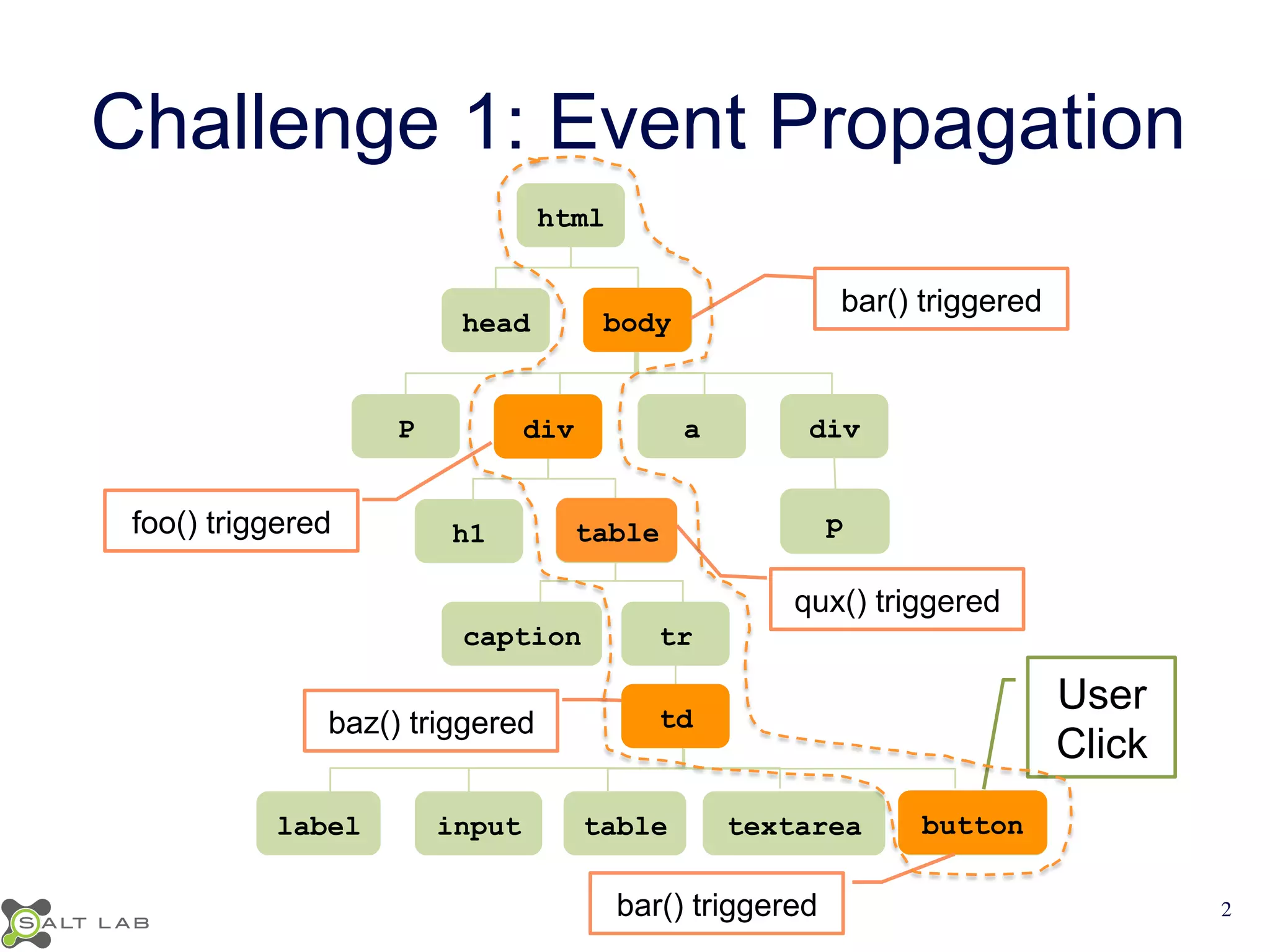
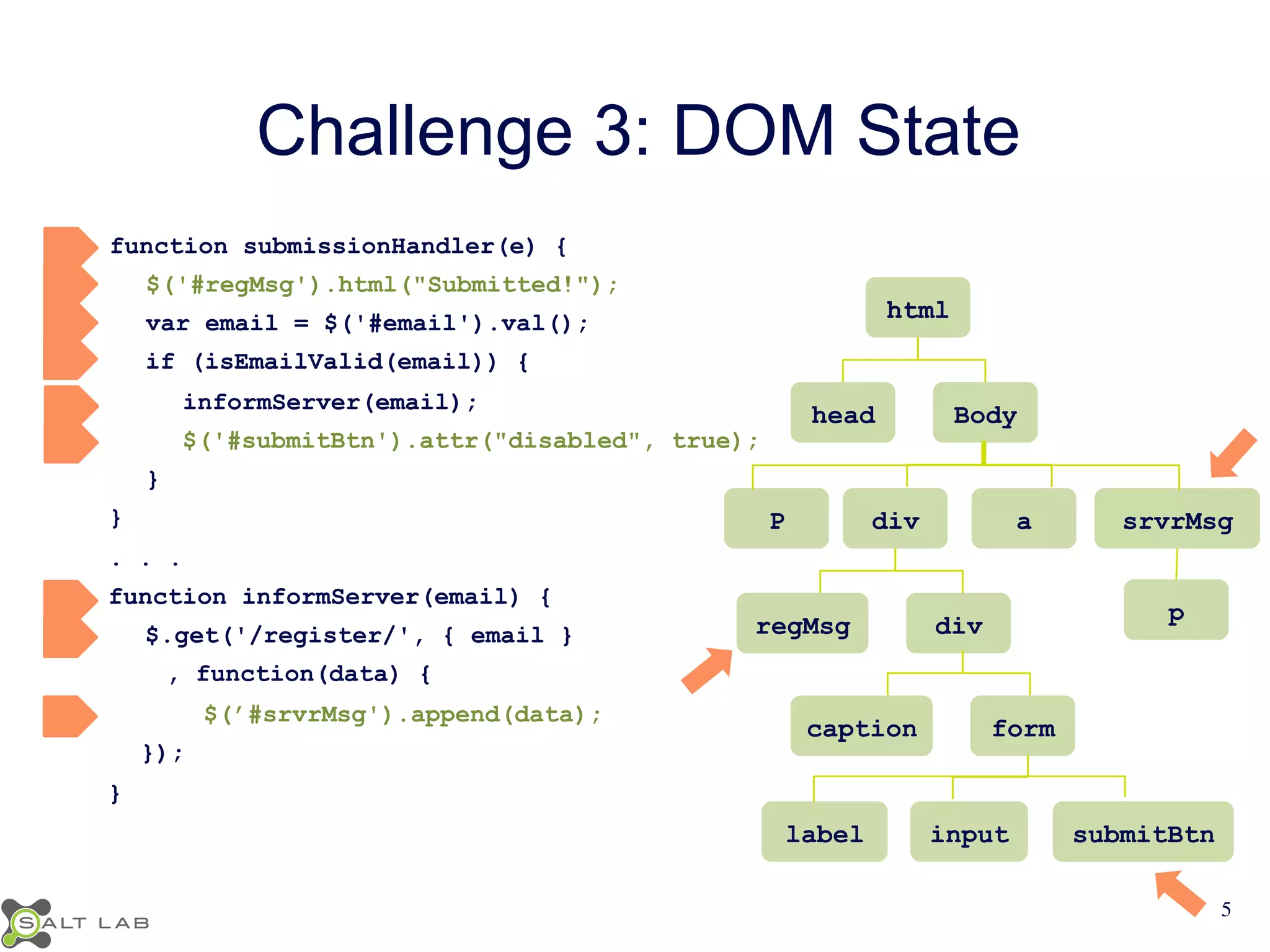
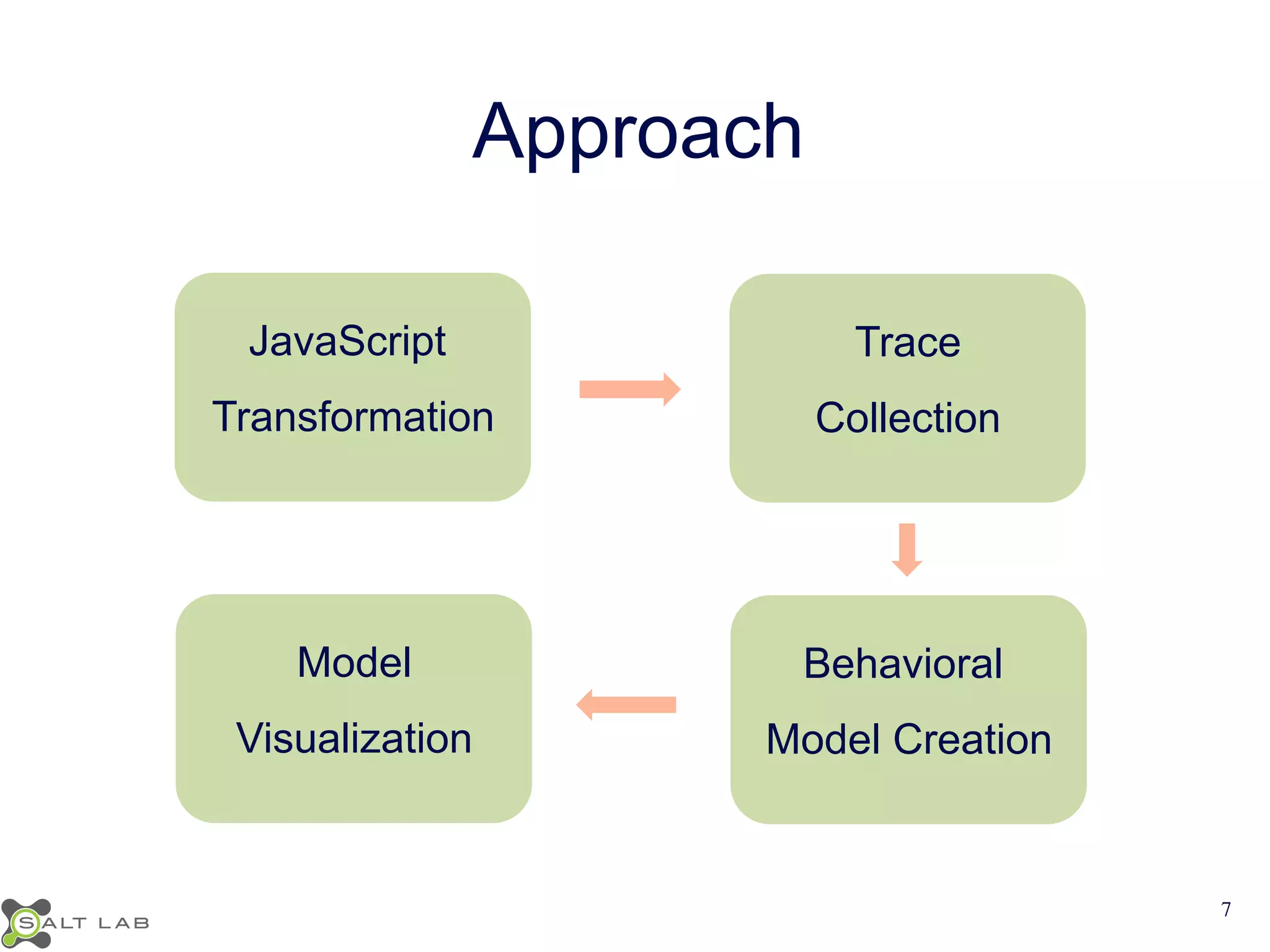
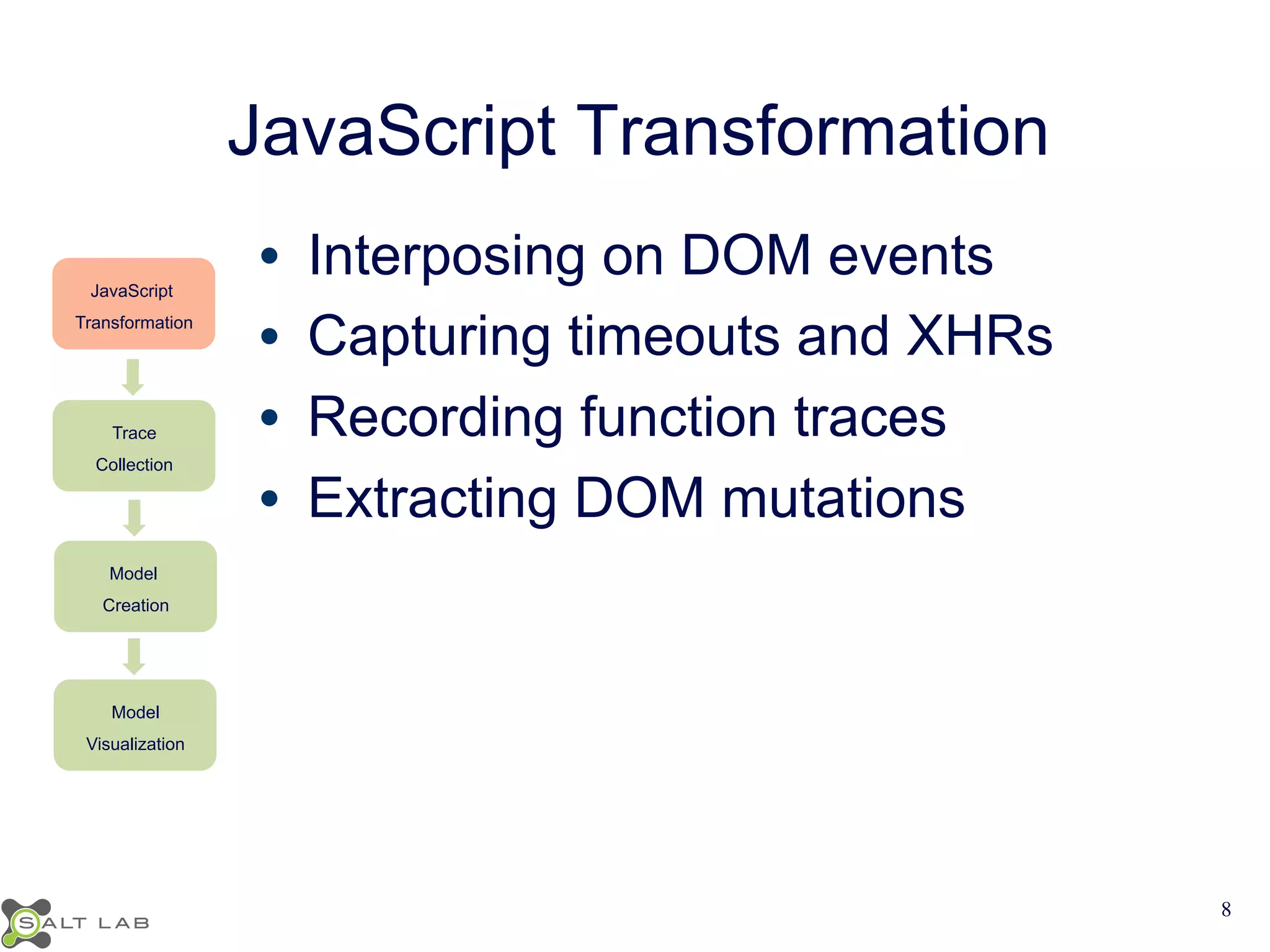
