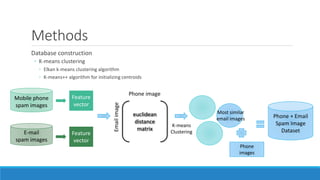
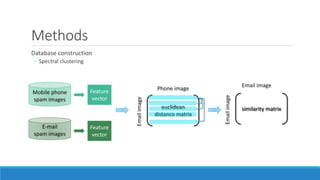
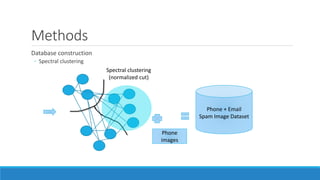
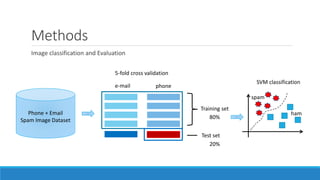
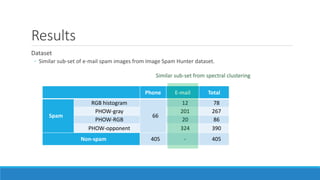
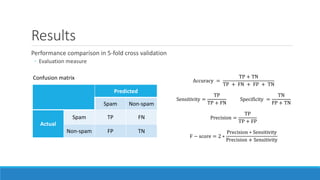
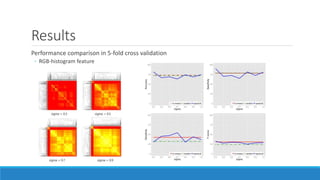
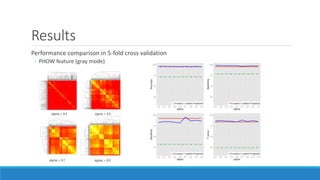
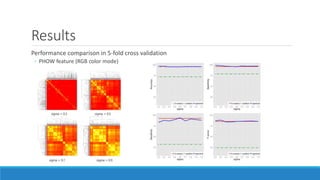
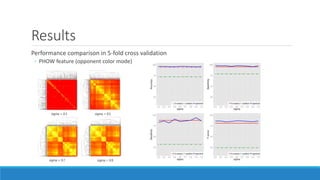
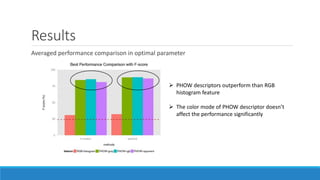
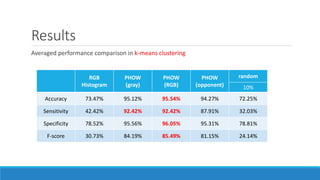
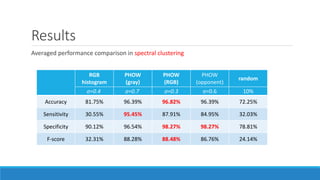
This document presents a method for detecting spam images in mobile phones using image classification. It extracts features from images using the Pyramid Histogram of Visual Words (PHOW) descriptor and clusters similar images. A support vector machine classifier is trained on the clustered image data and evaluated through cross-validation. The results show that PHOW outperforms RGB histograms and spectral clustering improves over k-means clustering. PHOW considers both color and geometric information, allowing it to better group similar email and phone spam images.