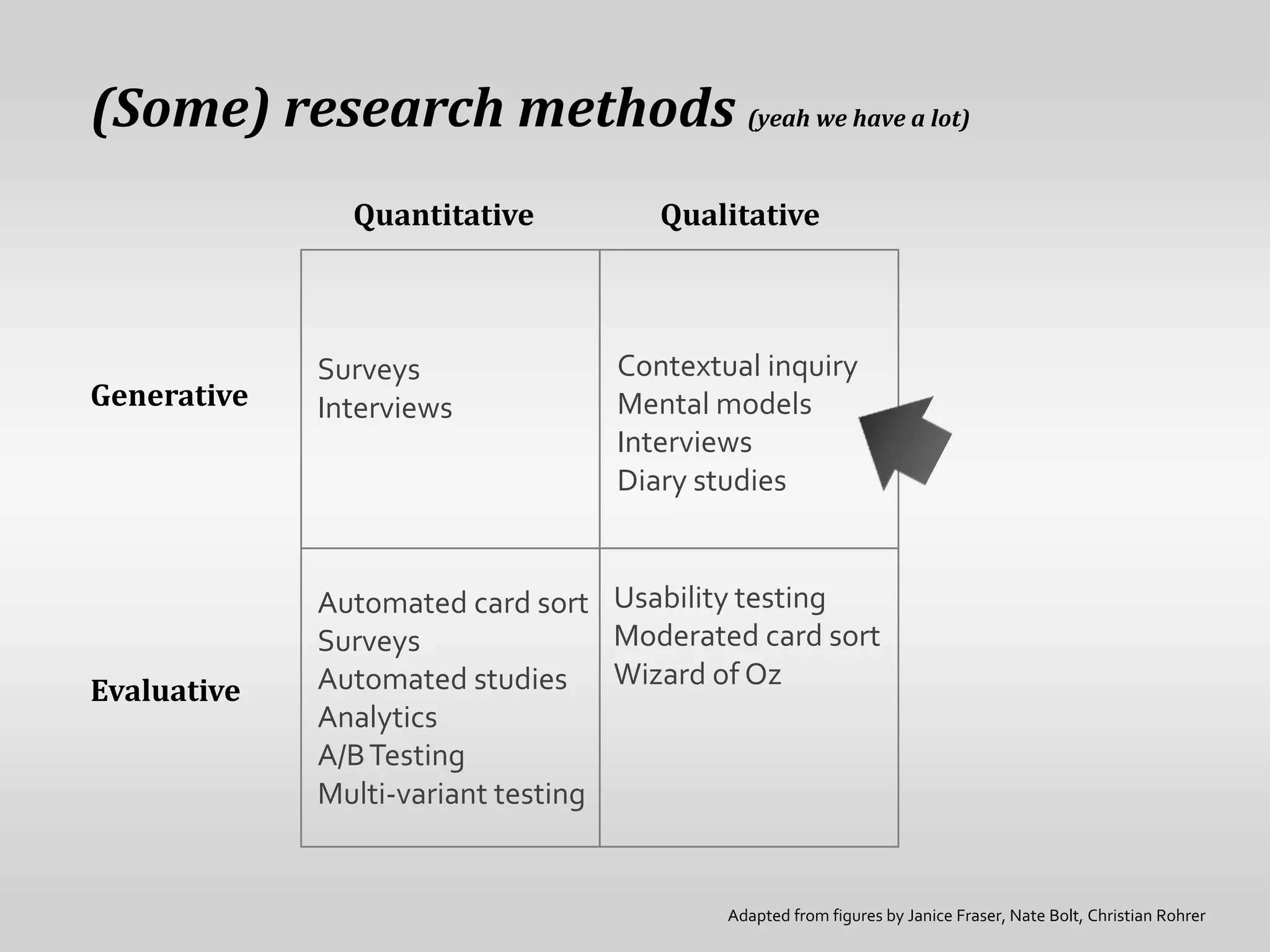
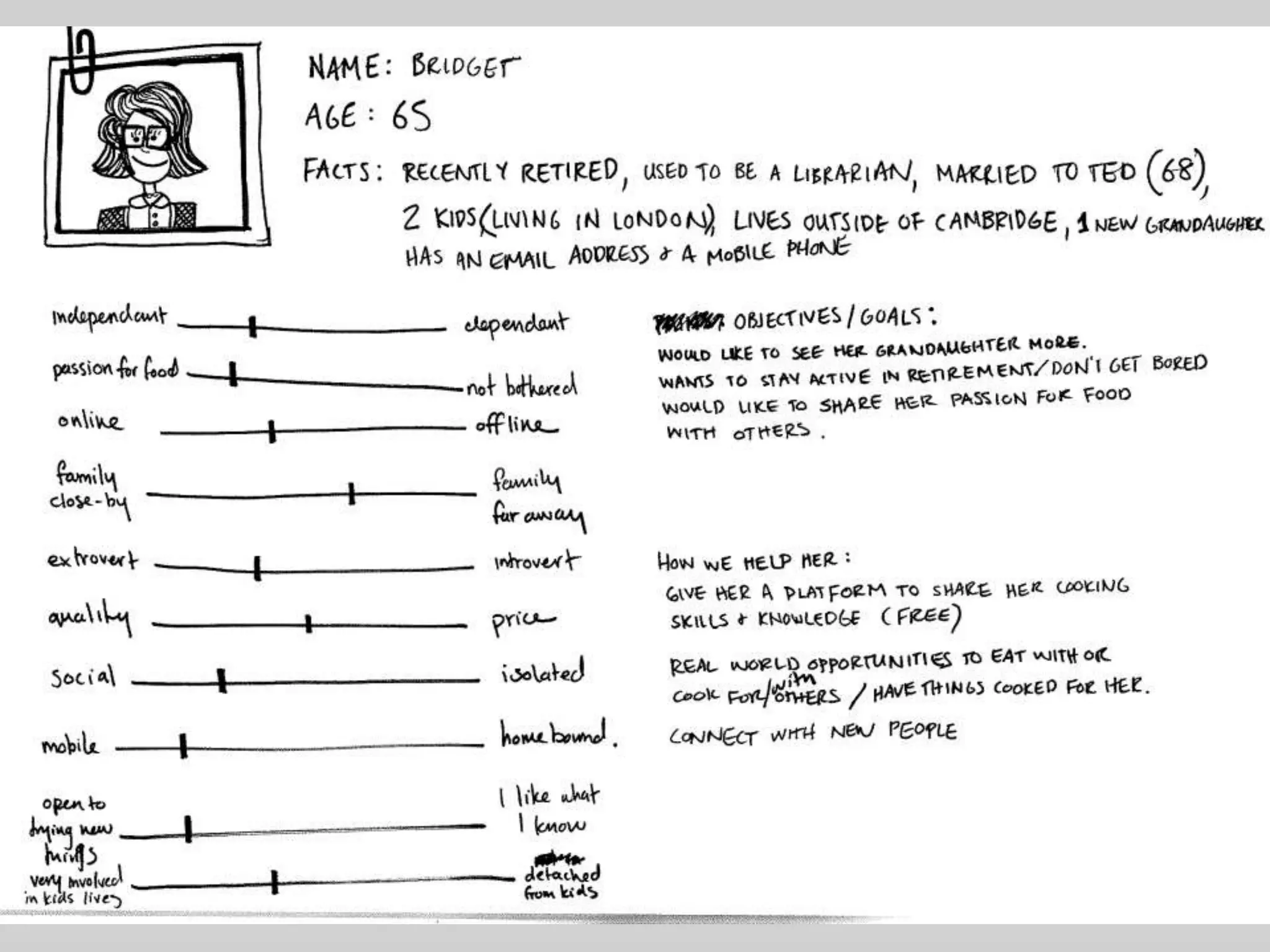
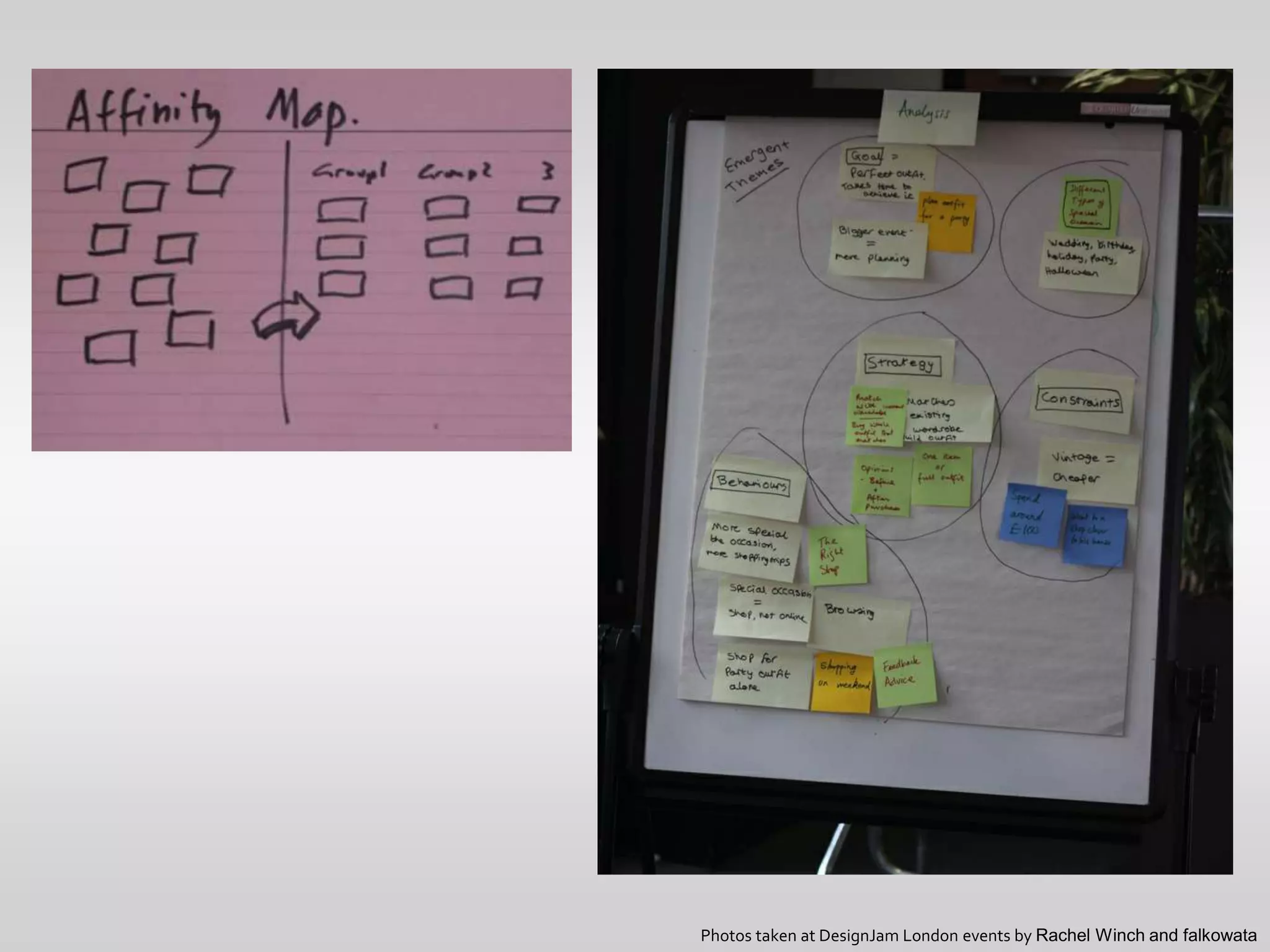