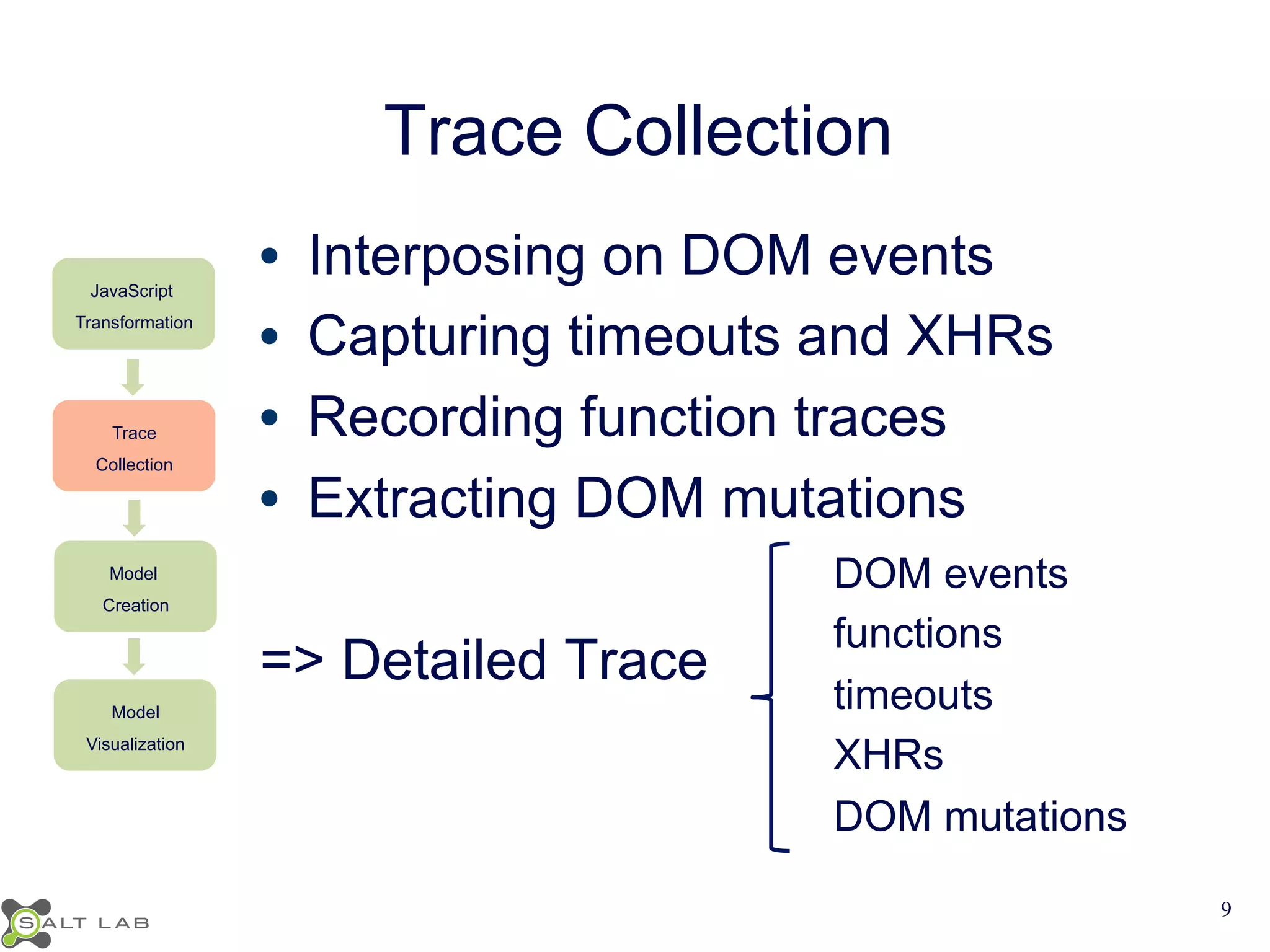
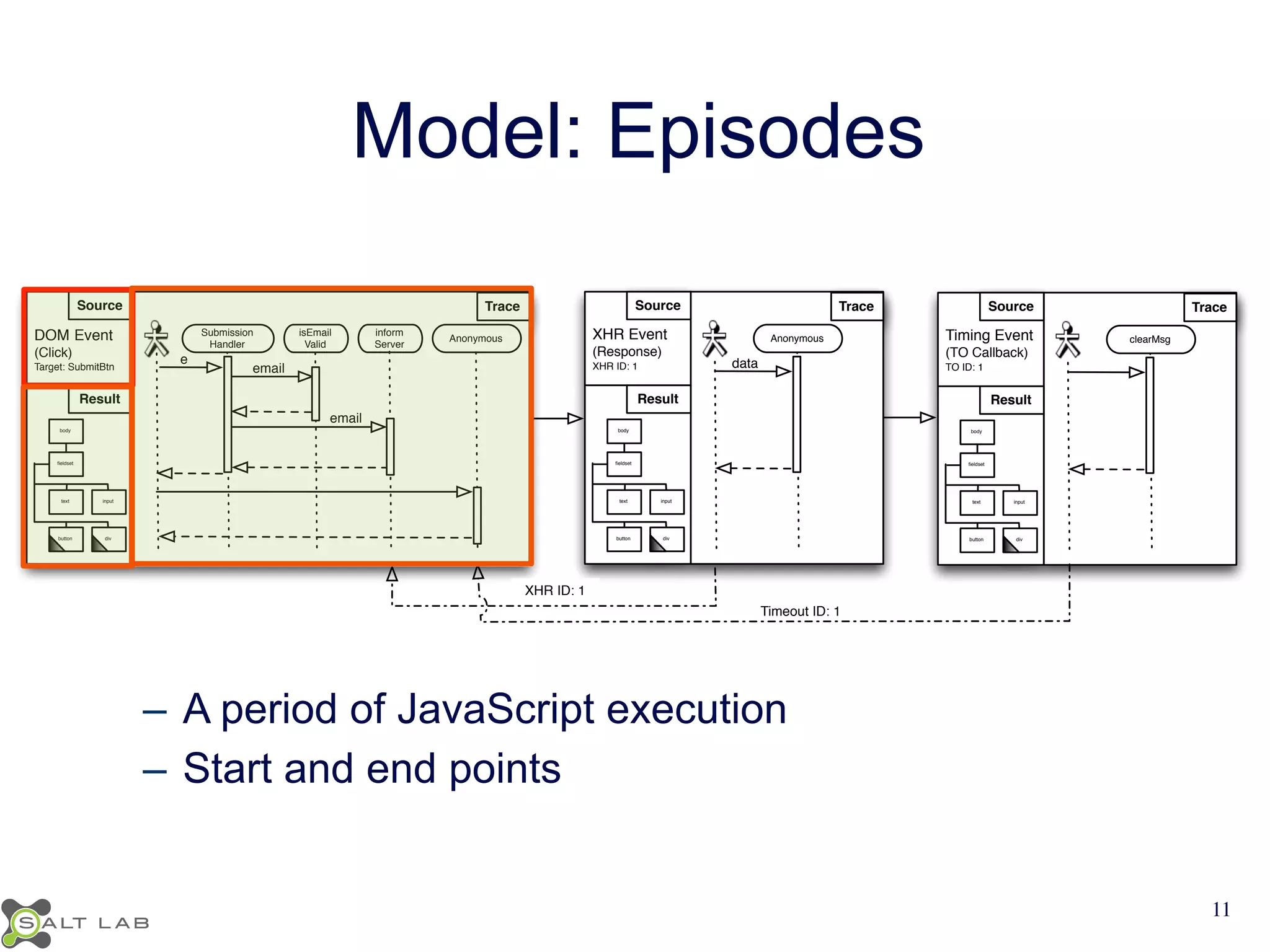
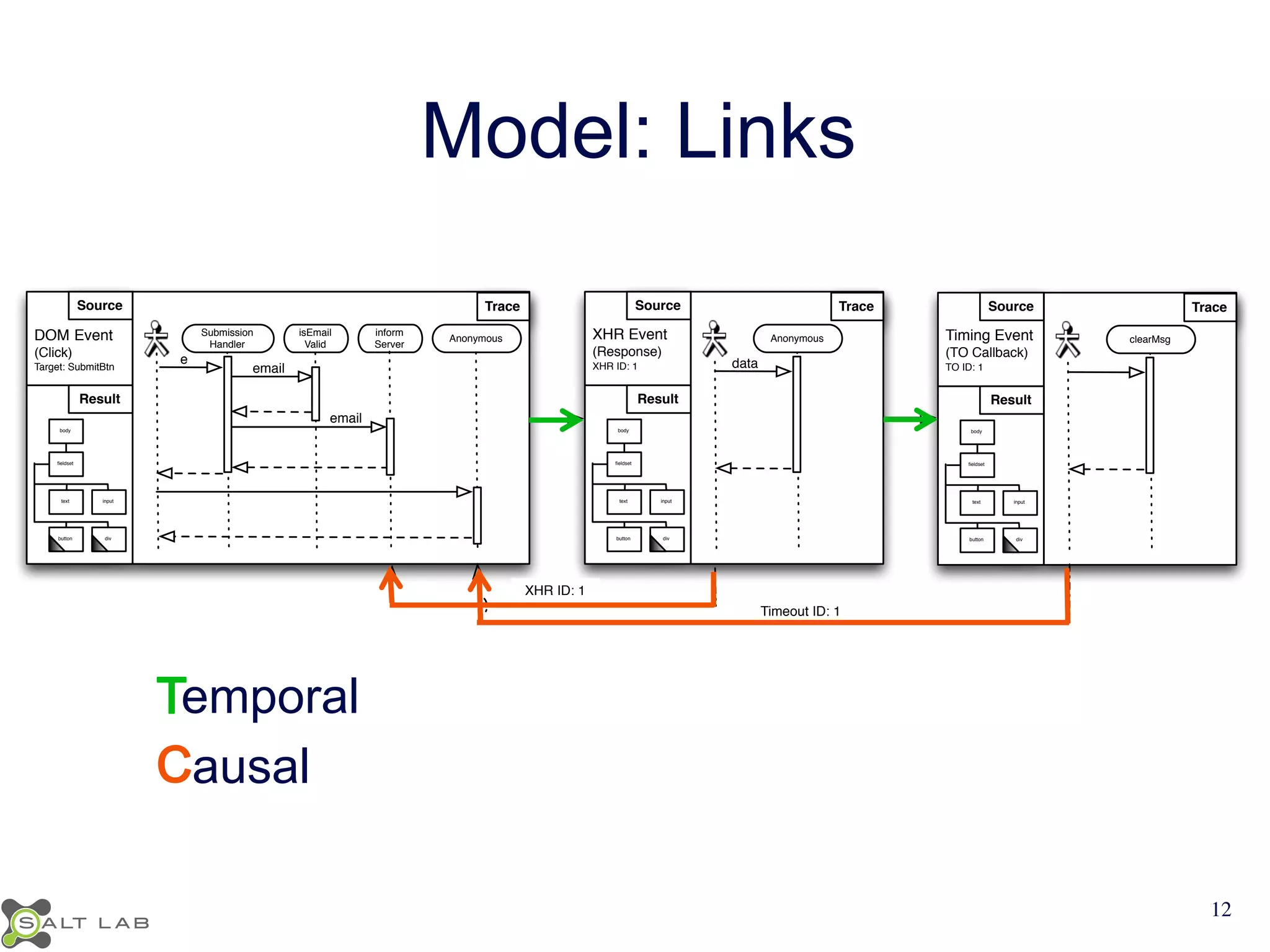
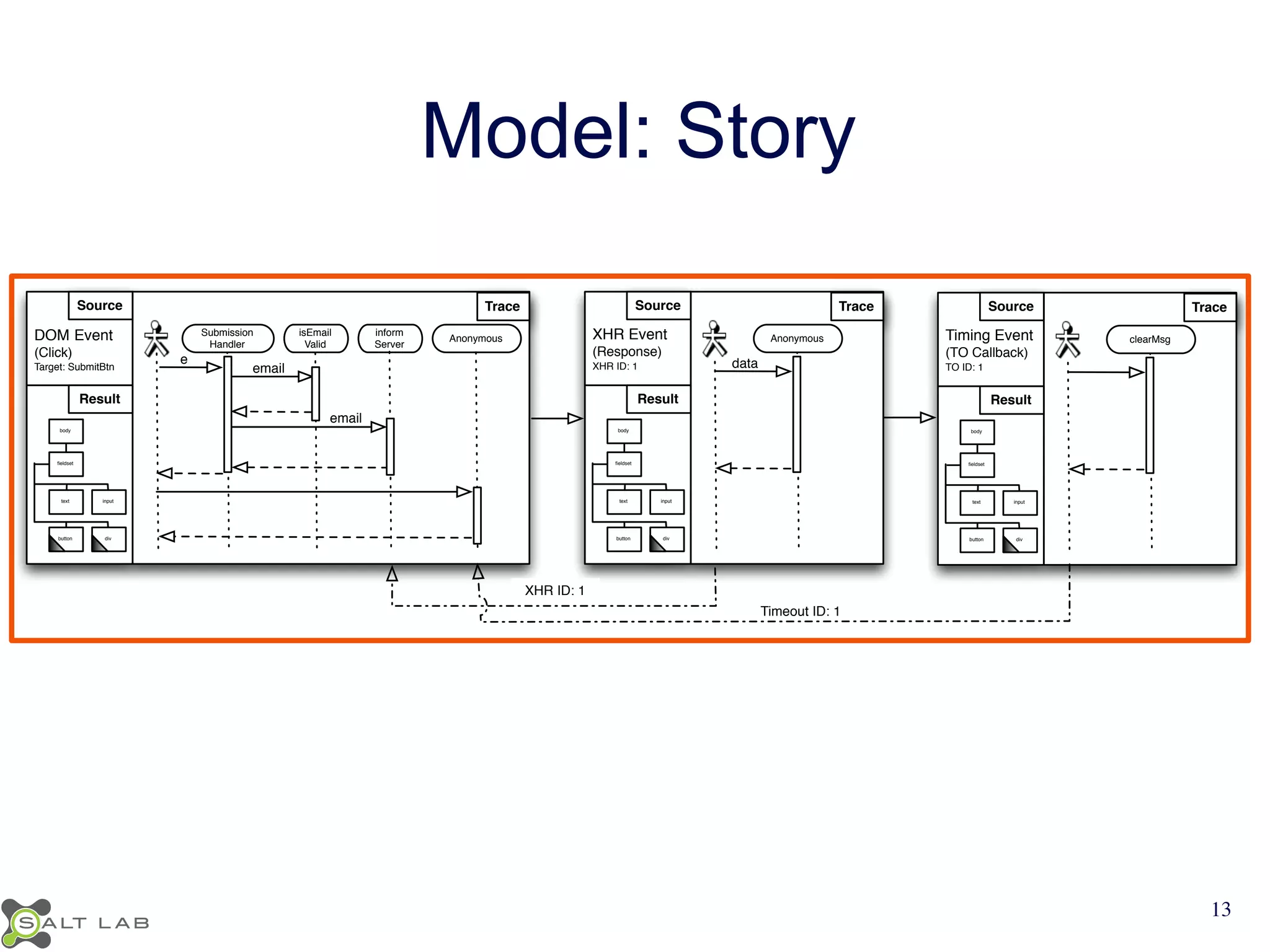
