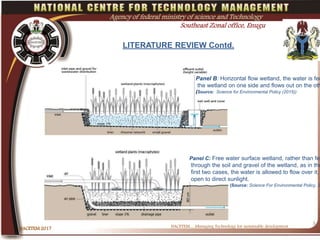
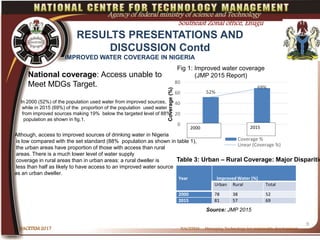
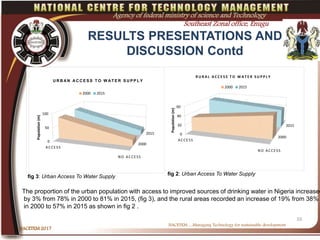
This document discusses water development in Nigeria and the role of technology innovation. It finds that access to improved water sources is low in Nigeria, especially in rural areas, and has not met MDG targets. It analyzes trends in urban and rural access between 2000 and 2015. The document recommends that Nigeria promote technology innovation methods for water supply to achieve faster, more sustainable and cost-effective solutions. These include wastewater treatment and wetland ecosystem approaches. Nigeria must also strengthen investment and encourage participation to apply such innovation.