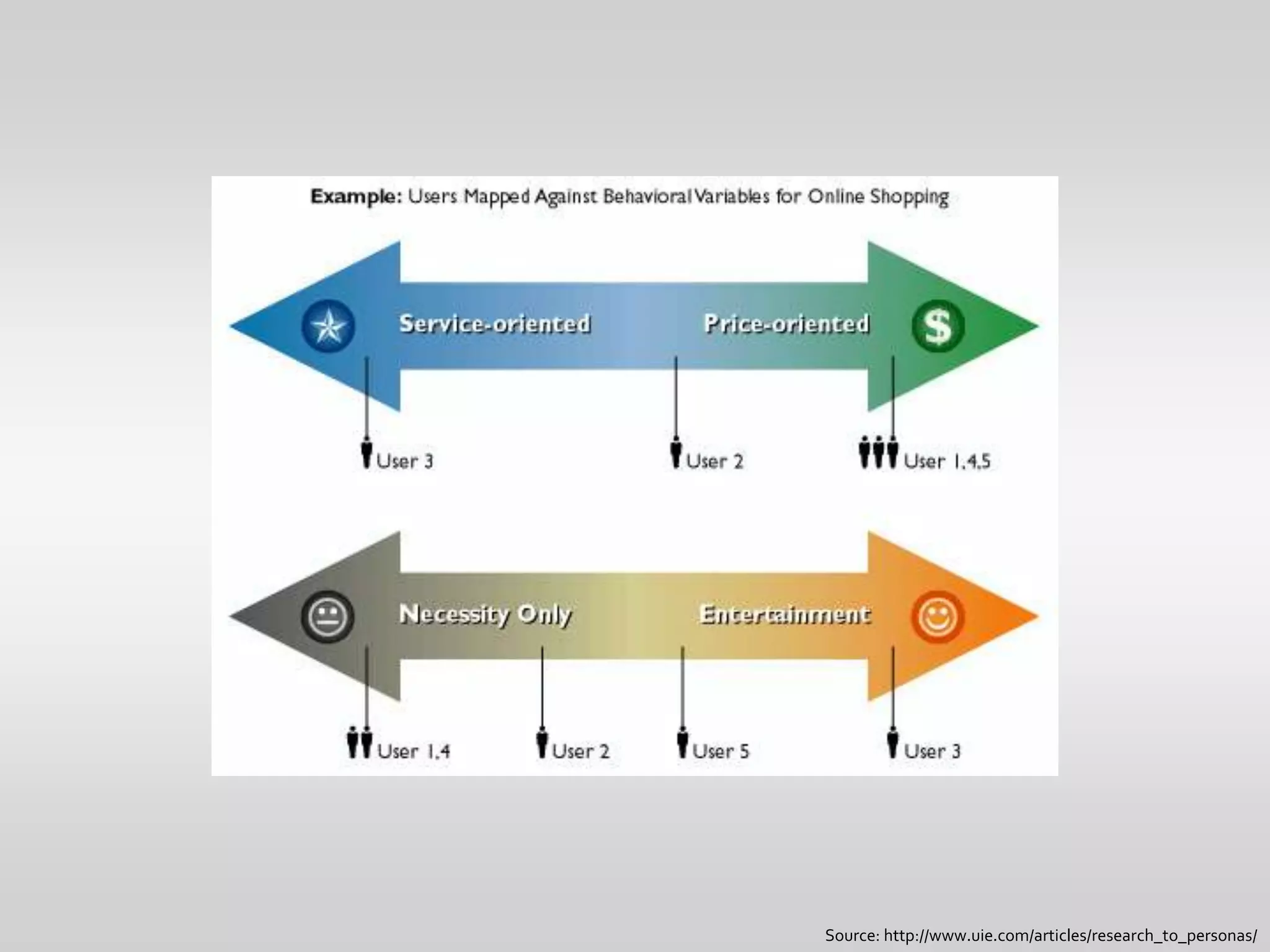
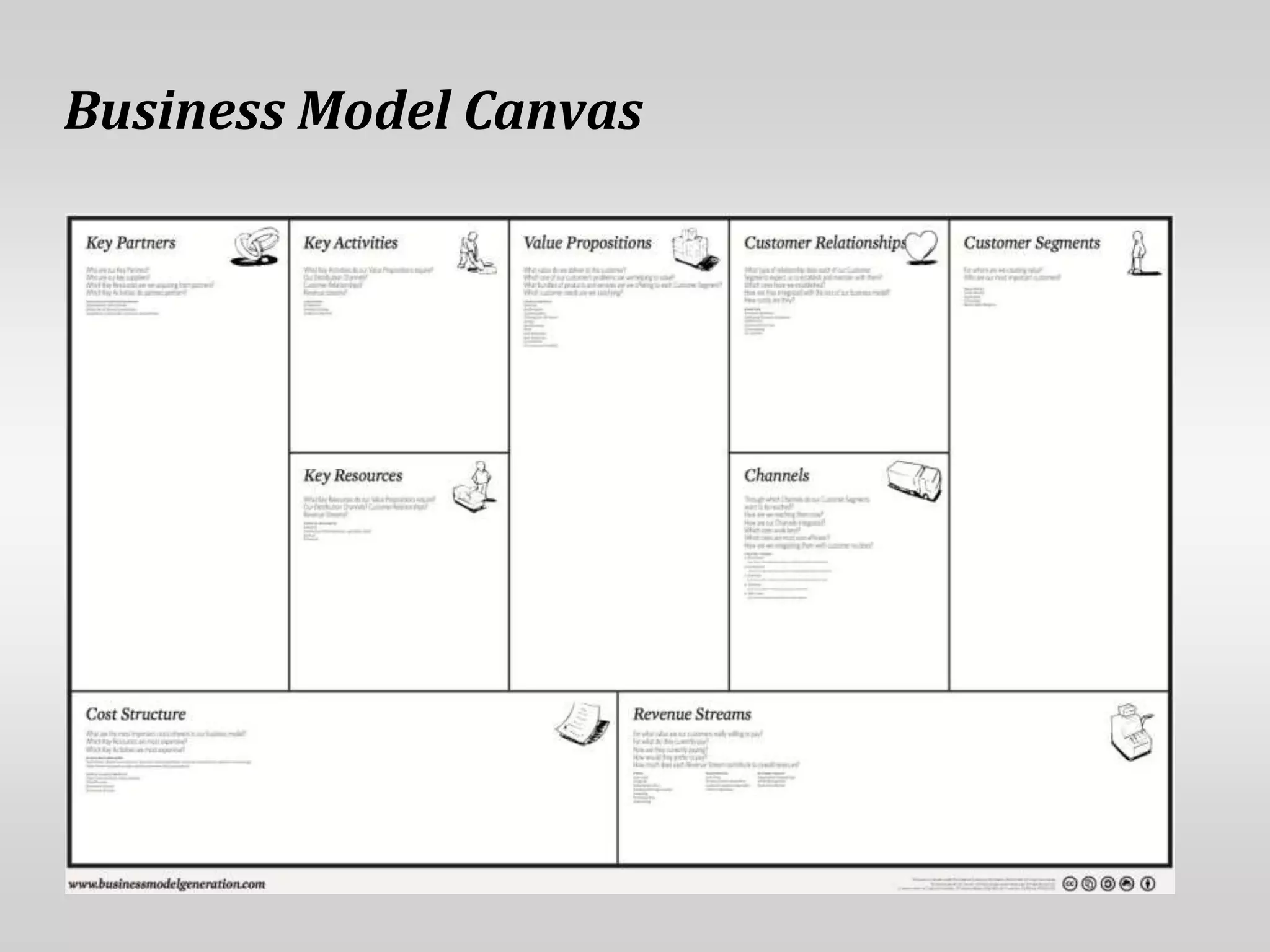
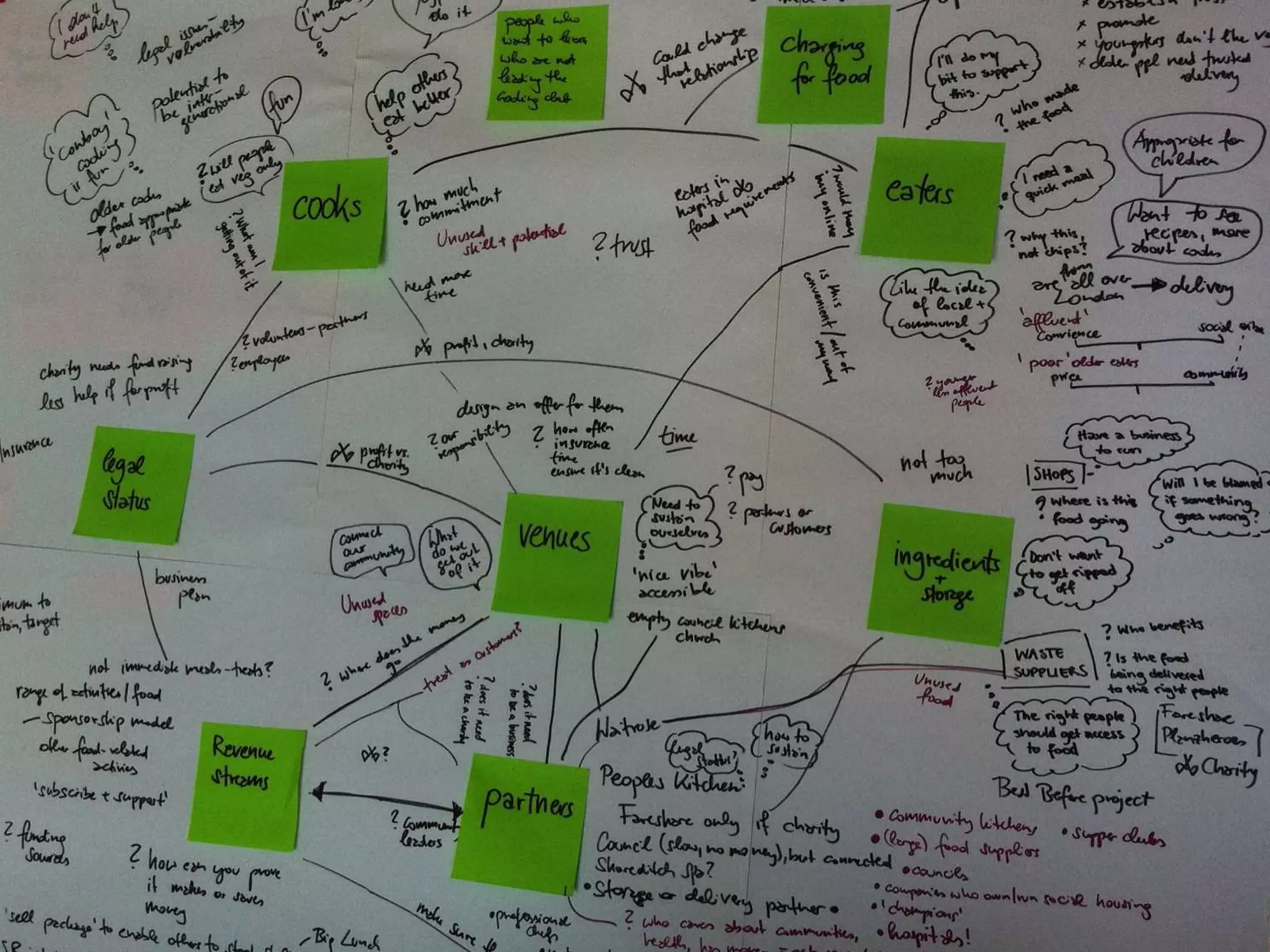