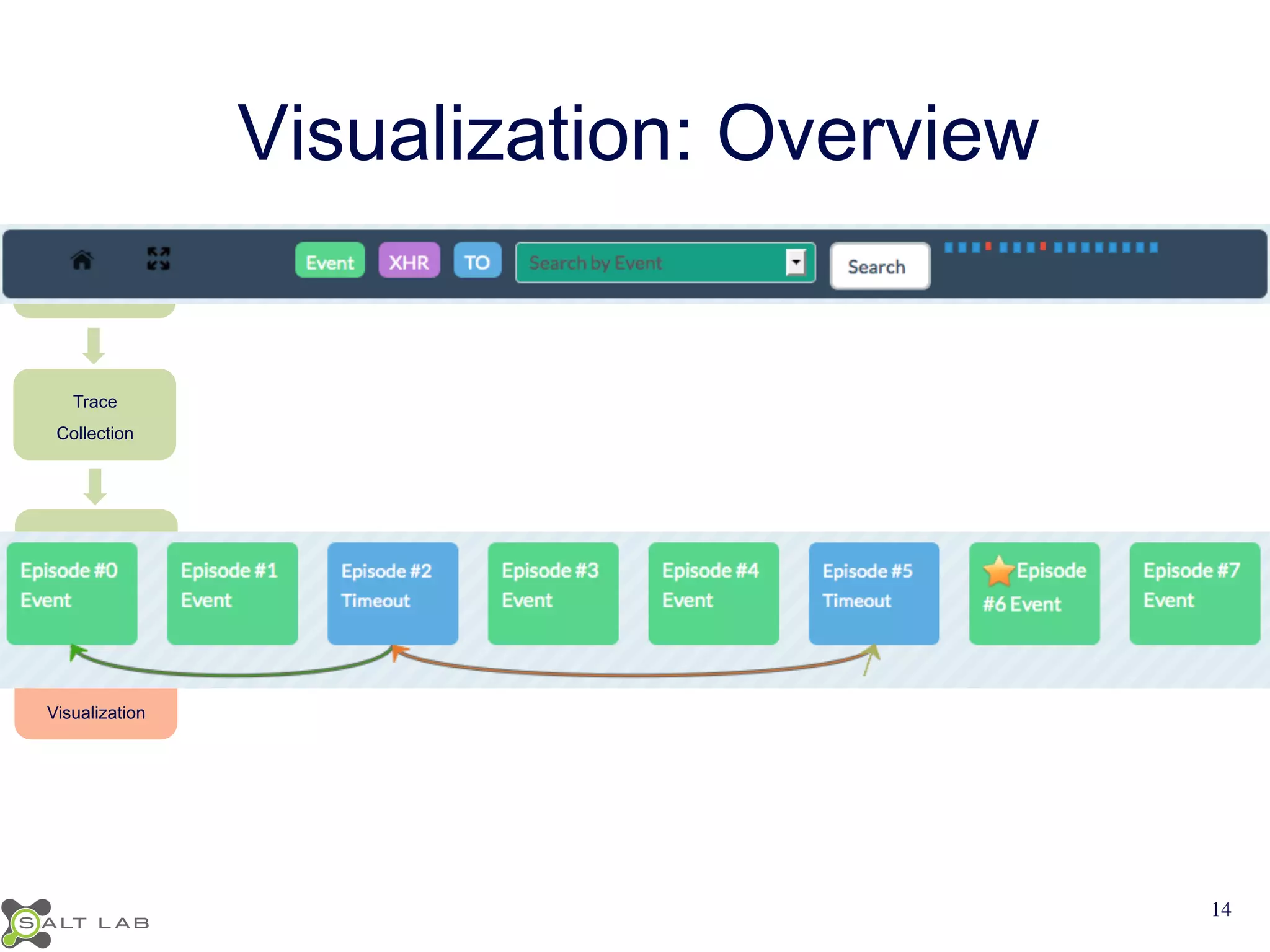
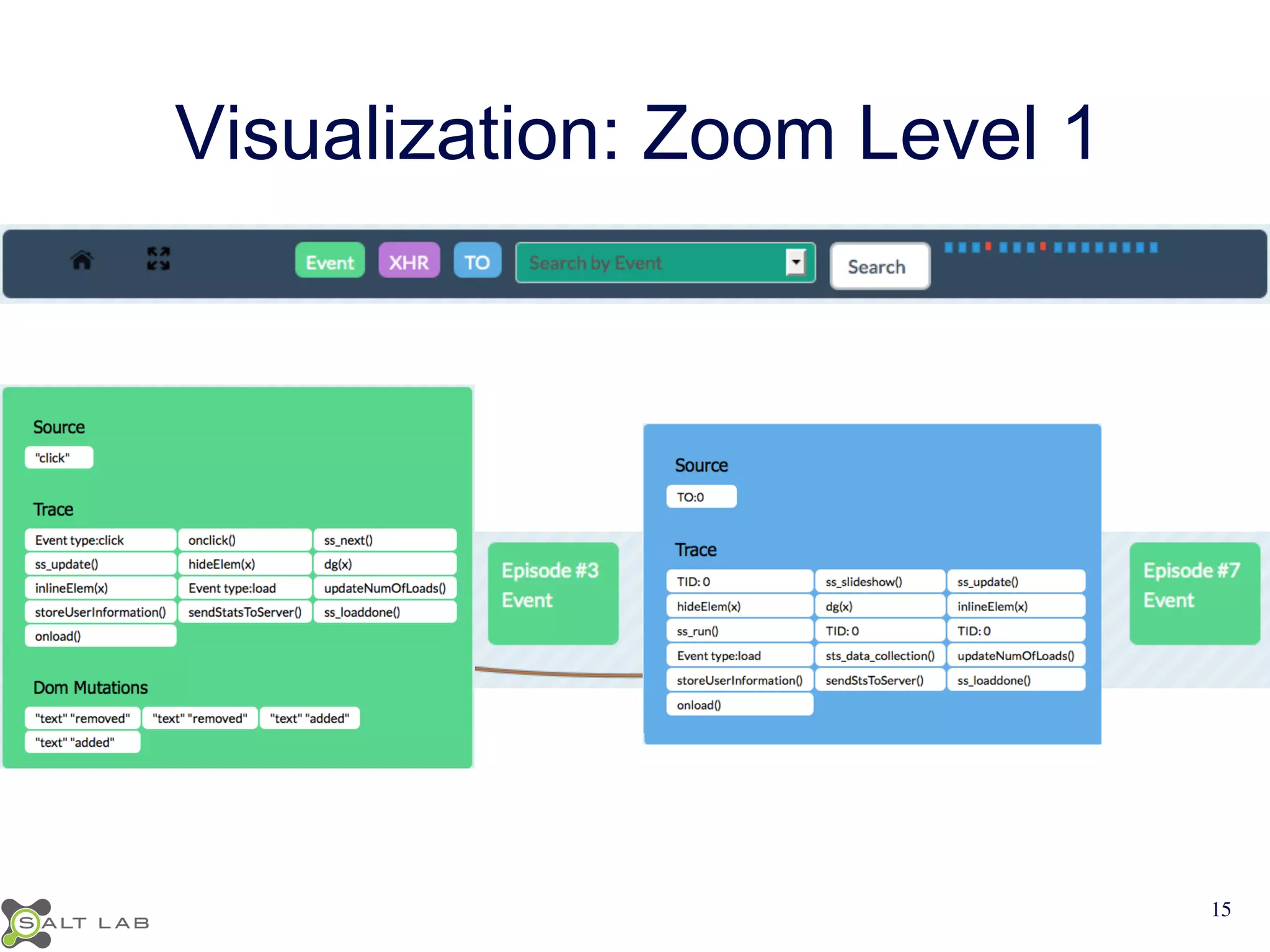
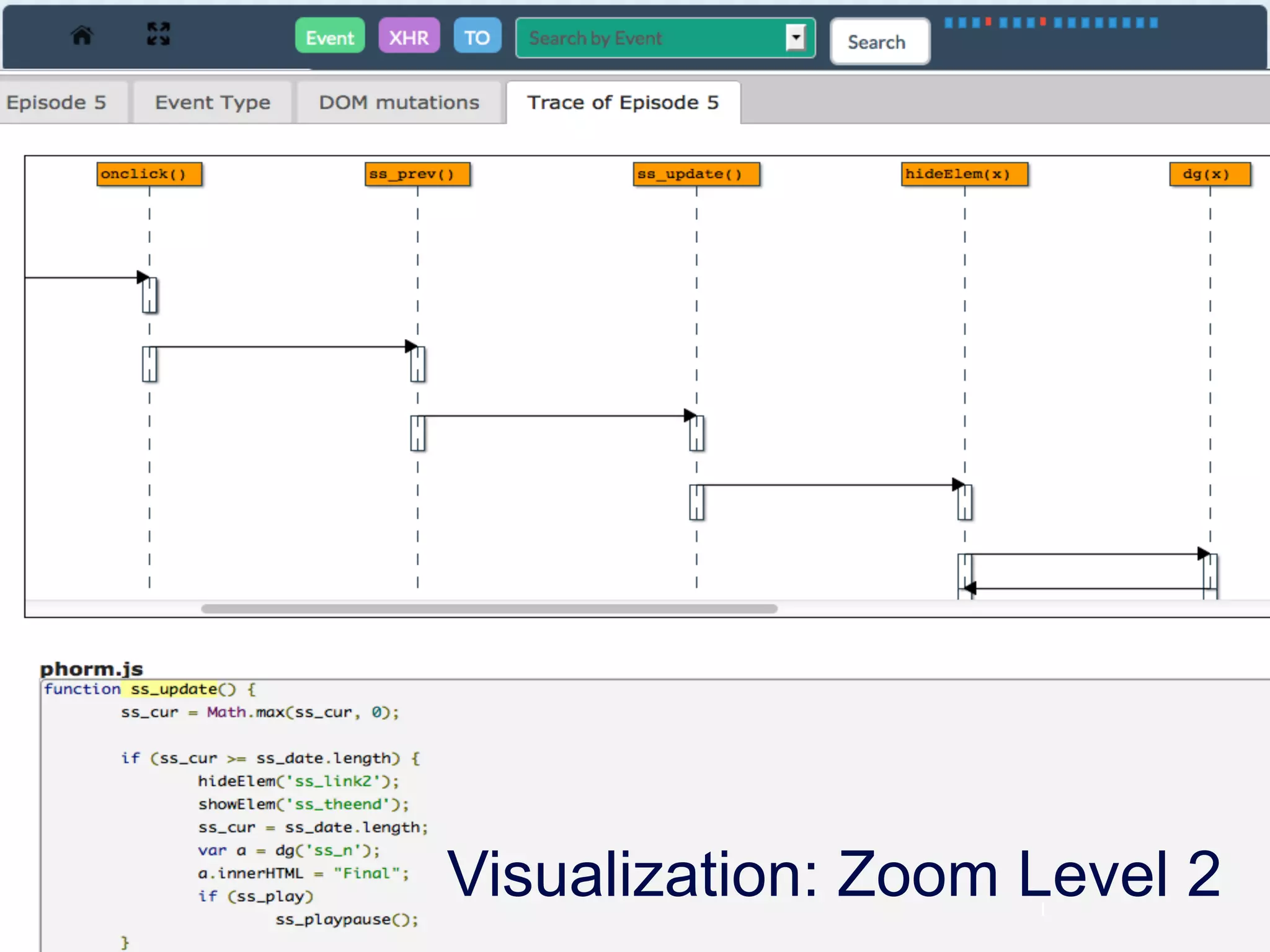
