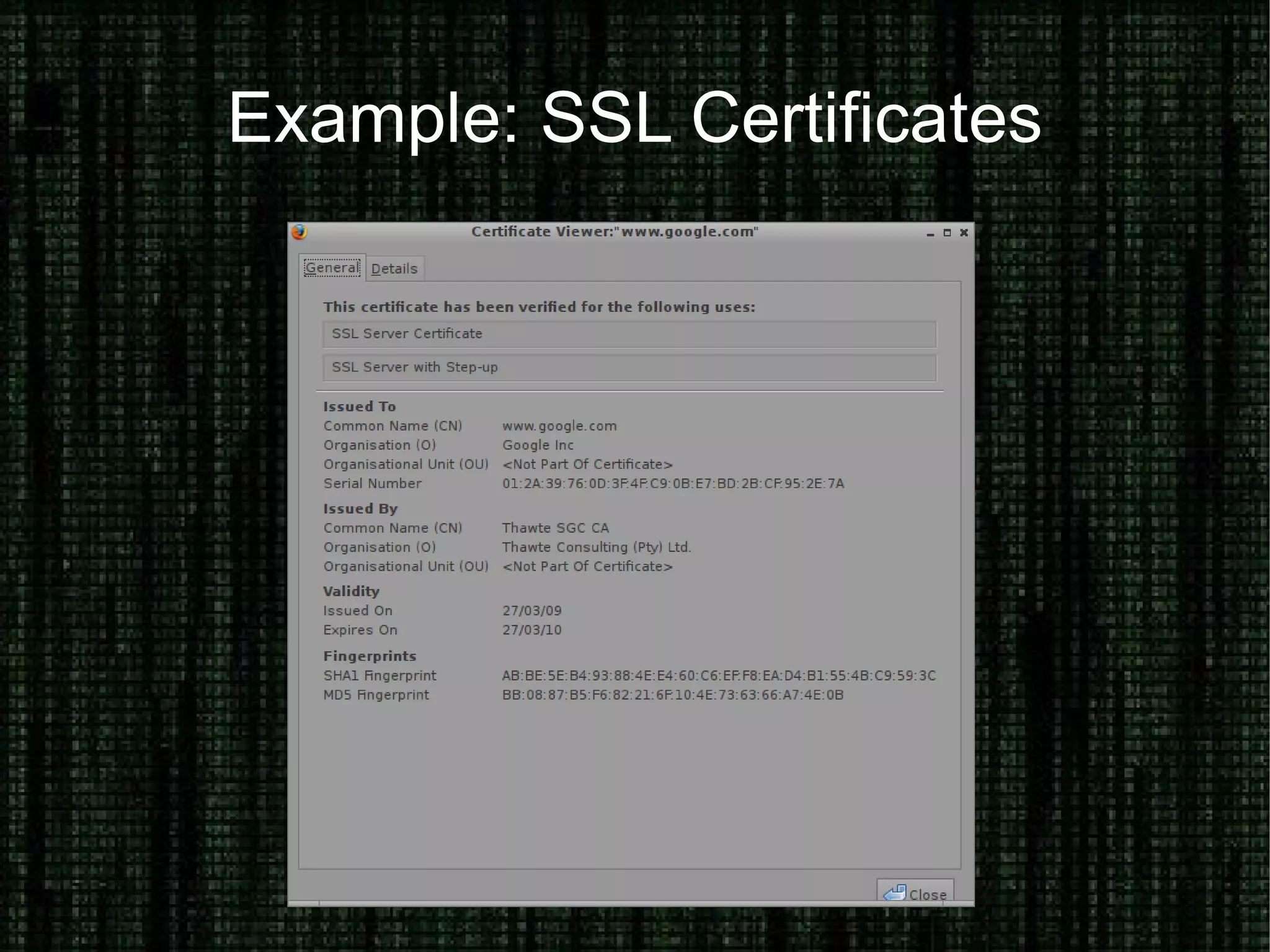
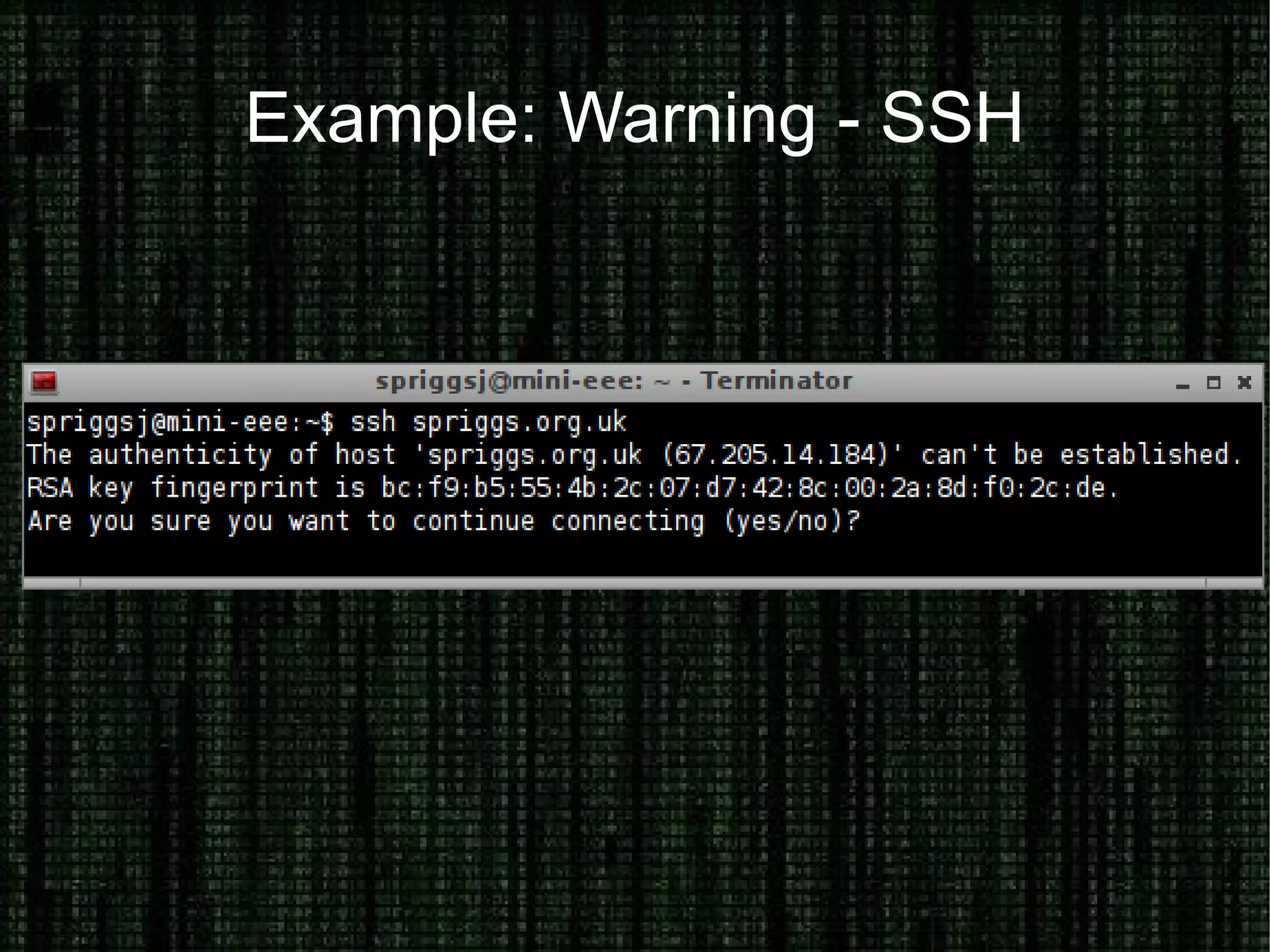
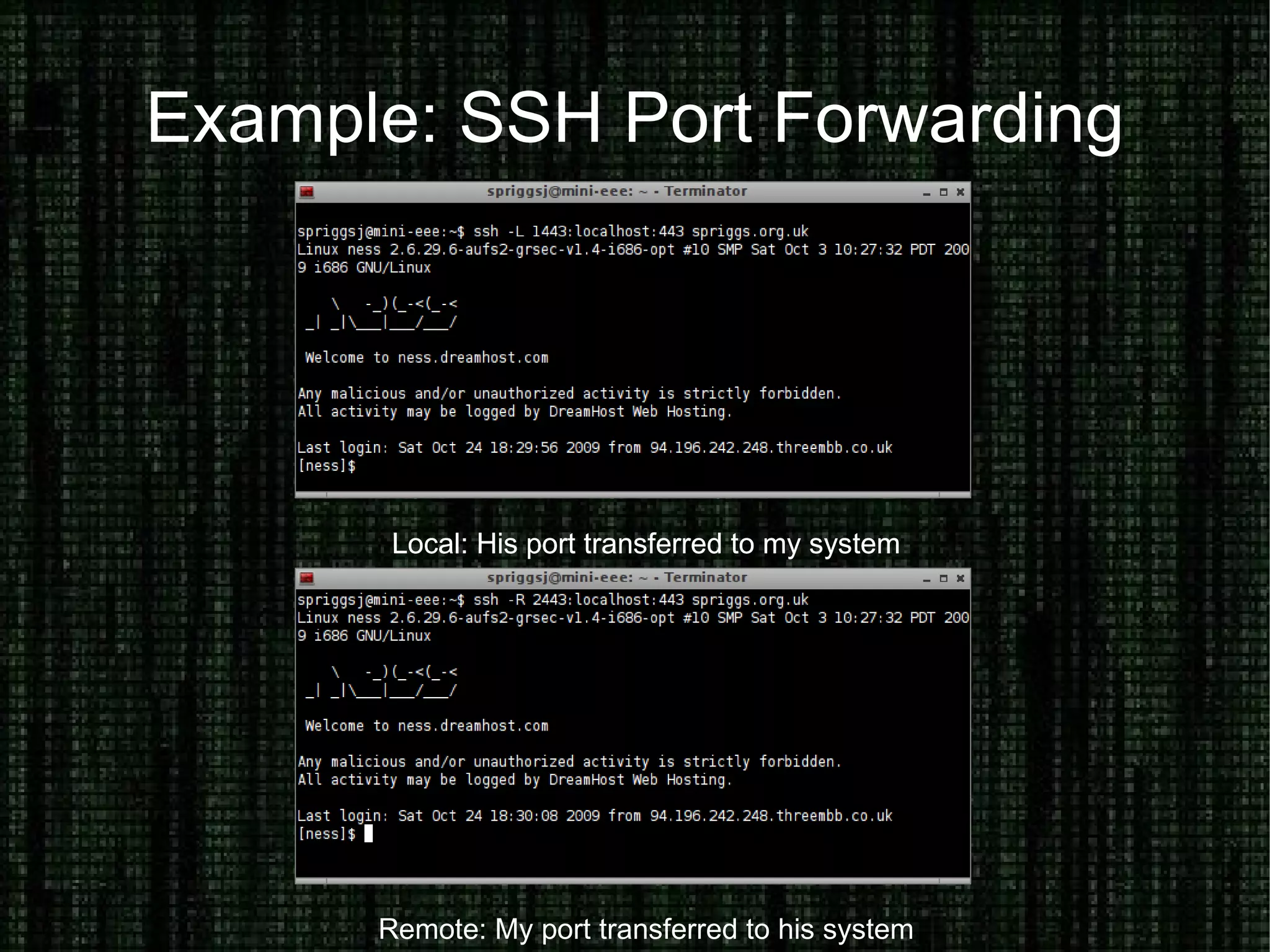
The document provides an overview of how to prove and hide one's identity on the internet, discussing methods like username and authentication for proving identity, while also covering tools such as PGP, VPN, SSL/TLS, and SSH for securing data. It also explains various options for anonymity, including anonymous proxies, tunnels, Tor, and Freenet, while emphasizing the nuances of trustworthiness in these systems. Overall, it aims to equip users with knowledge on enhancing both identity verification and anonymity online.