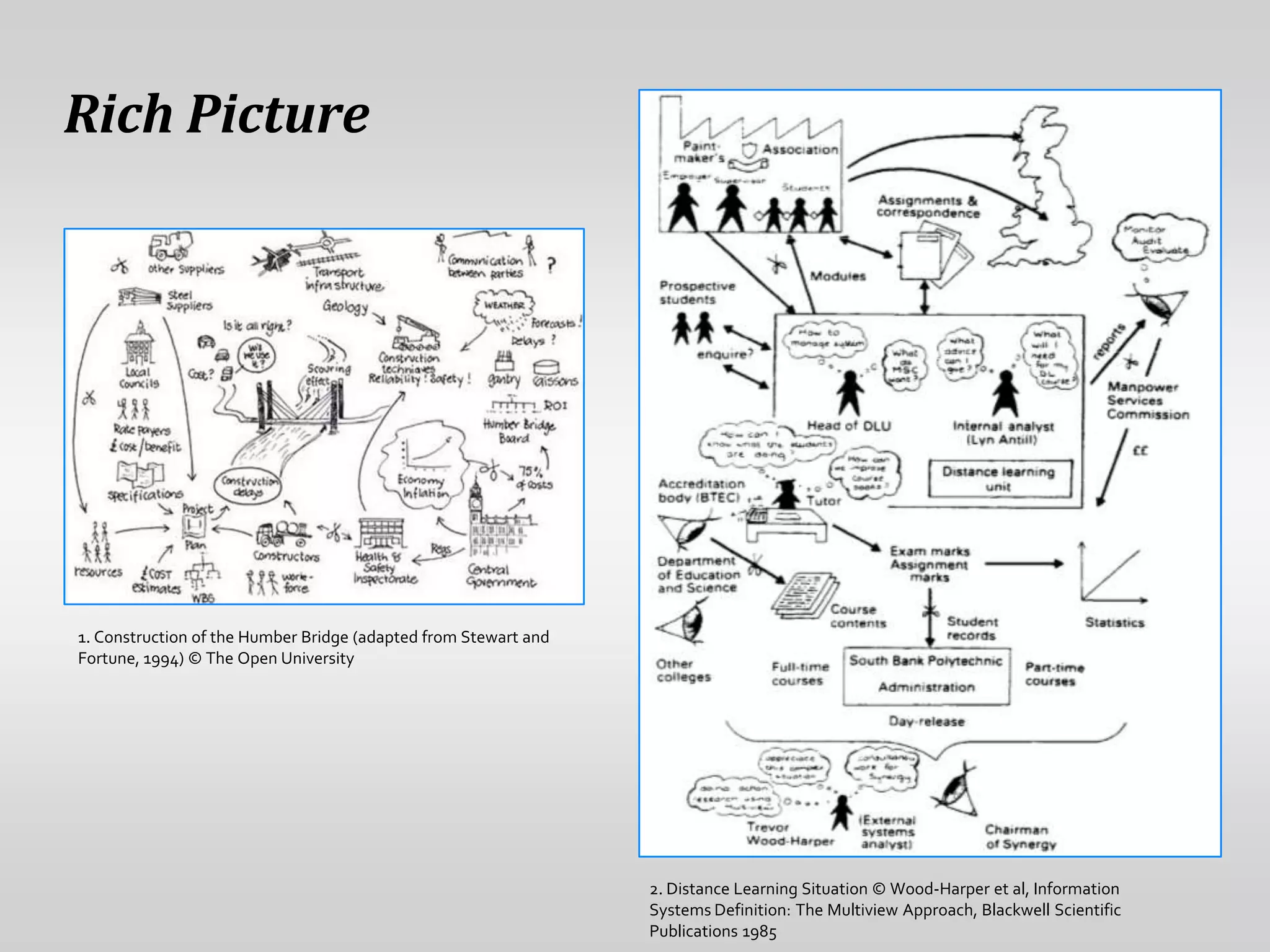
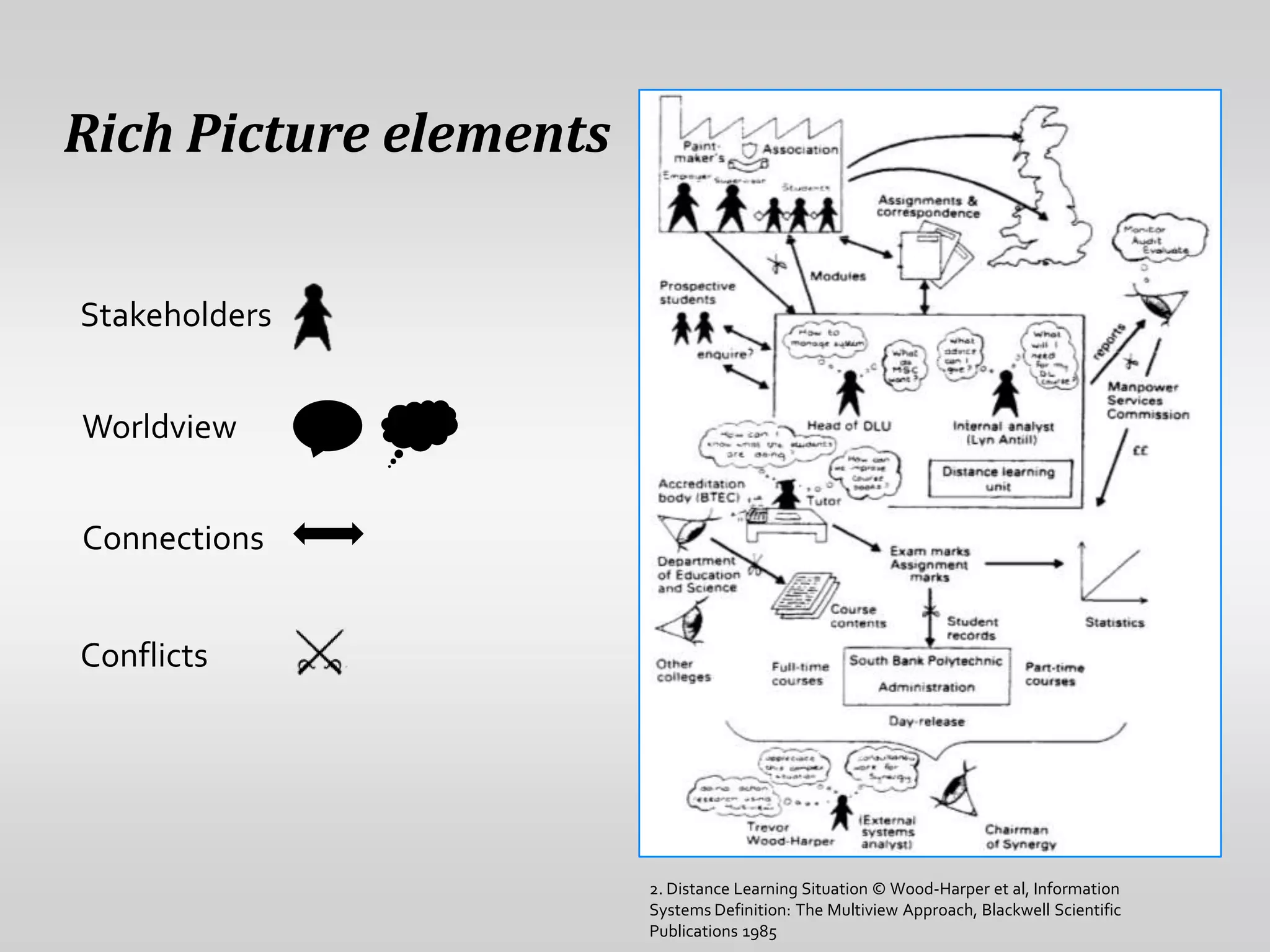
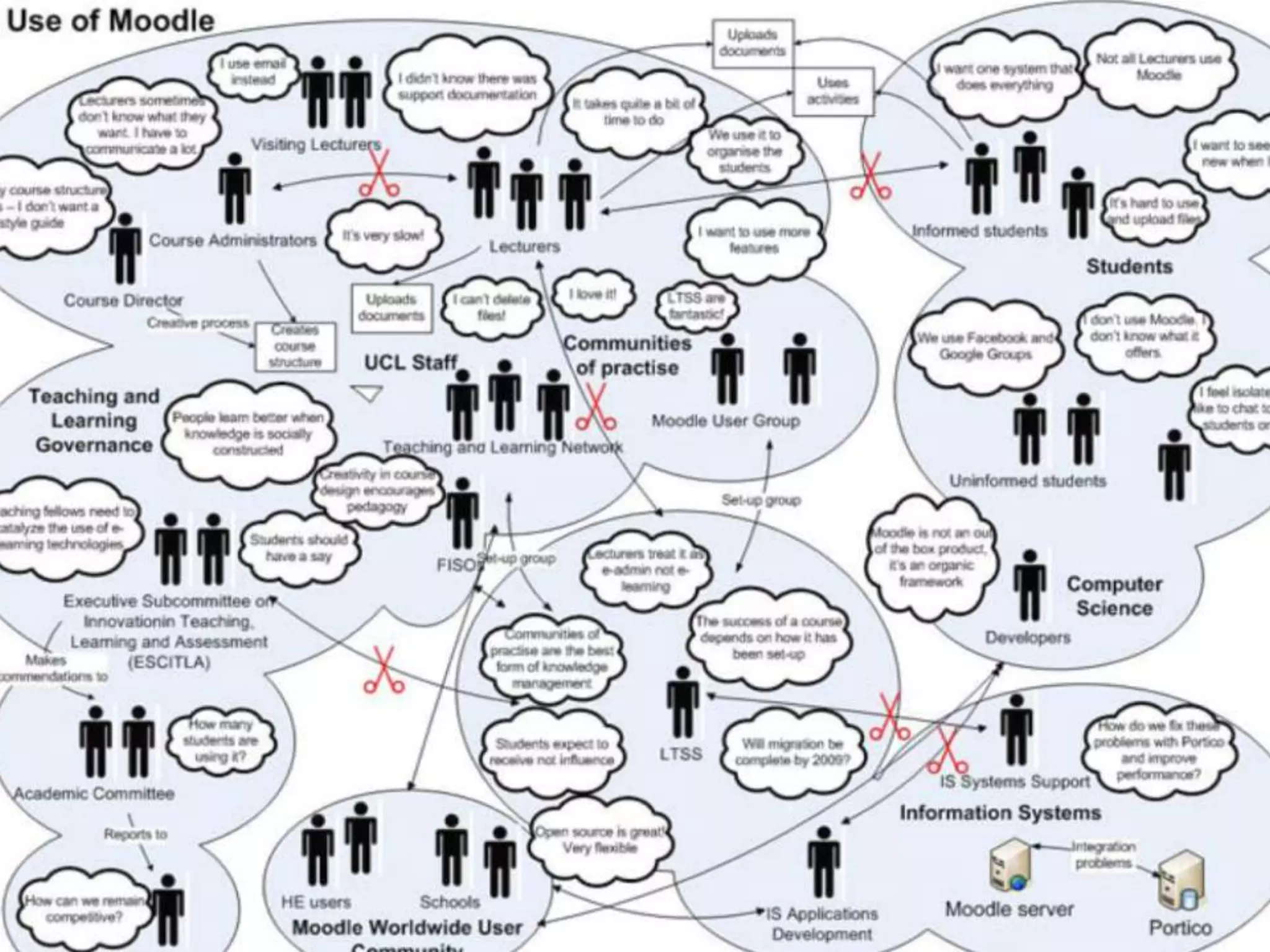