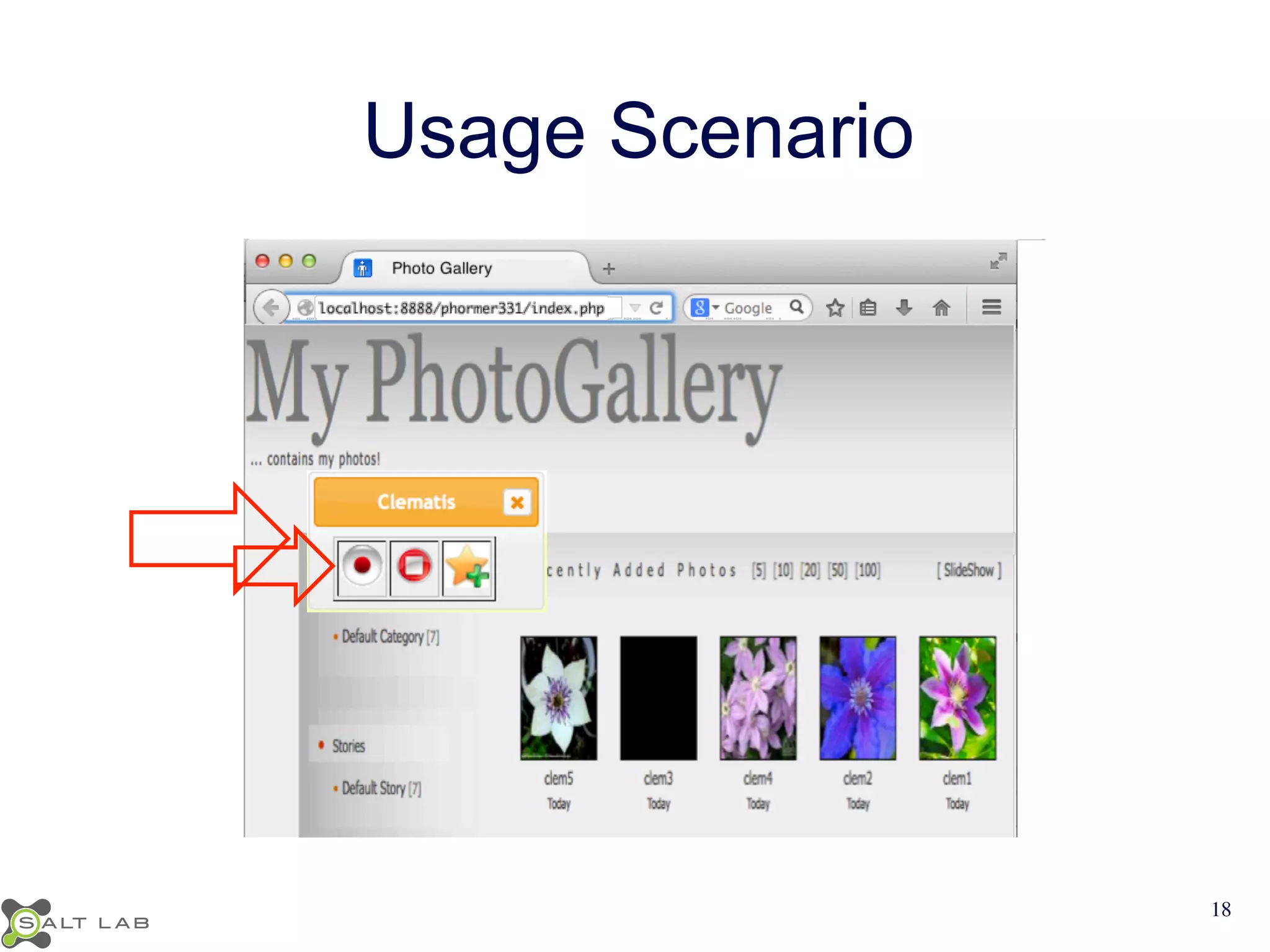
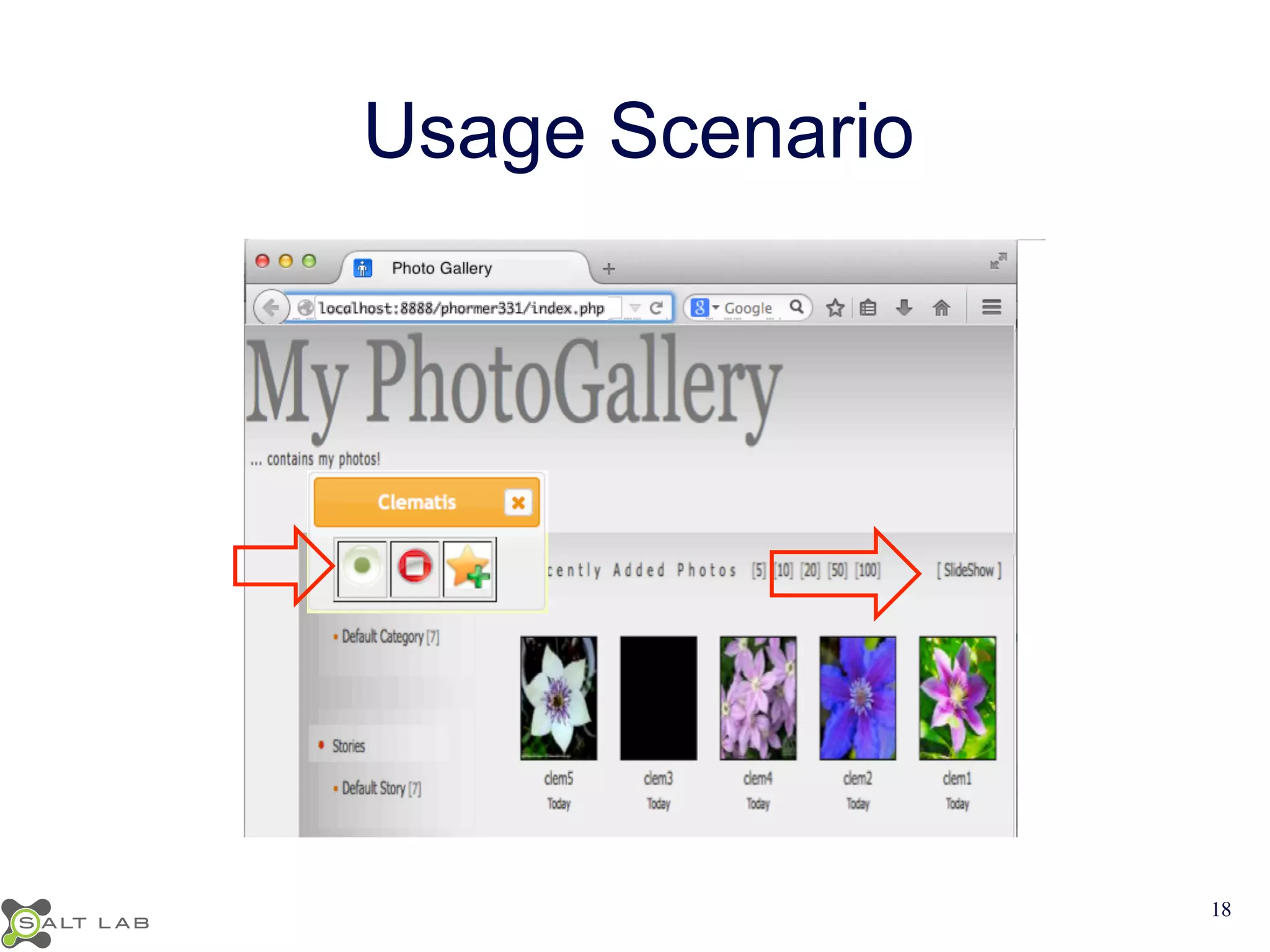
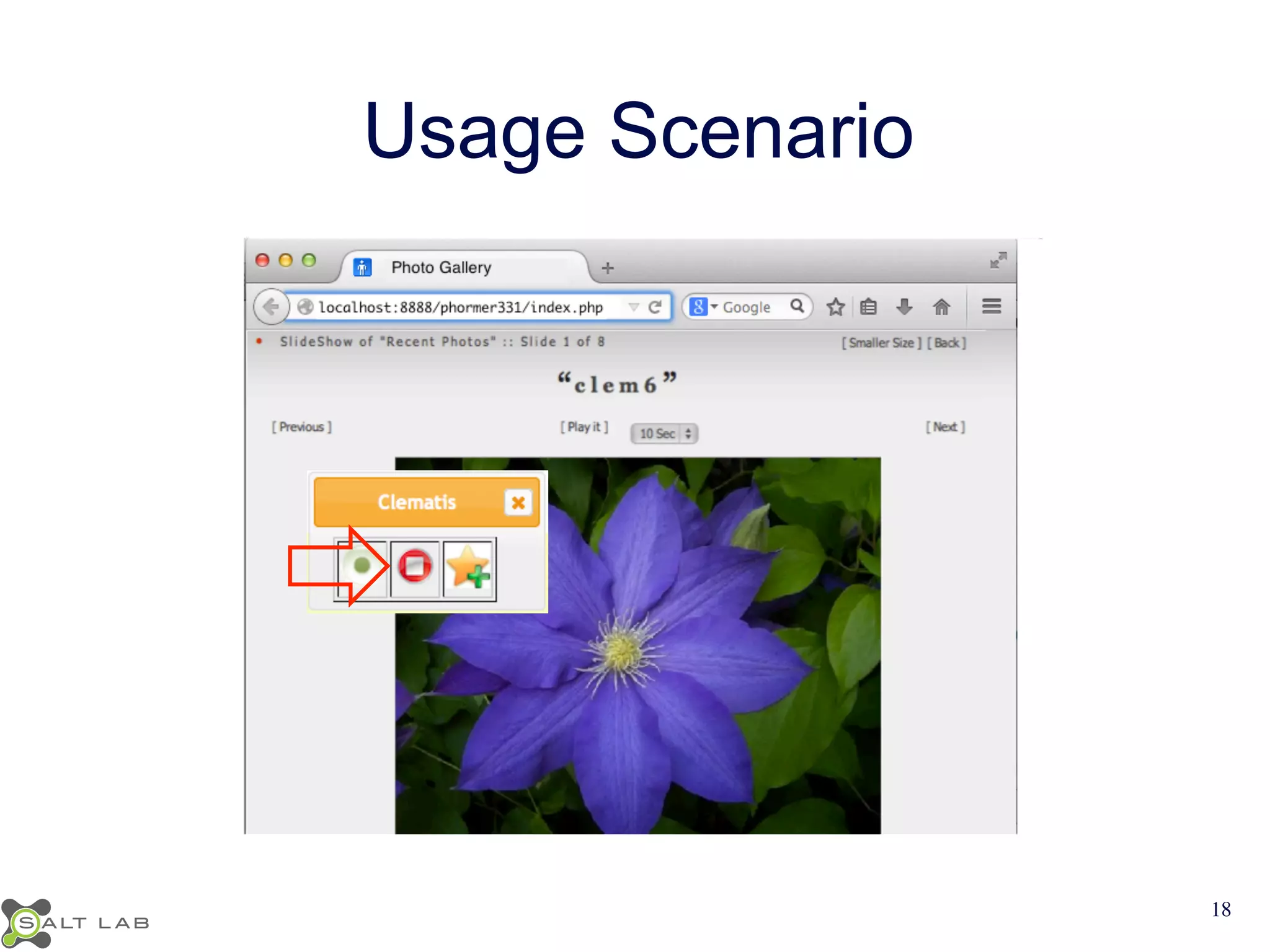
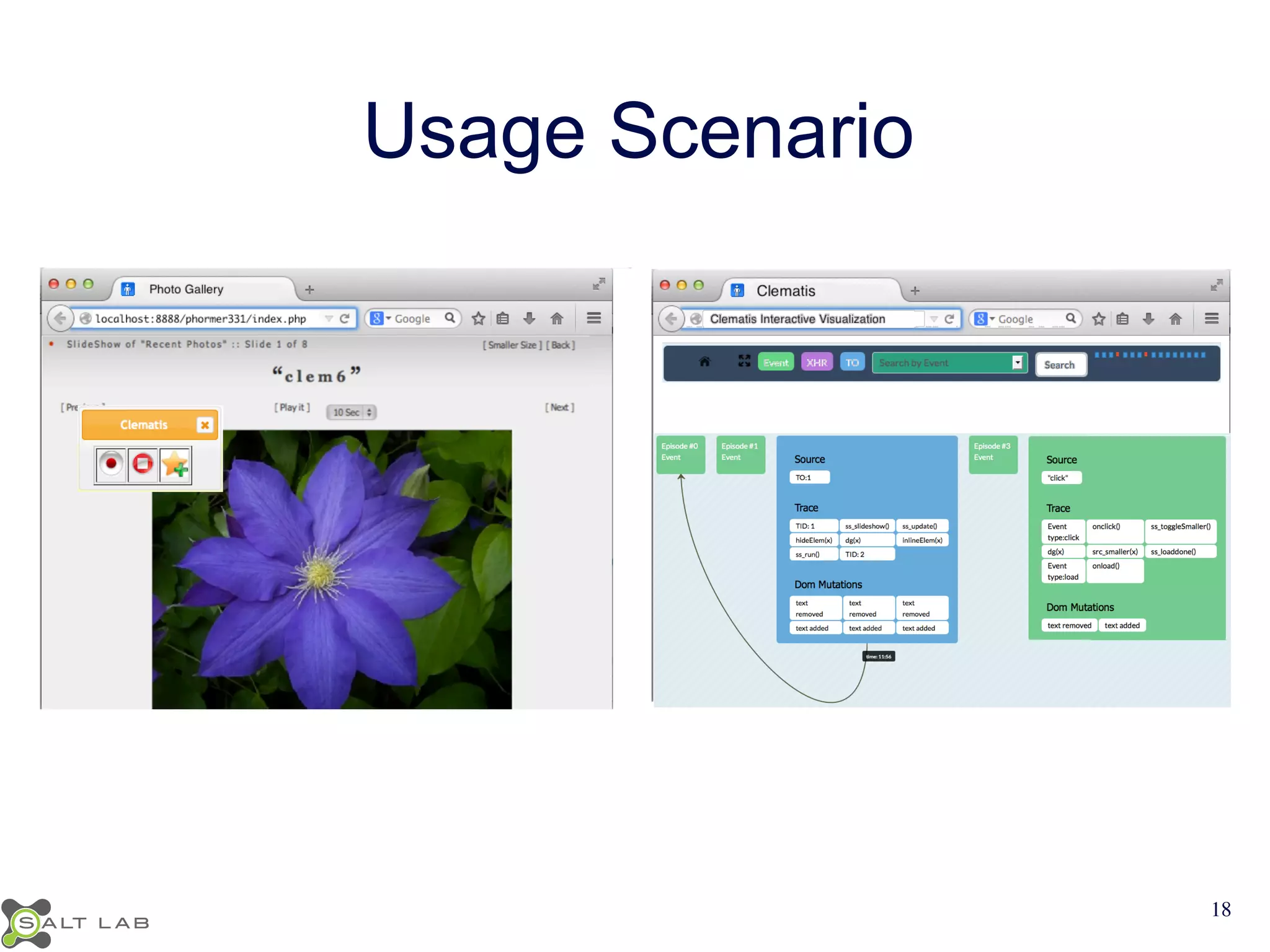
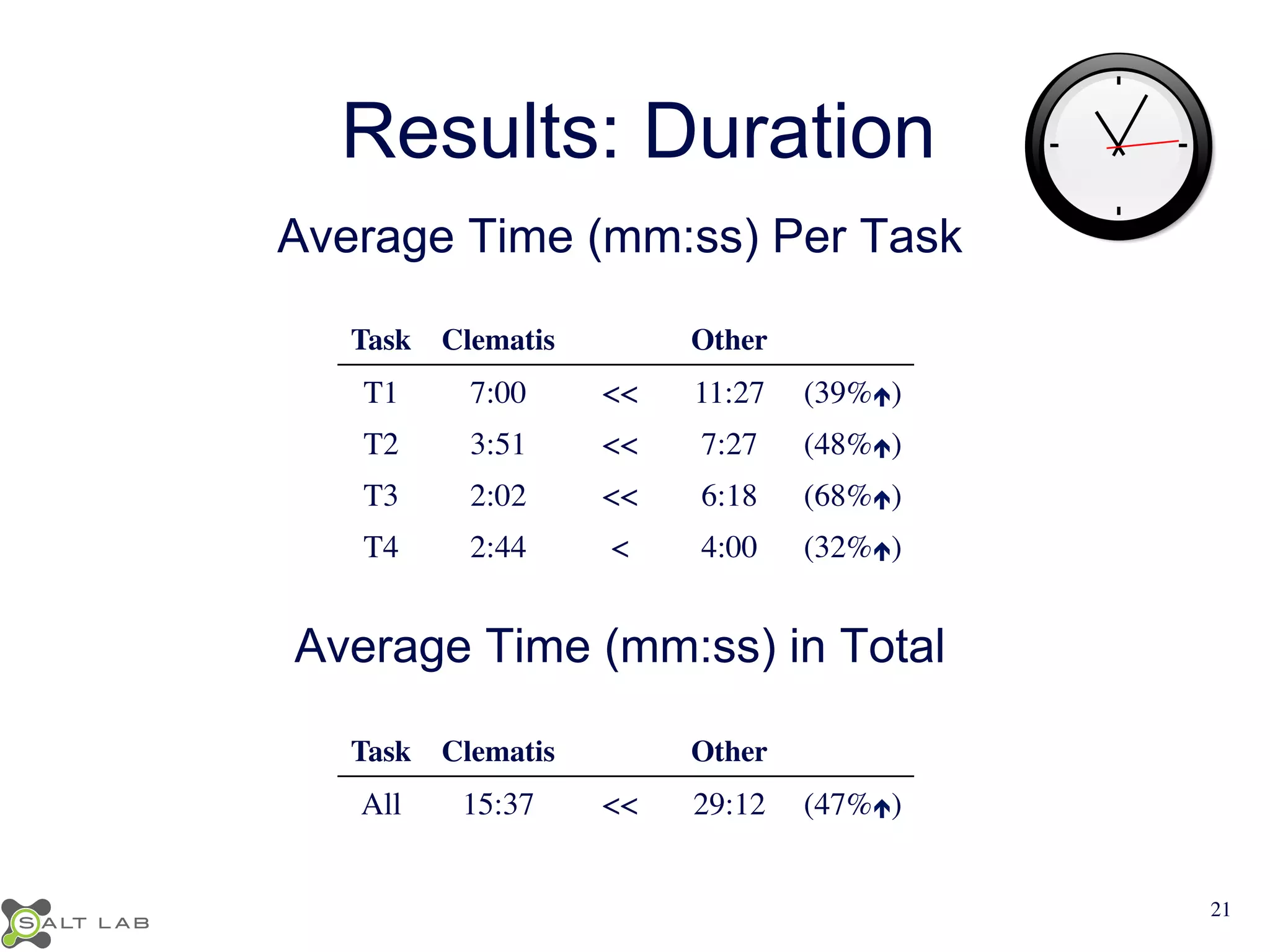
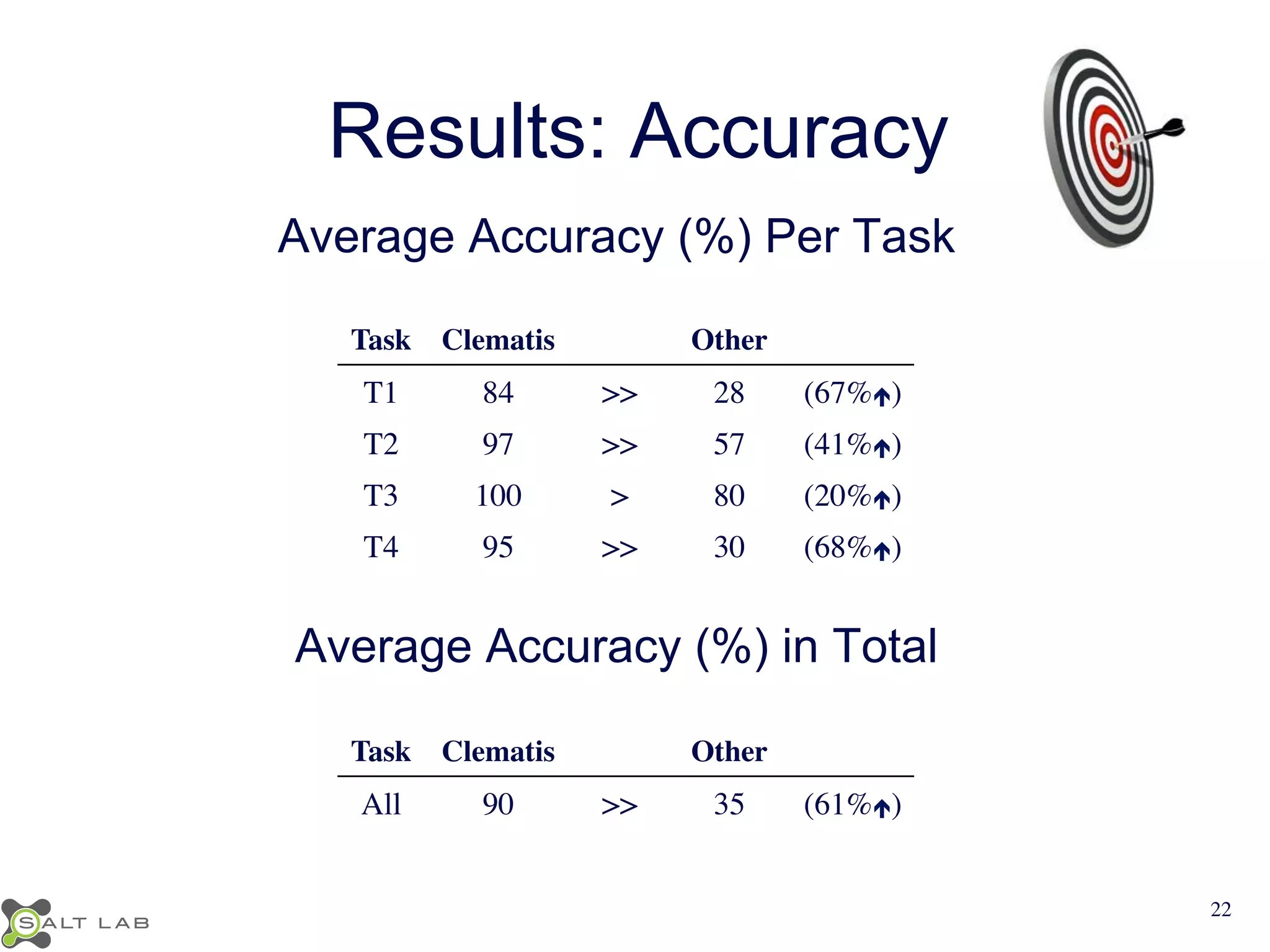
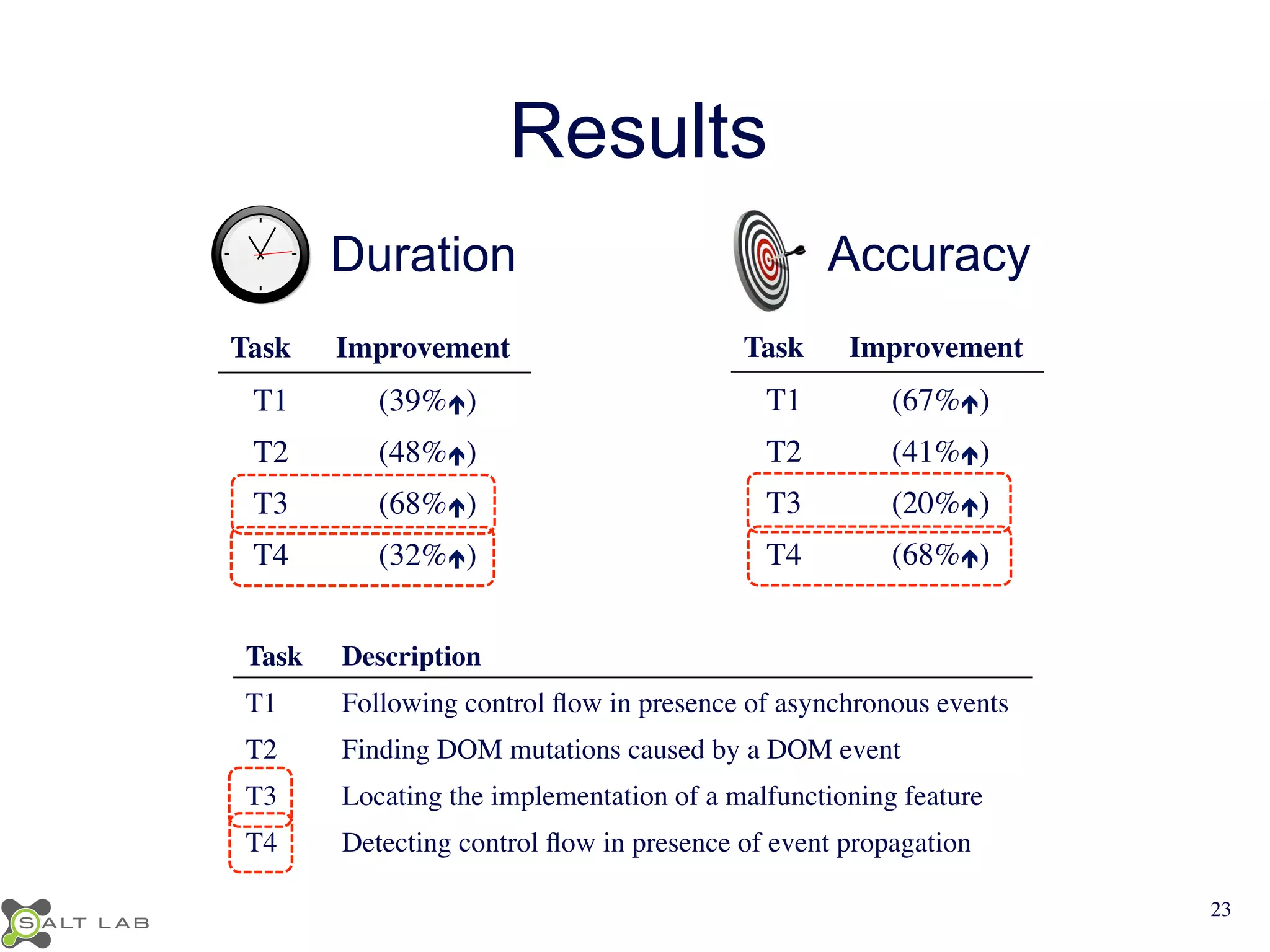
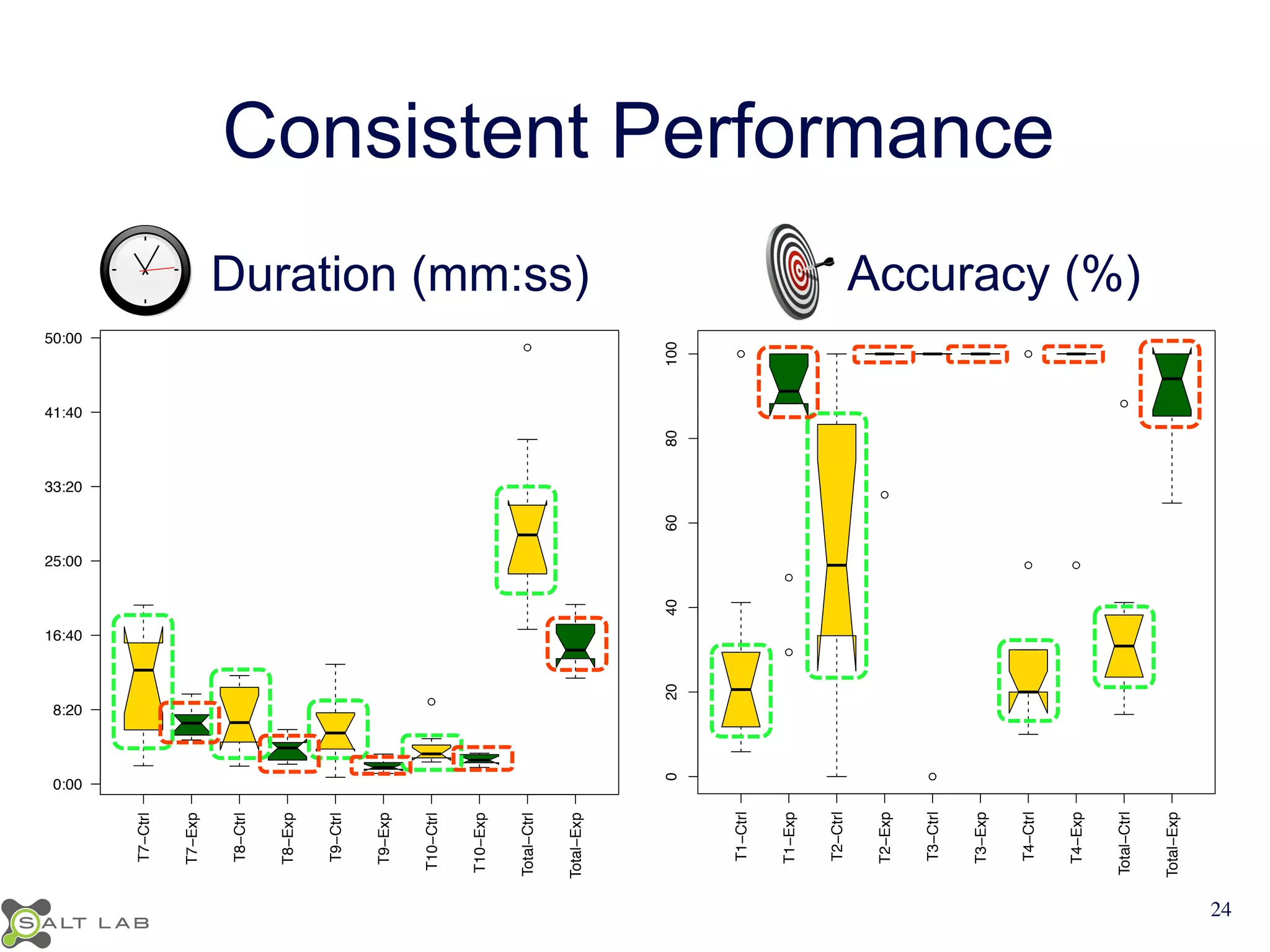
The document discusses challenges in understanding JavaScript event-based interactions and proposes an approach using Clematis, a tool that transforms JavaScript, collects execution traces, creates a behavioral model, and provides a visualization. Clematis reduces the time and improves the accuracy of developers' comprehension of web applications compared to traditional tools by visualizing the control flow including asynchronous events and DOM mutations.