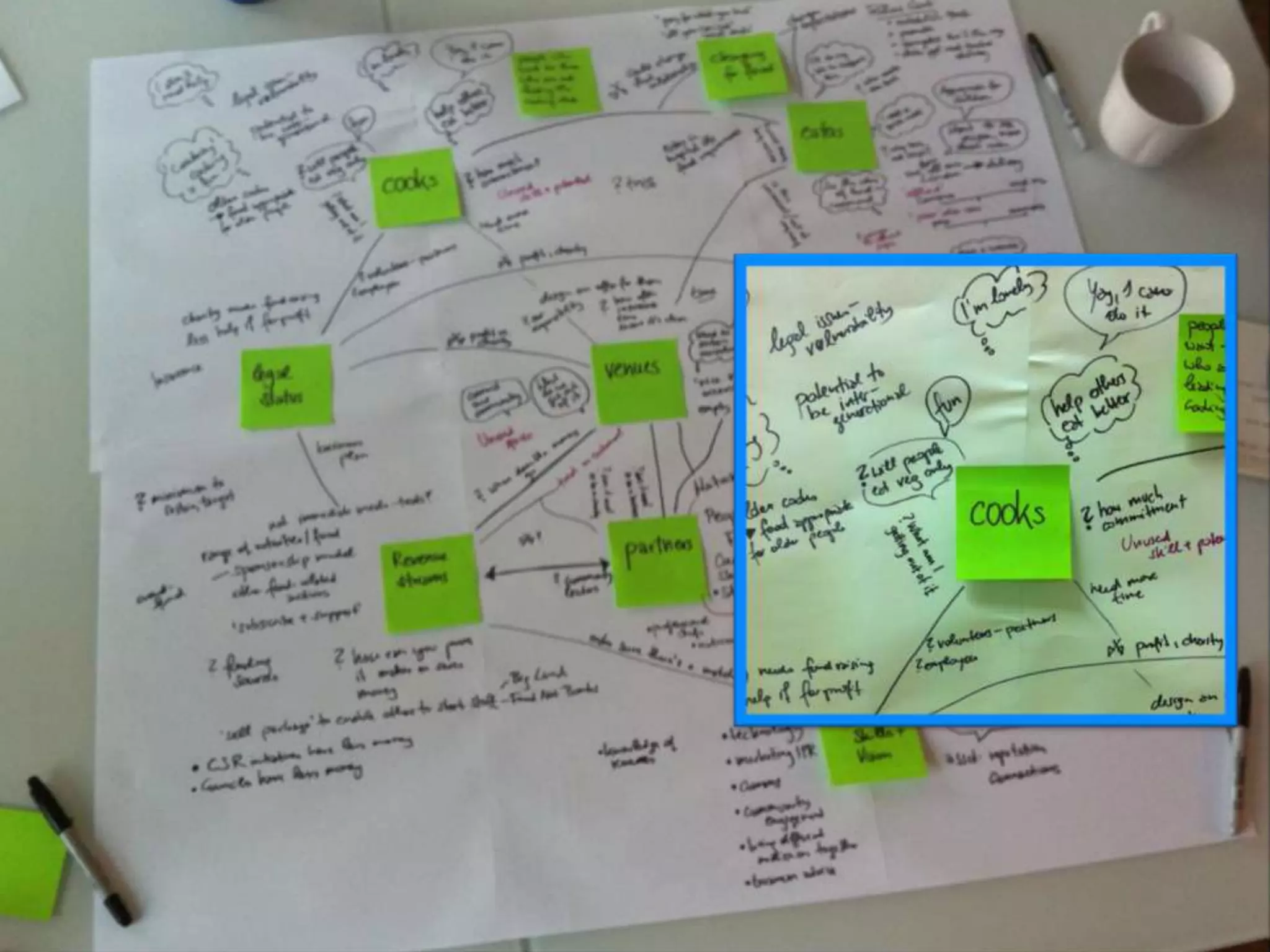
This document provides guidance on conducting qualitative user research interviews. It discusses planning interviews, including determining topics and having open-ended prompt questions ready. It recommends asking open questions without leading, and provides examples of good all-purpose questions. The document also offers tips for conducting interviews, such as being a learner not an expert and listening well. It cautions against being interrogative or asking for solutions during interviews. Lastly, it notes the importance of making sense of what was observed and heard from interviews.